ASTM F512-12(2017)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Smooth-Wall Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Conduit and Fittings for Underground Installation
Standard Specification for Smooth-Wall Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Conduit and Fittings for Underground Installation
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the dimensional, design, and performance requirements for five types (Types EB-20, EB-35, DB-60, DB-100, and DB-120) of smooth-wall poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) conduits and fittings for underground communication and electrical power wires and cables. Conduits and fittings shall be evaluated on impact resistance and strength, joint tightness, pipe stiffness, and extrusion quality.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for single wall and coextruded cellular core smooth-wall poly(vinyl chloride) conduit and fittings for underground communication and electrical power wire and cables. Plastics which does not meet the material requirements specified in Section 5 is excluded from single layer and all coextruded layers.
1.2 The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 8, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F512 −12 (Reapproved 2017) An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
Smooth-Wall Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Conduit and
Fittings for Underground Installation
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF512;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope moplastic Pipe and Fittings
D2152 Test Method for Adequacy of Fusion of Extruded
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for single
Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Molded Fittings by
wall and coextruded cellular core smooth-wall poly(vinyl
Acetone Immersion
chloride) conduit and fittings for underground communication
D2412 Test Method for Determination of External Loading
and electrical power wire and cables. Plastics which does not
Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loading
meet the material requirements specified in Section 5 is
D2444 Test Method for Determination of the Impact Resis-
excluded from single layer and all coextruded layers.
tance of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings by Means of a
1.2 The values given in parentheses are for information
Tup (Falling Weight)
only.
D2466 Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
Pipe Fittings, Schedule 40
test method portion, Section 8, of this specification: This D2564 Specification for Solvent Cements for Poly(Vinyl
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Piping Systems
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user D2855 Practice for the Two-Step (Primer and Solvent Ce-
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
ment) Method of Joining Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) or
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita- Chlorinated Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Pipe and
tions prior to use.
Piping Components with Tapered Sockets
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor- F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3. Terminology
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.1 Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F412
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
and abbreviations are in accordance with Terminology D1600,
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
unless otherwise specified. The abbreviation for poly(vinyl
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
chloride) is PVC.
2. Referenced Documents
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
2.1 ASTM Standards: 3.2.1 cellular plastic—a plastic containing numerous cells,
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing intentionally introduced, interconnecting or not, distributed
D1600 Terminology forAbbreviatedTerms Relating to Plas- throughout the mass.
tics
3.2.2 coextruded pipe—pipe consisting of two or more
D1784 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
concentric layers of material bonded together in processing by
Compounds and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride)
any combination of temperature, pressure, grafting, cross-
(CPVC) Compounds
linking or adhesion.
D2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
3.2.3 coextrusion—a process whereby two or more heated
or unheated plastic material streams, forced through one or
more shaping orifice(s), become one continuously formed
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
piece.
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.25 on Vinyl
Based Pipe.
3.2.4 external recycled material—industrial rework gener-
Current edition approved April 1, 2017. Published April 2017. Originally
ated by a different company manufacturing to this specifica-
approved in 1977. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as F512–12. DOI:
tion. Composition is known by the industrial source of the
10.1520/F0512-12R17.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
material.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3.2.5 post-consumer recycled material—finished goods that
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. have been purchased by the public, then returned to industry
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F512−12 (2017)
and reprocessed into raw materials. Identity of finished goods blowing agent. The pipe produced shall meet all of the
is known by the reprocessing company. requirements of this specification.
3.2.6 certificate of composition—a certificate describing the
5.3 Recycled PVC Materials—RecycledPVCmaterialscon-
certain properties of an external recycled material of a post
forming to the cell classification of this specification may be
consumer recycled material.
used provided they are clean and free from foreign materials
and provided that the conduit or fittings produced meet all
3.2.7 composition disclosure—a document describing the
requirements of this specification.
formulation of an external recycled material.
5.4 Solvent Cement—The solvent cement shall meet the
4. Classification
requirements of Specification D2564.
