ASTM B560-00(2010)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Modern Pewter Alloys
Standard Specification for Modern Pewter Alloys
ABSTRACT
This specification covers three modern alloy types, made from tin, antimony, and copper, used in the fabrication of pewter articles by casting, spinning, drawing, or forming. These alloy types include: castings (Type I), sheets (Type 2), and special-purpose alloys (Type 3). The metal may be supplied in the form of bar, ingot, rolled sheet, and circle, all of which shall be available in the specified nominal dimensions (thickness, width, length, and/or diameter) and mass. Pewter alloy shall be defined as having a composition within the prescribed range for tin, antimony, and copper, and shall conform to the specified impurity limits for lead, arsenic, iron, and zinc.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers three alloy types, made from tin, antimony, and copper, used in the fabrication of pewter articles by casting, spinning, drawing, or forming. The metal may be supplied in the form of bars, ingots, rolled sheet, and circles.
1.2 Pewter alloy shall be defined as having a composition within the range from 90 to 98 % tin, 1 to 8 % antimony, and 0.25 to 3 % copper. Compositions are given in Table 1.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to become familiar with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for this product/material as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate safety and health practices, and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:B560 −00(Reapproved2010)
Standard Specification for
Modern Pewter Alloys
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B560; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Classification
1.1 This specification covers three alloy types, made from 3.1 The hardness and workability of pewter varies with the
tin, antimony, and copper, used in the fabrication of pewter amount of antimony and copper alloyed with the tin. Casting
articles by casting, spinning, drawing, or forming. The metal alloys generally contain less copper and a slightly higher tin
may be supplied in the form of bars, ingots, rolled sheet, and content than sheet alloys. The composition for castings (Type
circles. 1) and sheet (Type 2) are shown in Table 1 , but individual
fabricators may choose compositions in the range given for
1.2 Pewter alloy shall be defined as having a composition
each type.Aspecial-purpose alloy (Type 3), high in tin, is used
within the range from 90 to 98 % tin, 1 to 8 % antimony, and
for articles requiring a softer metal.All types must conform to
0.25 to 3 % copper. Compositions are given in Table 1.
the impurity limits shown in Table 1.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3.2 The following applies to all specified limits in this
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
standard: For purposes of determining conformance with these
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
specifications an observed value or a calculated value shall be
and are not considered standard.
rounded “to the nearest unit” in the last right-hand place of
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
figures used in expressing the limiting value, in accordance
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
with the rounding method of Practice E29.
responsibility of the user of this standard to become familiar
4. Ordering Information
with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for this product/material
4.1 Orders for material under this specification should
as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate
include the following:
safety and health practices, and determine the applicability of
4.1.1 Quantity,
regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.1.2 Form—bars, sheet, or circles,
4.1.3 Type and composition (Table 1),
2. Referenced Documents
4.1.4 Size (sheet—thickness, width and length; circles—
2.1 ASTM Standards:
thickness and diameter), and
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
4.1.5 Marking.
Determine Conformance with Specifications
5. Materials and Manufacture
E51 Method for Spectrographic Analysis of Tin Alloys by
the Powder Technique (Withdrawn 1983)
5.1 The manufacturer shall use care to have each shipment
E57 Methods for ChemicalAnalysis ofWhite Metal Bearing
of each form as uniform in quality and composition as possible
Alloys (Withdrawn 1986)
and of a commercially satisfactory appearance.
E88 Practice for Sampling Nonferrous Metals and Alloys in
6. Chemical Composition
Cast Form for Determination of Chemical Composition
6.1 The material shall conform to the requirements as to
chemical composition specified in Table 1. Nominal
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B02 on
Nonferrous Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee compositions, agreed upon by the manufacturer and purchaser,
B02.02 on Refined Lead, Tin, Antimony, and Their Alloys.
may be prescribed under this specification.
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published April 2010. Originally
approved in 1972. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as B560 - 00 (2005).
7. Dimensions, Mass, and Permissible Variations
DOI: 10.1520/B0560-00R10.
