ASTM B456-17(2022)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings of Copper Plus Nickel Plus Chromium and Nickel Plus Chromium
Standard Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings of Copper Plus Nickel Plus<brk/> Chromium and Nickel Plus Chromium
ABSTRACT
This specification establishes the requirements for several types and grades of electrodeposited copper plus nickel plus chromium and nickel plus chromium coatings on steel, copper, copper alloys, Type 300 and 400 series stainless steels, aluminum, aluminum alloys, and zinc alloys for application where both appearance and protection of the basis metal against corrosion are important. This specification does not cover plating on plastics. Each coating shall be designated a classification code, which comprises of the following numbers and symbols: service condition number, which indicates the severity of exposure for which the coating is intended; coating classification number, which contains the chemical symbol of each metallic element that comprises the basis metal, or the designated AISI number in the case of stainless steels, and their corresponding thickness; and symbols for expressing the type of coating. Products shall be sampled and inspected accordingly for visual defects, thickness, adhesion, elongation, ductility, corrosion, sulfur content, density, and discontinuities.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers requirements for several types and grades of electrodeposited copper plus nickel plus chromium or nickel plus chromium coatings on steel, nickel plus chromium coatings on copper and copper alloys, nickel plus chromium coatings on Type 300 and 400 series stainless steel and copper plus nickel plus chromium coatings on aluminum and its alloys and zinc alloys for applications where both appearance and protection of the basis metal against corrosion are important. Five grades of coatings are provided to correspond with the service conditions under which each is expected to provide satisfactory performance: namely, extended very severe, very severe, severe, moderate, and mild. Definitions and typical examples of these service conditions are provided in Appendix X1.
1.2 This specification does not cover the requirements for the plating on plastics, see Specification B604.
1.3 The following hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portions, Appendix X2, Appendix X3, Appendix X4, and Appendix X5 of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:B456 −17 (Reapproved 2022)
Standard Specification for
Electrodeposited Coatings of Copper Plus Nickel Plus
Chromium and Nickel Plus Chromium
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B456; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This specification covers requirements for several types
B183Practice for Preparation of Low-Carbon Steel for
and grades of electrodeposited copper plus nickel plus chro-
Electroplating
mium or nickel plus chromium coatings on steel, nickel plus
B242Guide for Preparation of High-Carbon Steel for Elec-
chromium coatings on copper and copper alloys, nickel plus
troplating
chromium coatings on Type 300 and 400 series stainless steel
B252Guide for Preparation of Zinc Alloy Die Castings for
and copper plus nickel plus chromium coatings on aluminum
Electroplating and Conversion Coatings
and its alloys and zinc alloys for applications where both
B253Guide for Preparation of Aluminum Alloys for Elec-
appearance and protection of the basis metal against corrosion
troplating
are important. Five grades of coatings are provided to corre-
B254Practice for Preparation of and Electroplating on
spondwiththeserviceconditionsunderwhicheachisexpected
Stainless Steel
to provide satisfactory performance: namely, extended very
B281Practice for Preparation of Copper and Copper-Base
severe, very severe, severe, moderate, and mild. Definitions
Alloys for Electroplating and Conversion Coatings
and typical examples of these service conditions are provided
B320Practice for Preparation of Iron Castings for Electro-
in Appendix X1.
plating
B368Test Method for Copper-AcceleratedAceticAcid-Salt
1.2 This specification does not cover the requirements for
Spray (Fog) Testing (CASS Test)
the plating on plastics, see Specification B604.
B380Test Method for Corrosion Testing of Decorative
1.3 The following hazards caveat pertains only to the test Electrodeposited Coatings by the Corrodkote Procedure
B487Test Method for Measurement of Metal and Oxide
methods portions, Appendix X2, Appendix X3, Appendix X4,
Coating Thickness by Microscopical Examination of
and Appendix X5 of this specification: This standard does not
Cross Section
purport to address all of safety concerns, if any, associated
B489Practice for Bend Test for Ductility of Electrodepos-
with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard
ited and Autocatalytically Deposited Metal Coatings on
to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental
Metals
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
B490Practice for Micrometer Bend Test for Ductility of
tions prior to use.