4.1 This specification covers five types of underground
6. Requirements
conduit. There are two having lesser pipe stiffness values,
designed primarily for concrete encased burial (EB), and three
6.1 Workmanship—The conduit and fittings shall be homo-
with greater pipe stiffness values, designed primarily for direct
geneous throughout, and free from visible cracks, holes,
burial (DB). The complete designations follow:
foreign inclusions, or other injurious defects. The conduit and
Type EB-20 — Designed to be encased in concrete.
fittings shall be as uniform as is commercially practical in
Type EB-35 — Designed to be encased in concrete.
color, opacity, density, and other physical properties.
Type DB-60 — Designed for direct burial without encasement in concrete.
Type DB-100 — Designed for direct burial without encasement in concrete.
6.2 Dimensions:
Type DB-120 — Designed for direct burial without encasement in concrete.
6.2.1 Dimensions shall be determined in accordance with
4.2 This specification covers conduit with integral bells, or
Test Method D2122.
with either separate or attached couplings.
6.2.2 The dimensions and tolerances of the conduit shall be
as specified in Table 1.
4.3 This specification covers molded and fabricated fittings
6.2.3 Lengths—Conduit shall be supplied in lengths of 20 or
intended for use with all types of conduit.
25 ft, or as otherwise agreed upon between the purchaser and
5. Materials
the seller.Alength shall be considered to be the overall length
of the conduit, including integral bell, or coupling if attached,
5.1 Basic Materials—The conduit shall be made of virgin
unless otherwise specified. Tolerance on length shall be 61 in.
homopolymer PVC compound having a cell classification of
(625 mm).
12254, 12164 (with a minimum tensile strength of 4000 psi
6.2.4 Integral Bell Dimensions:
(28 MPa)), or 12264(with a minimum tensile modulus of
6.2.4.1 Two systems of fit for integral bells are in common
500 000 psi) as defined in Specification D1784. Molded
use. Unless otherwise specified, the manufacturer may employ
fittings shall be made from PVC compound having a cell
either of them.
classification of 12234 or 13343 as defined in Specification
6.2.4.2 Interference Fit System—The dimensions and toler-
D1784. Homopolymer PVC compounds must equal or exceed
ances listed in Columns A and B of Table 1 in Specification
the requirements of the listed cell classification numbers.
D2466 provide a satisfactory interference fit system between
5.2 Rework Materials—Rework material from the manufac-
pipe and socket.
turer’s own conduit or fittings production may be used by the
6.2.4.3 Clearance Fit System—The dimensions and toler-
same manufacturer, provided that the conduit or fittings pro-
ances listed in Table 2 of this specification provide a satisfac-
duced meet all of the requirements of this specification.
tory clearance fit system.
Rework material from the manufacture’s coextruded cellular
6.2.5 The wall thickness of integral bells and sweeps shall
core conduit shall be used in the core if it contains any residual
be considered satisfactory if formed from conduit which meets
the minimum requirements of this specification.
6.2.6 Socket depths for integral bells shall conform to the
Supporting data have been filed at ASTM International Headquarters and may
requirements listed in Table 2.
be obtained by requesting Research Report RR:F17-1002.
TABLE 1 Conduit Dimensions and Tolerances, in.
A
Tolerance on Minimum Wall Thickness
Average
Nominal
Outside Minimum Modulus 400 000 psi Minimum Modulus 500 000 psi
Out-of
Size
Average
B
Diameter
Round
EB-20 EB-35 DB-60 DB-100 DB-120 EB-20 EB-35 DB-60 DB-100 DB-120
1 1.315 ±0.005 0.060 — — — — 0.060 — — — — 0.060
1 ⁄2 1.900 ±0.006 0.060 — — 0.060 — 0.065 — — — — 0.060
2 2.375 ±0.006 0.060 — 0.060 0.065 — 0.083 0.060 — 0.060 — 0.077
3 3.500 ±0.008 0.060 0.067 0.082 0.100 0.121 0.127 0.061 0.076 0.092 0.112 0.118
3 ⁄2 4.000 ±0.008 0.100 0.078 0.095 0.115 0.138 0.147 0.072 0.088 0.107 0.128 0.136
4 4.500 ±0.009 0.100 0.089 0.109 0.131 0.155 0.166 0.082 0.100 0.121 0.145 0.154
5 5.563 ±0.010 0.100 0.112 0.136 0.164 0.192 0.205 0.103 0.126 0.152 0.179 0.191
6 6.625 ±0.011 0.100 0.135 0.164 0.196 0.229 0.244 0.125 0.152 0.182 0.213 0.227
A
Tolerance on wall thickness is +12, −0 % or +0.030, −0.000 in. whichever is greater.