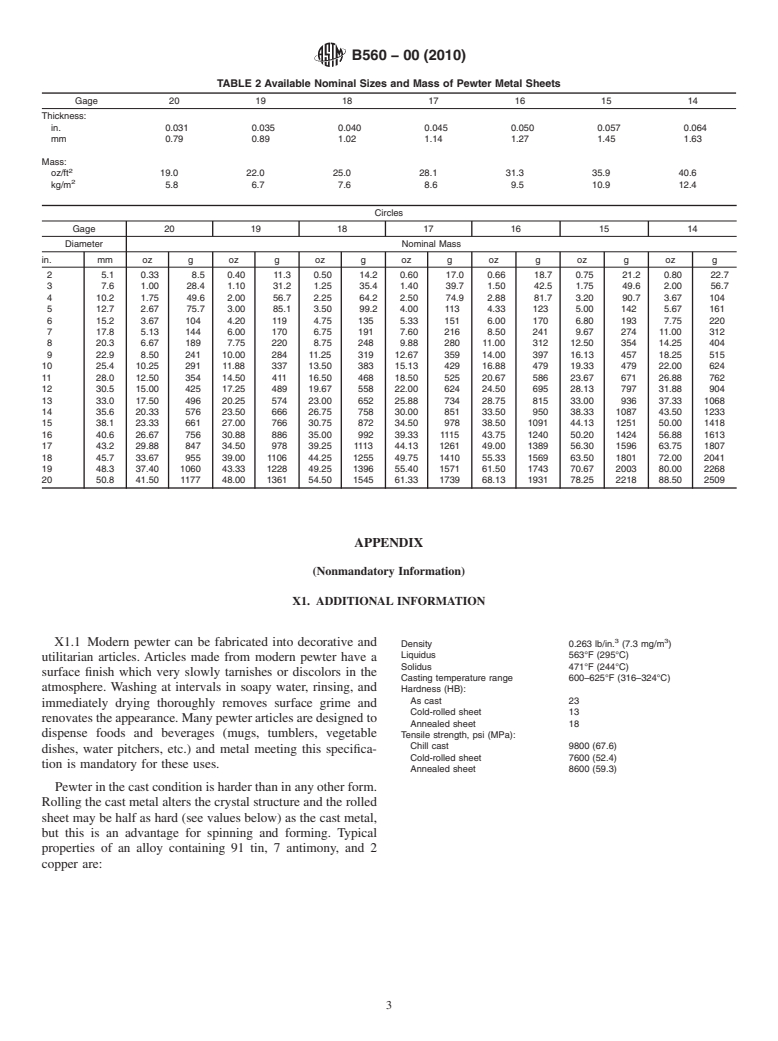
7.1 Sheet pewter is commercially available in thicknesses
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
from 0.031 to 0.064 6 0.002 in. (0.79 to 1.63 mm) (Table 2).
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Thinner sheet down to a thickness of 0.010 in. (0.25 mm) can
the ASTM website.
be supplied to special order. Sheet can be supplied in widths up
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org. to 2 ft (0.6 m) and lengths up to 4 ft (1.2 m).
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
B560−00(2010)
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
9.3 Check analyses samples shall consist of three bars or
Composition, -wt% ingots selected to represent a shipment of less than 1000 lb
B
Element
Type 1 Casting Type 2 Sheet Alloy Type 3 Special (454 kg) and five bars or ingots to represent a shipment of over
A
Alloy Purpose Alloys
1000 lb (454 kg). The bars shall be selected at random,
UNS Number L13911 L13912 L13963
preferably under such conditions that every piece in the lot is
accessible for selection (for example, while shipment is being
Tin 90–93 90–93 95–98
Antimony 6–8 5–7.5 1.0–3.0 loaded or unloaded).Asaw cut shall be made entirely through
Copper 0.25–2.0 1.5–3.0 1.0–2.0
the piece on its long axis and the saw chips collected. Sawings
Lead, max 0.05 0.05 0.05
thoroughly mixed and split into three parts shall constitute the
Arsenic, max 0.05 0.05 0.05
Iron, max 0.015 0.015 0.015
samples for chemical analysis (Practice E88).
Zinc, max 0.005 0.005 0.005
9.4 For sheet, circles, and discs, a sample shall consist of
A
Nominal Type 1 alloy composition: 92 Sn, 7.5 Sb, and 0.5 Cu.
B
clippings from not more than 2 % of the shipment. The
Nominal Type 2 alloy composition: 91 Sn, 7 Sb, and 2 Cu.
minimum mass of sample shall be 250 g.
10. Chemical Analysis
7.2 Circles are available in diameters from 2 to 20 in. (50.8
10.1 In case of dispute, the c
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.