Electrodeposits
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
B499Test Method for Measurement of CoatingThicknesses
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
by the Magnetic Method: Nonmagnetic Coatings on
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Magnetic Basis Metals
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
B504Test Method for Measurement of Thickness of Metal-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
lic Coatings by the Coulometric Method
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
B530Test Method for Measurement of CoatingThicknesses
by the Magnetic Method: Electrodeposited Nickel Coat-
ings on Magnetic and Nonmagnetic Substrates
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B08 on
Metallic and Inorganic Coatings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
B08.05 on Decorative Coatings. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2022. Published October 2022. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1967. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as B456–17. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/B0456-17R22. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
B456−17 (2022)
B537Practice for Rating of Electroplated Panels Subjected 4.2.1 Theserviceconditionnumberindicatestheseverityof
to Atmospheric Exposure exposure for which the grade of coating is intended:
B568Test Method for Measurement of Coating Thickness SC 5 extended severe service
by X-Ray Spectrometry SC 4 very severe service,
B571Practice for Qualitative Adhesion Testing of Metallic SC 3 severe service,
Coatings SC 2 moderate service, and
B602Guide for Attribute Sampling of Metallic and Inor- SC 1 mild service.
ganic Coatings 4.2.2 Typical service conditions for which the various
B604Specification for Decorative Electroplated Coatings of service condition numbers are appropriate are given in Appen-
Copper Plus Nickel Plus Chromium on Plastics dix X1.
B659Guide for Measuring Thickness of Metallic and Inor-
4.3 Coating Classification Number—The coating classifica-
ganic Coatings
tion number comprises:
B697Guide for Selection of Sampling Plans for Inspection
4.3.1 The chemical symbol for the basis metal (or for the
of Electrodeposited Metallic and Inorganic Coatings
principalmetalifanalloy)followedbyaslashmark,exceptin
B762GuideofVariablesSamplingofMetallicandInorganic
the case of stainless steel. In this case, the designation shall be
Coatings
SS followed by the designated AISI number followed by a
B764Test Method for Simultaneous Thickness and Elec-
slash, that is, SS463/,
trode Potential Determination of Individual Layers in
4.3.2 The chemical symbol for copper (Cu) (if copper is
Multilayer Nickel Deposit (STEP Test)
used),
B995Test Method for Chloride Resistance Test for Chro-
4.3.3 A number indicating the minimum thickness of the
mium Electroplated Parts (Russian Mud Test)
copper coating in micrometers (if copper is used),
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
4.3.4 A lower-case letter designating the type of copper
D3951Practice for Commercial Packaging
deposit (if copper is used) (see 4.4 and 6.2.3),
E50Practices for Apparatus, Reagents, and Safety Consid-
4.3.5 The chemical symbol for nickel (Ni),
erations for Chemical Analysis of Metals, Ores, and
4.3.6 A number indicating the minimum thickness of the
Related Materials
nickel coating, in micrometers,
G85Practice for Modified Salt Spray (Fog) Testing
4.3.7 A lower-case letter designating the type of nickel
2.2 ISO Standards:
deposit (see 4.4 and 6.2.4),
ISO 1456Metallic coatings—Electrodeposited coatings of
4.3.8 The chemical symbol for chromium (Cr), and
nickel plus chromium and of copper plus nickel plus
4.3.9 A letter (or letters) designating the type of chromium
chromium
depositanditsminimumthicknessinmicrometers(see4.4and
6.2.5).
3. Terminology
4.4 Symbols for Expressing Classification—The following
3.1 Definitions:
lower-case letters shall be used in coating classification num-
3.1.1 significant surfaces—those surfaces normally visible
bers to describe the types of coatings:
(directlyorbyreflection)thatareessentialtotheappearanceor
a —ductile copper deposited from acid-type baths
serviceabilityofthearticle,orboth,whenassembledinnormal
b —single-layer nickel deposited in the fully-bright condition
position; or that can be the source of corrosion products that
d —double- or triple-layer nickel coatings
r —regular (that is, conventional) chromium
deface visible surfaces on the assembled article. When
mc —microcracked chromium
necessary, the significant surfaces shall be specified by the
mp —microporous chromium
purchaser and shall be indicated on the drawings of the parts,
4.5 Example of Complete Classification Numbers—A coat-
or by the provision of suitably marked samples.
ing on steel comprising 15 µm minimum (ductile acid) copper
3.1.2 p-points—specific points of measurement that are
plus 25 µm minimum (duplex) nickel plus 0.25µ m minimum
encouraged to be determined and agreed upon with the
(micro-cracked) chromium has the classification number: Fe/
customer early in the contract review process. These are used
Cu15aNi25d Cr mc (see 4.3 and 6.2 for explanation of
for measurement of critical characteristics that vary with
symbols).
current density such as thickness, STEP, active sites, etc. and
may be designated at multiple locations per part.
5. Ordering Information
5.1 When ordering articles to be electroplated in confor-
4. Classification
mance with this standard, the purchaser shall state the follow-
4.1 Five grades of coatings designated by service condition
ing:
numbersandseveraltypesofcoatingsdefinedbyclassification
5.1.1 The ASTM designation number of this standard.
numbers are covered by this specification.