B
“Out-of-round” is defined as maximum diameter minus minimum diameter.
F512−12 (2017)
TABLE 2 Belled End Dimensions (Clearance Fit System), in. TABLE 3 Types of Conduit Fittings
Average Average Tolerance Out-of Socket Depth 1. Couplings
Nominal
Entrance Bottom on Round 2. Domed caps
min max
Size
A
Diameter Diameter Diameters Tolerance 3. Flat caps
4. Fittings plugs
1 1.331 1.320 ±0.005 0.060 1.000 1.750
5. Tapered plugs
1 ⁄2 1.921 1.906 ±0.006 0.060 1.375 2.125
6. Bends (5, 22 ⁄2, 30, 45, and 90°)
2 2.400 2.381 ±0.006 0.060 1.750 2.500
7. Sweeps (5, 22 ⁄2, 30, 45, and 90°)
3 3.538 3.508 ±0.008 0.060 2.875 3.625
8. Angle Couplings (5°)
3 ⁄2 4.041 4.008 ±0.008 0.100 3.125 3.875
9. Fiber conduit adapters
4 4.544 4.509 ±0.009 0.100 3.375 4.125
10. Cement-asbestos conduit adapters
5 5.614 5.573 ±0.010 0.100 4.000 4.750
11. Water-tight expansion couplings
6 6.687 6.636 ±0.011 0.100 5.000 5.750
12. Spigot-ended reducers
A
“Out-of-round” is defined as maximum diameter minus minimum diameter.
13. Socket end-bells
TABLE 4 Fittings Socket Dimensions, in.
