ASTM D5329-96
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Sealants and Fillers, Hot-Applied, For Joints and Cracks in Asphaltic and Portland Cement Concrete Pavements
Standard Test Methods for Sealants and Fillers, Hot-Applied, For Joints and Cracks in Asphaltic and Portland Cement Concrete Pavements
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover tests for hot-applied types of joint and crack sealants and fillers for portland cement concrete and asphaltic concrete pavements. There are numerous standard material specifications that use these test methods. Refer to the respective standard material specification of interest to determine which of the following test methods to use. For sample melting and concrete block preparation see their respective standard practices.
1.2 The test methods appear in the following sections: Section Artificial Weathering 15 Asphalt Compatibility 14 Bond, Non-Immersed 9 Bond, Fuel-Immersed 11 Bond, Water-Immersed 10 Cone Penetration, Non-Immersed 6 Cone Penetration, Fuel-Immersed 7 Flexibility 18 Flow 8 Resilience 12 Resilience, Oven-Aged 13 Solubility (Change in Weight) 17 Tensile Adhesion 16
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information purposes only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 5329 – 96
Standard Test Methods for
Sealants and Fillers, Hot-Applied, For Joints and Cracks in
Asphaltic and Portland Cement Concrete Pavements
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5329; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D 217 Test Methods for Cone Penetration of Lubricating
Grease
1.1 These test methods cover tests for hot-applied types of
D 471 Test Method for Rubber Property-Effect of Liquids
joint and crack sealants and fillers for portland cement concrete
D 1074 Test Method for Compressive Strength of Bitumi-
and asphaltic concrete pavements. There are numerous stan-
nous Mixtures
dard material specifications that use these test methods. Refer
D 1190 Specification for Concrete Joint Sealer, Hot-Poured
to the respective standard material specification of interest to
Elastic Type
determine which of the following test methods to use. For
D 1559 Test Method for Resistance to Plastic Flow of
sample melting and concrete block preparation see their
Bituminous Mixtures Using Marshall Apparatus
respective standard practices.
D 1561 Practice for Preparation of Bituminous Mixture Test
1.2 The test methods appear in the following sections:
Specimens by Means of California Kneading Compactor
Section
D 1985 Practice for Preparing Concrete Blocks for Testing
Artificial Weathering 15
Asphalt Compatibility 14
Sealants, for Joints and Cracks
Bond, Non-Immersed 9
D 3381 Specification for Viscosity-Graded Asphalt Cement
Bond, Fuel-Immersed 11
for Use in Pavement Construction
Bond, Water-Immersed 10
Cone Penetration, Non-Immersed 6
D 3405 Specification for Joint Sealants, Hot-Applied, for
Cone Penetration, Fuel-Immersed 7
Concrete and Asphalt Pavements
Flexibility 18
D 5167 Practice for Melting of Hot-Applied Joint and
Flow 8
Resilience 12
Crack Sealant for Evaluation
Resilience, Oven-Aged 13
E 145 Specification for Gravity-Convection and Forced-
Solubility (Change in Weight) 17
Ventilation Ovens
Tensile Adhesion 16
E 171 Specification for Standard Atmospheres for Condi-
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
tioning and Testing Materials
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
G 23 Practice for Operating Light-Exposure Apparatus
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
(Carbon-Arc Type) With and Without Water for Exposure
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
of Nonmetallic Material
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3. Significance and Use
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided
3.1 These test methods describe procedures for determining
for information purposes only.
specification conformance for hot-applied, field-molded joint
and crack sealants and fillers.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4. Sample Melting
D 5 Test Method for Penetration of Bituminous Materials
4.1 See Practice D 5167.
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-4 on
Road and Paving Materials and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D04.33 on Formed-In-Place Sealants for Joints and Cracks in Pavements. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
Current edition approved Jan. 10, 1996. Published March 1996. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 09.01.
published as D 5329 – 92. Last previous edition D 5329 – 95. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
2 6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.03. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.09.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 5329
NOTE 1—A release agent should be used to coat molds and spacers to
5. Standard Conditions
prevent them from bonding to the sealants. Extreme care should be
5.1 The laboratory atmospheric conditions, hereinafter re-
exercised to avoid contaminating the area where the joint sealant makes
ferred to as standard conditions, shall be in accordance with
contact with the blocks. A non-toxic release agent is recommended for this
Specification E 171 (73.4 6 3.6°F (23 6 2°C)).
purpose. Two examples that have been found suitable for this purpose are
KY jelly (available at drug stores) and a release agent prepared by
grinding a mixture of approximately 50 % talc, 35 % glycerine, and 15 %
6. Cone Penetration, Non-Immersed
by weight, of a water-soluble medical lubricant into a smooth paste.
6.1 Apparatus—Conduct this test using the apparatus de-
8.1.2 Oven—Forced draft type conforming to Specification
scribed in Test Method D 5, except as specified herein. Use a
E 145 and capable of controlling its temperature6 2°F.
penetration cone in place of the standard penetration needle.