5.1.2 Eithertheclassificationnumberofthespecificcoating
4.2 Service Condition Number:
required (see 4.3) or the substrate material and the service
condition number denoting the severity of the conditions it is
requiredtowithstand(see4.2).Iftheserviceconditionnumber
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de
isquotedandnottheclassificationnumber,themanufactureris
la Voie-Creuse, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://
www.iso.ch. free to supply any of the types of coatings designated by the
B456−17 (2022)
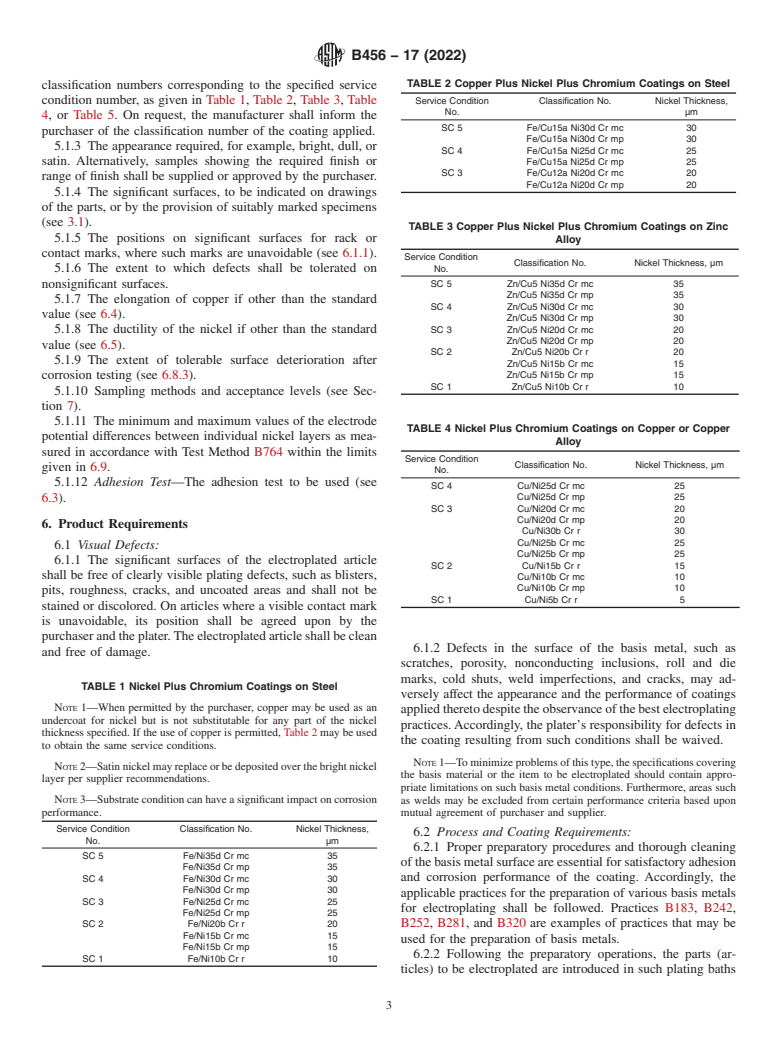
TABLE 2 Copper Plus Nickel Plus Chromium Coatings on Steel
classification numbers corresponding to the specified service
condition number, as given in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table Service Condition Classification No. Nickel Thickness,
No. µm
4,or Table 5. On request, the manufacturer shall inform the
SC 5 Fe/Cu15a Ni30d Cr mc 30
purchaser of the classification number of the coating applied.
Fe/Cu15a Ni30d Cr mp 30
5.1.3 The appearance required, for example, bright, dull, or
SC 4 Fe/Cu15a Ni25d Cr mc 25
satin. Alternatively, samples showing the required finish or Fe/Cu15a Ni25d Cr mp 25
SC 3 Fe/Cu12a Ni20d Cr mc 20
range of finish shall be supplied or approved by the purchaser.
Fe/Cu12a Ni20d Cr mp 20
5.1.4 The significant surfaces, to be indicated on drawings
of the parts, or by the provision of suitably marked specimens
(see 3.1).
TABLE 3 Copper Plus Nickel Plus Chromium Coatings on Zinc
5.1.5 The positions on significant surfaces for rack or
Alloy
contact marks, where such marks are unavoidable (see 6.1.1).
Service Condition
Classification No. Nickel Thickness, µm
5.1.6 The extent to which defects shall be tolerated on No.
SC 5 Zn/Cu5 Ni35d Cr mc 35
nonsignificant surfaces.