6.2.7 Integral belled ends shall be centered to provide a
visible shoulder around the entire circumference. NOTE 1—Thermoformed fittings may employ the dimensions listed in
Table 4, or the dimensions listed in Table 2 for integral bell ends.
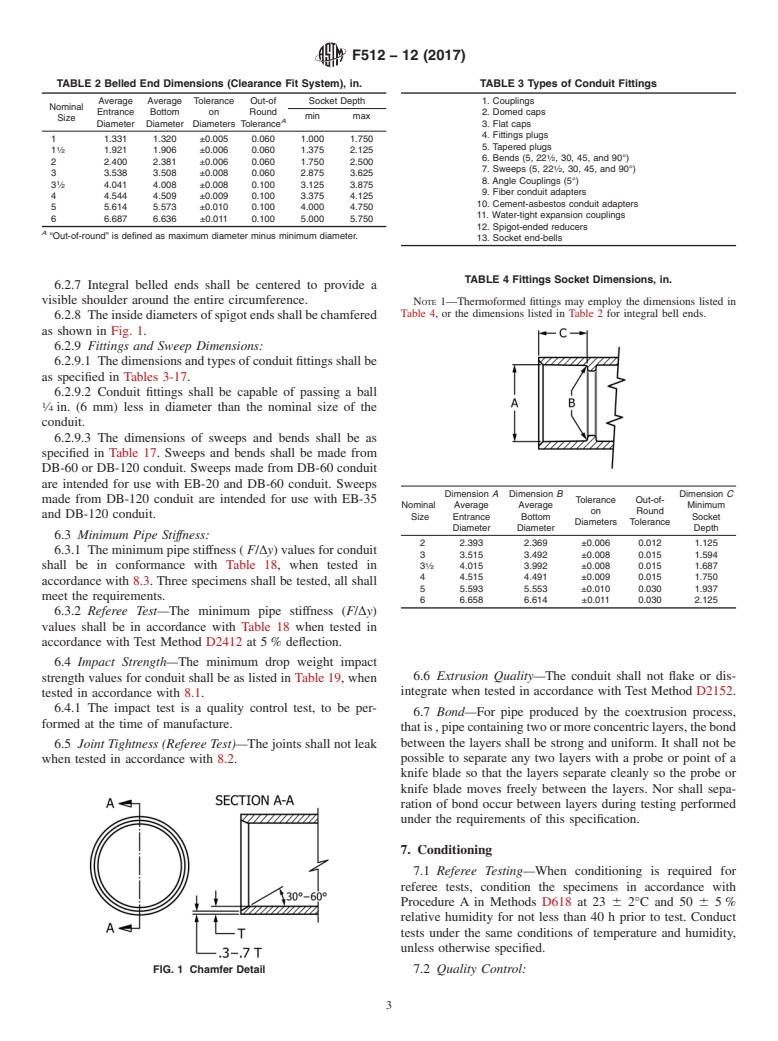
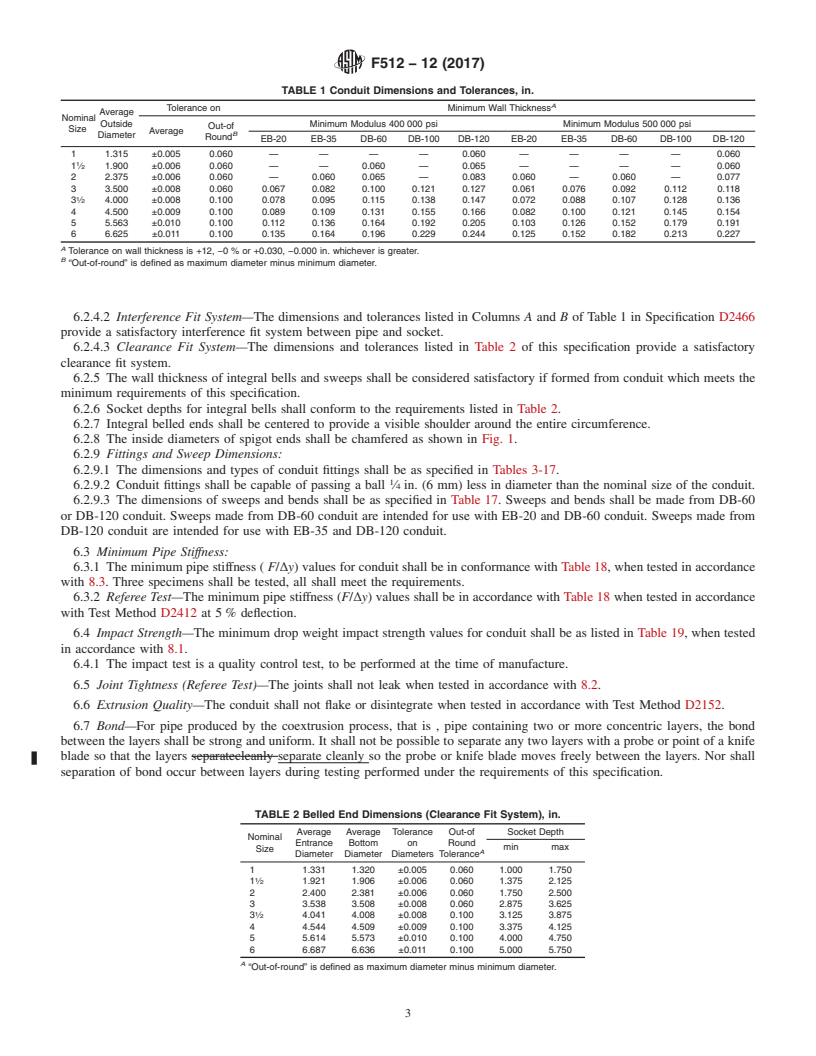
6.2.8 Theinsidediametersofspigotendsshallbechamfered
as shown in Fig. 1.
6.2.9 Fittings and Sweep Dimensions:
6.2.9.1 The dimensions and types of conduit fittings shall be
as specified in Tables 3-17.
6.2.9.2 Conduit fittings shall be capable of passing a ball
⁄4 in. (6 mm) less in diameter than the nominal size of the
conduit.
6.2.9.3 The dimensions of sweeps and bends shall be as
specified in Table 17. Sweeps and bends shall be made from
DB-60 or DB-120 conduit. Sweeps made from DB-60 conduit
are intended for use with EB-20 and DB-60 conduit. Sweeps
Dimension A Dimension B Dimension C
made from DB-120 conduit are intended for use with EB-35 Tolerance Out-of-
Nominal Average Average Minimum
on Round
and DB-120 conduit.
