ASTM D5940-96
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Injection Moulding of Test Specimens of Thermoplatic Materials-Plates (Withdrawn 1998)
Standard Test Method for Injection Moulding of Test Specimens of Thermoplatic Materials-Plates (Withdrawn 1998)
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 5940 – 96
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Practice for
Preparing Small Plate Test Specimens of Thermoplastics by
1
Injection Moulding
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5940; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Impact Behaviour of Rigid Plastics—Part 1: Falling Dart
Method
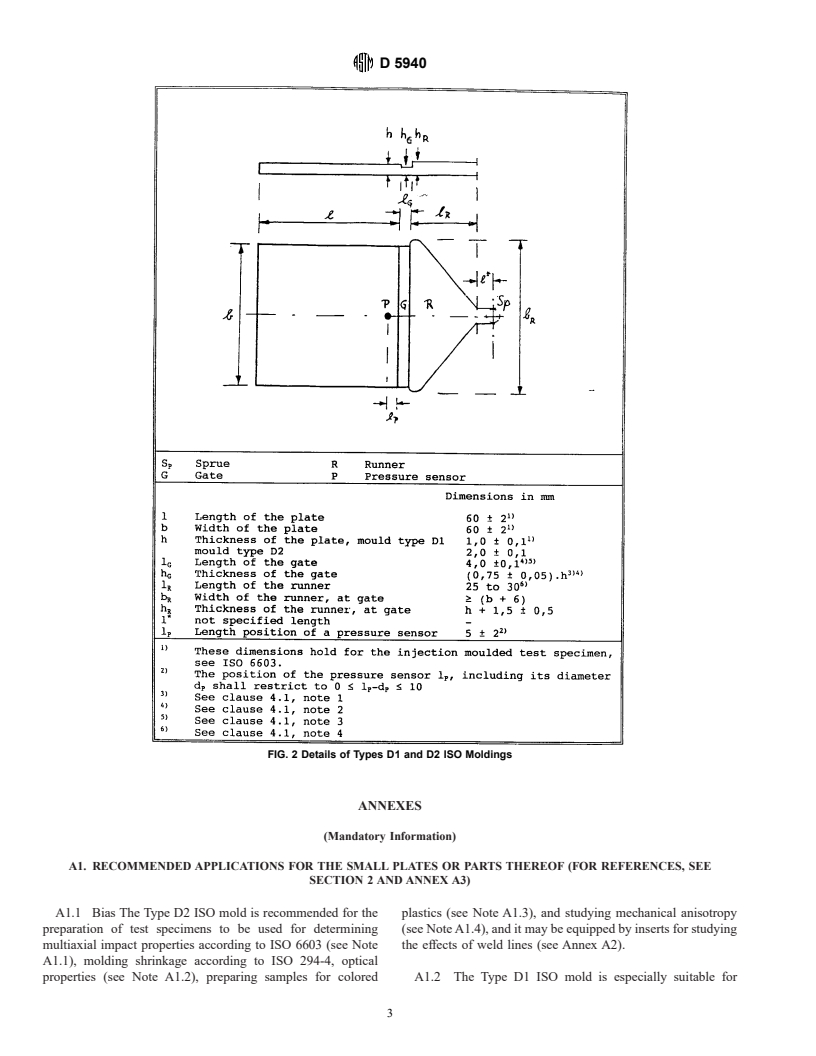
1.1 In this part of this practice, the two-cavity ISO molds,
ISO 6603-2:1989 Plastics—Determination of Multiaxial
Types D1 and D2, are defined for injection molding small
Impact Behaviour of Rigid Plastics—Part 2: Instrumented
plates 60 by 60 mm, with the preferred thicknesses of 1 mm
Puncture Test
(Type D1) and 2 mm (Type D2), which can be used for a
variety of tests (see Annex A1). The molds may additionally be
3. Terminology
equipped by inserts for studying the action of weld lines (see
3.1 Definitions—See Practice D 5939, Section 3.
Annex A2).
1.2 This practice is identical to ISO 294-3.
4.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
5. Apparatus
only.
5.1 ISO Molds, Type D:
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
5.1.1 Plates 60 by 60 mm shall be molded in the Type D
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
two-cavity ISO molds; see Fig. 1. The small plates molded by
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Type D shall have dimensions as given in Fig. 2.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.1.2 The main construction details of the Type D ISO
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
molds shall conform to Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 and to the following
requirements:
2. Referenced Documents
5.1.2.1 See Practice D 5939, 4.1.3.1.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1.2.2 Not relevant;
D 5935 Practice for Plastics—Acquisition and Presentation
5.1.2.3 See Practice D 5939, 4.1.3.3 and 4.1.3.5.
2
of Comparable Single-Point Data
5.1.2.4 Not relevant;
D 5938 Guide Describing the General Principles for Deter-
5.1.2.5 See Practice D 5939, 4.1.3.6.
2
mination of Tensile Properties of Plastics
5.1.2.6 See Practice D 5939, 4.1.3.7, but relating to ISO
D 5939 Practice for Preparing Multipurpose Test Specimens
6603; the essential dimensions in mm are as follows (see Fig.
2
and Bars of Thermoplastics by Injection Molding
2):
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
Length of the plate, 60 to 62
ISO 294-3 Injection Moulding of Test Specimens of Ther-
Width of the plate, 60 to 62
moplastic Materials—Part 3: Plates (ISO Moulds Type D) Thickness of the plate, Type D2, 2.0 to 2.1
Thickness of the plate, Type D1, 1.0 to 1.1
ISO 294-1 Plastics—Injection Moulding of Test Specimens
of Thermoplastics—Part 1: General Principles,
5.1.2.7 See Practice D 5939, 4.1.3.8 through 4.1.3.10.
Multipurpose-Test Specimens (ISO Mould Type A) and
5.1.2.8 Fig. 2 shows the position of a pressure sensor, P,
Bars (ISO Mould Type B)
within the cavity, which is mandatory for the measurement of
ISO 294-4 Plastics—Injection Moulding of Test Specimens
molding shrinkage only; see ISO 294-4. However, it may be
of Thermoplastics—Part 4: Determination of Moulding
suitable for controlling the injection period using any ISO
Shrinkage
mold; see Practice D 5939, 4.1.3.11. The pressure sensor shall
ISO 6603-1:1985 Plastics—Determination of Multiaxial
be coplanar with the mold surface in order to prevent distur-
bance from flow.
5.1.2.9 See Practice D 5939, 4.1.3.12 through 4.1.3.15.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on Plastics
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.61 on USA Technical Advisory
NOTE 1—Gates with strongly reduced thickness have a great influence
Group for ISO/TC 61 on Plastics.
on the orientation of the material within the plate up to large distances
Current edition approved June 10, 1996. Published August 1996.
from the gate. Therefore, the thickness step at the gate has been chosen at
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.03.
3 a minimum value to facilitate measuring the molding shrinkage mechani-
Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
cally; see ISO 294-4.
Floor, New York, NY 10036.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D 5940
this distance at 80 mm gives the advantage that the cutting machine can
be used commonly for taking bars 80 by 10 by 4 mm from the central parts
of the multipurpose test specimens; see Practice D 5939, 4.1.3.12.
5.2 Injection Mol
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.