Zn/Cu5 Ni35d Cr mp 35
5.1.7 The elongation of copper if other than the standard
SC 4 Zn/Cu5 Ni30d Cr mc 30
value (see 6.4).
Zn/Cu5 Ni30d Cr mp 30
SC 3 Zn/Cu5 Ni20d Cr mc 20
5.1.8 The ductility of the nickel if other than the standard
Zn/Cu5 Ni20d Cr mp 20
value (see 6.5).
SC 2 Zn/Cu5 Ni20b Cr r 20
5.1.9 The extent of tolerable surface deterioration after
Zn/Cu5 Ni15b Cr mc 15
corrosion testing (see 6.8.3). Zn/Cu5 Ni15b Cr mp 15
SC 1 Zn/Cu5 Ni10b Cr r 10
5.1.10 Sampling methods and acceptance levels (see Sec-
tion 7).
5.1.11 The minimum and maximum values of the electrode
TABLE 4 Nickel Plus Chromium Coatings on Copper or Copper
potential differences between individual nickel layers as mea-
Alloy
sured in accordance with Test Method B764 within the limits
Service Condition
Classification No. Nickel Thickness, µm
given in 6.9.
No.
5.1.12 Adhesion Test—The adhesion test to be used (see
SC 4 Cu/Ni25d Cr mc 25
Cu/Ni25d Cr mp 25
6.3).
SC 3 Cu/Ni20d Cr mc 20
Cu/Ni20d Cr mp 20
6. Product Requirements
Cu/Ni30b Cr r 30
Cu/Ni25b Cr mc 25
6.1 Visual Defects:
Cu/Ni25b Cr mp 25
6.1.1 The significant surfaces of the electroplated article
SC 2 Cu/Ni15b Cr r 15
shall be free of clearly visible plating defects, such as blisters,
Cu/Ni10b Cr mc 10
Cu/Ni10b Cr mp 10
pits, roughness, cracks, and uncoated areas and shall not be
SC 1 Cu/Ni5b Cr r 5
stained or discolored. On articles where a visible contact mark
is unavoidable, its position shall be agreed upon by the
purchaserandtheplater.Theelectroplatedarticleshallbeclean
6.1.2 Defects in the surface of the basis metal, such as
and free of damage.
scratches, porosity, nonconducting inclusions, roll and die
marks, cold shuts, weld imperfections, and cracks, may ad-
TABLE 1 Nickel Plus Chromium Coatings on Steel
versely affect the appearance and the performance of coatings
NOTE 1—When permitted by the purchaser, copper may be used as an
appliedtheretodespitetheobservanceofthebestelectroplating
undercoat for nickel but is not substitutable for any part of the nickel
practices.Accordingly, the plater’s responsibilityfor defects in
thicknessspecified.Iftheuseofcopperispermitted, Table2maybeused
the coating resulting from such conditions shall be waived.
to obtain the same service conditions.
NOTE1—Tominimizeproblemsofthistype,thespecificationscovering
NOTE2—Satinnickelmayreplaceorbedepositedoverthebrightnickel
the basis material or the item to be electroplated should contain appro-
layer per supplier recommendations.
priate limitations on such basis metal conditions. Furthermore, areas such
NOTE3—Substrateconditioncanhaveasignificantimpactoncorrosion
as welds may be excluded from certain performance criteria based upon
performance. mutual agreement of purchaser and supplier.
Service Condition Classification No. Nickel Thickness,
6.2 Process and Coating Requirements:
No. µm
6.2.1 Proper preparatory procedures and thorough cleaning
SC 5 Fe/Ni35d Cr mc 35
ofthebasismetalsurfaceareessentialforsatisfactoryadhesion
Fe/Ni35d Cr mp 35
SC 4 Fe/Ni30d Cr mc 30 and corrosion performance of the coating. Accordingly, the
Fe/Ni30d Cr mp 30
applicable practices for the preparation of various basis metals
SC 3 Fe/Ni25d Cr mc 25
for electroplating shall be followed. Practices B183, B242,
Fe/Ni25d Cr mp 25
SC 2 Fe/Ni20b Cr r 20 B252, B281, and B320 are examples of practices that may be
Fe/Ni15b Cr mc 15
used for the preparation of basis metals.
Fe/Ni15b Cr mp 15
6.2.2 Following the preparatory operations, the parts (ar-
SC 1 Fe/Ni10b Cr r 10
ticles) to be electroplated are introduced in such plating baths
B456−17 (2022)
A
TABLE 5 Nickel Plus Chromium on Stainless Steels, AISI
haveaminimumductilityof11%.Iftherearethreelayers,the
B
Designated Type 300 and 400 Series, and Copper P
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.