Size Entrance Bottom Socket
Diameters Tolerance
Diameter Diameter Depth
6.3 Minimum Pipe Stiffness:
2 2.393 2.369 ±0.006 0.012 1.125
6.3.1 The minimum pipe stiffness ( F/∆y) values for conduit
3 3.515 3.492 ±0.008 0.015 1.594
shall be in conformance with Table 18, when tested in 3 ⁄2 4.015 3.992 ±0.008 0.015 1.687
4 4.515 4.491 ±0.009 0.015 1.750
accordance with 8.3. Three specimens shall be tested, all shall
5 5.593 5.553 ±0.010 0.030 1.937
meet the requirements.
6 6.658 6.614 ±0.011 0.030 2.125
6.3.2 Referee Test—The minimum pipe stiffness (F/∆y)
values shall be in accordance with Table 18 when tested in
accordance with Test Method D2412 at 5 % deflection.
6.4 Impact Strength—The minimum drop weight impact
6.6 Extrusion Quality—The conduit shall not flake or dis-
strength values for conduit shall be as listed in Table 19, when
integrate when tested in accordance with Test Method D2152.
tested in accordance with 8.1.
6.4.1 The impact test is a quality control test, to be per-
6.7 Bond—For pipe produced by the coextrusion process,
formed at the time of manufacture.
thatis,pipecontainingtwoormoreconcentriclayers,thebond
between the layers shall be strong and uniform. It shall not be
6.5 Joint Tightness (Referee Test)—The joints shall not leak
possible to separate any two layers with a probe or point of a
when tested in accordance with 8.2.
knife blade so that the layers separate cleanly so the probe or
knife blade moves freely between the layers. Nor shall sepa-
ration of bond occur between layers during testing performed
under the requirements of this specification.
7. Conditioning
7.1 Referee Testing—When conditioning is required for
referee tests, condition the specimens in accordance with
Procedure A in Methods D618 at 23 6 2°C and 50 6 5%
relative humidity for not less than 40 h prior to test. Conduct
tests under the same conditions of temperature and humidity,
unless otherwise specified.
FIG. 1 Chamfer Detail 7.2 Quality Control:
F512−12 (2017)
TABLE 5 Coupling Dimensions, in. TABLE 7 Domed Cap Dimensions, in.
Nominal Size M, max SH, max N,min
Nominal Size W, max M, max
13 1
11 ⁄64 0.070 ⁄16
3 13
22 ⁄32 2 ⁄16
1 9 1
1 ⁄2 2 ⁄32 0.070 ⁄16
334 ⁄32
47 3
22 ⁄64 0.075 ⁄32
1 1 5
3 ⁄2 3 ⁄8 4 ⁄8
31 7
33 ⁄32 0.076 ⁄64
31 13
43 ⁄64 5 ⁄64
1 1 7
3 ⁄2 4 ⁄2 0.087 ⁄64
27 1
54 ⁄64 6 ⁄4
1 7
45 ⁄32 0.097 ⁄64
7 25
65 ⁄32 7 ⁄64
1 9
56 ⁄4 0.118 ⁄64
1 9
67 ⁄2 0.140 ⁄64
TABLE 8 Flat Cap Dimensions, in.
TABLE 6 5° Angle Couplings, in.
Nominal Size F,min M, max
19 35
2 ⁄32 2 ⁄64
1 45
3 ⁄16 3 ⁄64
1 5 7
3 ⁄2 ⁄64 4 ⁄32
3 3
4 ⁄32 4 ⁄4
3 53
5 ⁄32 5 ⁄64
1 61
6 ⁄8 6 ⁄64
TABLE 9 Fitting Plug Dimensions, in.
Nominal Size M, max N,min X and Tolerance Y, min Bend R
22 ⁄16 1.50 2.375 ± 0.006 2.62 30
33 ⁄32 1.55 3.500 ± 0.008 3.14 36
44 ⁄64 1.39 4.500 ± 0.009 3.14 36
55 ⁄64 2.25 5.563 ± 0.010 4.19 48
67 ⁄64 3.12 6.625
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F512 − 12 F512 − 12 (Reapproved 2017) An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
Smooth-Wall Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Conduit and
Fittings for Underground Installation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F512; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*Scope
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for single wall and coextruded cellular core smooth-wall poly(vinyl chloride)
conduit and fittings for underground communication and electrical power wire and cables. Plastics which does not meet the
material requirements specified in Section 5 is excluded from single layer and all coextruded layers.
1.2 The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 8, of this specification:This standard
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
D1784 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Compounds and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC)
Compounds
D2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings
D2152 Test Method for Adequacy of Fusion of Extruded Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Molded Fittings by Acetone
Immersion
D2412 Test Method for Determination of External Loading Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loading
D2444 Test Method for Determination of the Impact Resistance of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings by Means of a Tup (Falling
Weight)
D2466 Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Pipe Fittings, Schedule 40
D2564 Specification for Solvent Cements for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Piping Systems
D2855 Practice for the Two-Step (Primer and Solvent Cement) Method of Joining Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) or Chlorinated
Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Pipe and Piping Components with Tapered Sockets
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F412 and abbreviations are in accordance with Terminology D1600, unless
otherwise specified. The abbreviation for poly(vinyl chloride) is PVC.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 cellular plastic—a plastic containing numerous cells, intentionally introduced, interconnecting or not, distributed
throughout the mass.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.25 on Vinyl Based
Pipe.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2012April 1, 2017. Published September 2012April 2017. Originally approved in 1977. Last previous edition approved in 20062012 as
F51206.–12. DOI: 10.1520/F0512-12.10.1520/F0512-12R17.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F512 − 12 (2017)
3.2.2 coextruded pipe—pipe consisting of two or more concentric layers of material bonded together in processing by any
combination of temperature, pressure, grafting, cross-linking or adhesion.
3.2.3 coextrusion—a process whereby two or more heated or unheated plastic material streams, forced through one or more
shaping orifice(s), become one continuously formed piece.
3.2.4 external recycled material—industrial rework generated by a different company manufacturing to this specification.
Composition is known by the industrial source of the material.
3.2.5 post-consumer recycled material—finished goods that have been purchased by the public, then returned to industry and
reprocessed into raw materials. Identity of finished goods is known by the reprocessing company.
3.2.6 certificate of composition—a certificate describing the certain properties of an external recycled material of a post
consumer recycled material.
3.2.7 composition disclosure—a document describing the formulation of an external recycled material.
4. Classification
4.1 This specification covers five types of underground conduit. There are two having lesser pipe stiffness values, designed
primarily for concrete encased burial (EB), and three with greater pipe stiffness values, designed primarily for direct burial (DB).
The complete designations follow:
Type EB-20 — Designed to be encased in concrete.
Type EB-35 — Designed to be encased in concrete.
Type DB-60 — Designed for direct burial without encasement in concrete.
Type DB-100 — Designed for direct burial without encasement in concrete.
Type DB-120 — Designed for direct burial without encasement in concrete.
4.2 This specification covers conduit with integral bells, or with either separate or attached couplings.
4.3 This specification covers molded and fabricated fittings intended for use with all types of conduit.
5. Materials
5.1 Basic Materials—The conduit shall be made of virgin homopolymer PVC compound having a cell classification of 12254,
12164 (with a minimum tensile strength of 4000 psi (28 MPa)), or 12264(with a minimum tensile modulus of 500 000 psi) as
defined in Specification D1784. Molded fittings shall be made from PVC compound having a cell classification of 12234 or 13343
as defined in Specification D1784. Homopolymer PVC compounds must equal or exceed the requirements of the listed cell
classification numbers.
5.2 Rework Materials—Rework material from the manufacturer’s own conduit or fittings production may be used by the same
manufacturer, provided that the conduit or fittings produced meet all of the requirements of this specification. Rework material
from the manufacture’s coextruded cellular core conduit shall be used in the core if it contains any residual blowing agent. The
pipe produced shall meet all of the requirements of this specification.
5.3 Recycled PVC Materials—Recycled PVC materials conforming to the cell classification of this specification may be used
provided they are clean and free from foreign materials and provided that the conduit or fittings produced meet all requirements
of this specification.
5.4 Solvent Cement—The solvent cement shall meet the requirements of Specification D2564.
6. Requirements
6.1 Workmanship—The conduit and fittings shall be homogeneous throughout, and free from visible cracks, holes, foreign
inclusions, or other injurious defects. The conduit and fittings shall be as uniform as is commercially practical in color, opacity,
density, and other physical properties.
6.2 Dimensions:
6.2.1 Dimensions shall be determined in accordance with Test Method D2122.
6.2.2 The dimensions and tolerances of the conduit shall be as specified in Table 1.
6.2.3 Lengths—Conduit shall be supplied in lengths of 20 or 25 ft, or as otherwise agreed upon between the purchaser and the
seller. A length shall be considered to be the overall length of the conduit, including integral bell, or coupling if attached, unless
otherwise specified. Tolerance on length shall be 61 in. (625 mm).
6.2.4 Integral Bell Dimensions:
6.2.4.1 Two systems of fit for integral bells are in common use. Unless otherwise specified, the manufacturer may employ either
of them.
Supporting data have been filed at ASTM International Headquarters and may be obtained by requesting Research Report RR:F17-1002.
F512 − 12 (2017)
TABLE 1 Conduit Dimensions and Tolerances, in.
A
Tolerance on Minimum Wall Thickness
Average
Nominal
Outside Minimum Modulus 400 000 psi Minimum Modulus 500 000 psi
Out-of
Size
Average
B
Diameter
Round
EB-20 EB-35 DB-60 DB-100 DB-120 EB-20 EB-35 DB-60 DB-100 DB-120
1 1.315 ±0.005 0.060 — — — — 0.060 — — — — 0.060
1 ⁄2 1.900 ±0.006 0.060 — — 0.060 — 0.065 — — — — 0.060
2 2.375 ±0.006 0.060 — 0.060 0.065 — 0.083 0.060 — 0.060 — 0.077
3 3.500 ±0.008 0.060 0.067 0.082 0.100 0.121 0.127 0.061 0.076 0.092 0.112 0.118
3 ⁄2 4.000 ±0.008 0.100 0.078 0.095 0.115 0.138 0.147 0.072 0.088 0.107 0.128 0.136
4 4.500 ±0.009 0.100 0.089 0.109 0.131 0.155 0.166 0.082 0.100 0.121 0.145 0.154
5 5.563 ±0.010 0.100 0.112 0.136 0.164 0.192 0.205 0.103 0.126 0.152 0.179 0.191
6 6.625 ±0.011 0.100 0.135 0.164 0.196 0.229 0.244 0.125 0.152 0.182 0.213 0.227
A
Tolerance on wall thickness is +12, −0 % or +0.030, −0.000 in. whichever is greater.
B
“Out-of-round” is defined as maximum diameter minus minimum diameter.
6.2.4.2 Interference Fit System—The dimensions and tolerances listed in Columns A and B of Table 1 in Specification D2466
provide a satisfactory interference fit system between pipe and socket.
6.2.4.3 Clearance Fit System—The dimensions and tolerances listed in Table 2 of this specification provide a satisfactory
clearance fit system.
6.2.5 The wall thickness of integral bells and sweeps shall be considered satisfactory if formed from conduit which meets the
minimum requirements of this specification.
6.2.6 Socket depths for integral bells shall conform to the requirements listed in Table 2.
6.2.7 Integral belled ends shall be centered to provide a visible shoulder around the entire circumference.
6.2.8 The inside diameters of spigot ends shall be chamfered as shown in Fig. 1.
6.2.9 Fittings and Sweep Dimensions:
6.2.9.1 The dimensions and types of conduit fittings shall be as specified in Tables 3-17.
6.2.9.2 Conduit fittings shall be capable of passing a ball ⁄4 in. (6 mm) less in diameter than the nominal size of the conduit.
6.2.9.3 The dimensions of sweeps and bends shall be as specified in Table 17. Sweeps and bends shall be made from DB-60
or DB-120 conduit. Sweeps made from DB-60 conduit are intended for use with EB-20 and DB-60 conduit. Sweeps made from
DB-120 conduit are intended for use with EB-35 and DB-120 conduit.
6.3 Minimum Pipe Stiffness:
6.3.1 The minimum pipe stiffness ( F/Δy) values for conduit shall be in conformance with Table 18, when tested in accordance
with 8.3. Three specimens shall be tested, all shall meet the requirements.
6.3.2 Referee Test—The minimum pipe stiffness (F/Δy) values shall be in accordance with Table 18 when tested in accordance
with Test Method D2412 at 5 % deflection.
6.4 Impact Strength—The minimum drop weight impact strength values for conduit shall be as listed in Table 19, when tested
in accordance with 8.1.
6.4.1 The impact test is a quality control test, to be performed at the time of manufacture.
6.5 Joint Tightness (Referee Test)—The joints shall not leak when tested in accordance with 8.2.
6.6 Extrusion Quality—The conduit shall not flake or disintegrate when tested in accordance with Test Method D2152.
6.7 Bond—For pipe produced by the coextrusion process, that is , pipe containing two or more concentric layers, the bond
between the layers shall be strong and uniform. It shall not be possible to separate any two layers with a probe or point of a knife
blade so that the layers separatecleanly separate cleanly so the probe or knife blade moves freely between the layers. Nor shall
separation of bond occur between layers during testing performed under the requirements of this specification.
TABLE 2 Belled End Dimensions (Clearance Fit System), in.
Average Average Tolerance Out-of Socket Depth
Nominal
Entrance Bottom on Round
min max
Size
A
Diameter Diameter Diameters Tolerance
1 1.331 1.320 ±0.005 0.060 1.000 1.750
1 ⁄2 1.921 1.906 ±0.006 0.060 1.375 2.125
2 2.400 2.381 ±0.006 0.060 1.750 2.500
3 3.538 3.508 ±0.008 0.060 2.875 3.625
3 ⁄2 4.041 4.008 ±0.008 0.100 3.125 3.875
4 4.544 4.509 ±0.009 0.100 3.375 4.125
5 5.614 5.573 ±0.010 0.100 4.000 4.750
6 6.687 6.636 ±0.011 0.100 5.000 5.750
A
“Out-of-round” is defined as maximum diameter minus minimum diameter.
F512 − 12 (2017)
FIG. 1 Chamfer Detail
TABLE 3 Types of Conduit Fittings
1. Couplings
2. Domed caps
3. Flat caps
4. Fittings plugs
5. Tapered plugs
6. Bends (5, 22 ⁄2, 30, 45, and 90°)
7. Sweeps (5, 22 ⁄2, 30, 45, and 90°)
8. Angle Couplings (5°)
9. Fiber conduit adapters
10. Cement-asbestos conduit adapters
11. Water-tight expansion couplings
12. Spigot-ended reducers
13. Socket end-bells
TABLE 4 Fittings Socket Dimensions, in.
NOTE 1—Thermoformed fittings may employ the dimensions listed in
Table 4, or the dimensions listed in Table 2 for integral bell ends.
Dimension A Dimension B Dimension C
Tolerance Out-of-
Nominal Average Average Minimum
on Round
Size Entrance Bottom Socket
Diameters Tolerance
Diameter Diameter Depth
2 2.393 2.369 ±0.006 0.012 1.125
3 3.515 3.492 ±0.008 0.015 1.594
3 ⁄2 4.015 3.992 ±0.008 0.015 1.687
4 4.515 4.491 ±0.009 0.015 1.750
5 5.593 5.553 ±0.010 0.030 1.937
6 6.658 6.614 ±0.011 0.030 2.125
7. Conditioning
7.1 Referee Testing—When conditioning is required for referee tests, condition the specimens in accordance with Procedure A
in Methods D618 at 23 6 2°C and 50 6 5 % relative humidity for not less than 40 h prior to test. Conduct tests under the same
conditions of temperature and humidity, unless otherwise specified.
7.2 Quality Control:
7.2.1 For quality control tests, condition specimens for a minimum of 3 h in air, or 1 h in liquid at 23 6 2°C (70 to 77°F). Test
the specimens at 23 6 2°C without regard to relative humidity.
7.2.2 For the impact test, condition specimens for at least 30 min at 0 to 1.6°C (32 to 35°F).
F512 − 12 (2017)
TABLE 5 Coupling Dimensions, in.
Nominal Size M, max SH,
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.