8.2 Specimen Preparation—Pour a portion of the sample
The cone shall conform to the requirements given in Test
prepared in accordance with Practice D 5167 for melting
Methods D 217, except that the interior construction may be
samples into the mold described in 8.1. Fill the mold with an
modified as desired. The total moving weight of the cone and
excess of material. Allow the test specimen to cool at standard
attachments shall be 150.0 6 0.1 g.
conditions for at least ⁄2h, then trim the specimen flush with
6.2 Specimen Preparation—Pour a portion of the sample
the face of the mold with a heated metal knife or spatula and
prepared in accordance with Practice D 5167 into one 6 oz
remove the mold. Allow the specimen to cure under standard
(177 mL) tin measuring approximately 2.76 in. in diameter and
conditions as specified in its respective material specification.
1.77 in. in depth and fill flush with the rim of the tin. Allow the
8.3 Procedure—Mark reference lines on the panel at the
specimen to cure under standard conditions as specified in its
bottom edge of the sealant. Then place the panel containing the
respective material specification.
sample in a forced-draft oven maintained for the time and at the
6.3 Procedure—Place the specimen in a water bath main-
temperature specified in its respective material specification.
tained at 77 6 0.2°F (25 6 0.1°C) for 2 h immediately before
During the test, mount the panel so that the longitudinal axis of
testing. Remove the specimen from the bath and dry the
the specimen is at an angle of 75 6 1° with the horizontal, and
surface. Using the apparatus described in 6.1, make determi-
the transverse axis is horizontal. After the specified test period,
nations at three locations on 120° radii, and halfway between
remove the panel from the oven and measure the movement of
the center and outside of the specimen. Take care to ensure the
the specimen below the reference lines in millimeters.
cone point is placed on a point in the specimen that is
8.4 Report—Report the measurement obtained in 8.3 in
representative of the material itself and is free of dust, water,
millimeters.
bubbles or other foreign material. Clean and dry the cone point
after each determination.
9. Bond, Non-Immersed
6.4 Report—Average the three results and record the value
as the penetration of the specimen in ⁄10 mm units.
9.1 Apparatus:
9.1.1 Extension Machine—The extension machine used in
7. Cone Penetration, Fuel-Immersed
the bond test shall be so designed that the specimen can be
extended a minimum of 0.50 in. (12.7 mm) at a uniform rate of
7.1 Apparatus—Same as described in 6.1.
⁄8 6 0.010 in. (3.2 6 0.26 mm) per hour. It shall consist
7.2 Specimen Preparation—Pour a portion of the sample
essentially of one or more screws rotated by an electric motor
prepared in accordance with Practice D 5167 into one 6 oz tin,
through suitable gear reductions. Self aligning plates or grips,
then proceed as in 6.2.
one fixed and the other carried by the rotating screw or screws,
7.3 Specimen Preparation—Immerse the specimen pre-
shall be provided for holding the test specimen in position
pared as described in 6.2 for 24 h in approximately 0.53 qt (500
during the test.
mL) to provide a minimum of 0.50 in. cover of clean test fuel
9.1.2 Cold Chamber—The cold chamber shall be capable of
conforming to the requirements of Reference Fuel B of Test
maintaining the required cold test temperature within 62°F.
Method D 471, maintained in a water bath at a constant
9.2 Concrete-Block Preparation:
temperature of 120 6 2°F (40 6 1°C). Discard the test fuel
9.2.1 The concrete blocks shall be prepared in accordance
after each specimen immersion. After the 24 h immersion, dry
with Practice D 1985.
the specimen under a draft of an approximately 12 in. (30.5
9.3 Specimen Preparation:
mm) diameter electric fan at standard conditions for 1 h. The
9.3.1 Prepare three test specimens (3 specimens 3 2 5 6
placement of the fan shall be such as to maintain air velocity of
blocks) as follows: On removal from the storage water, again
150 to 500 ft/min (0.76 to 2.54 m/s) over the sample.
scrub the 2 by 3-in. (50 by 75-mm) saw-cut faces of the blocks
7.4 Procedure—Test as described in 6.3.
under running water. When this operation is completed on
7.5 Report—Record as described in 6.4.
individual blocks, again place them under clean, fresh water
8. Flow until all blocks to be used are prepared. When all blocks are
scrubbed, remove them from the water and lightly blot them
8.1 Apparatus:
with an oil-free, soft, absorbent cloth or paper to remove all
8.1.1 Mold—Construct a mold (see Note 1) 1.57 in. wide by
2.36 in. long by 0.125 in. deep (40 by 60 by 3.2 mm) and place
it on a bright tin panel. The tin plate must be free of dirt, oil,
etc. and be between 0.010 and 0.025 in. in thickness (0.25 to
A machine suitable for testing a minimum of three specimens simultaneously
0.64 mm). can be obtained from such sources as Applied Test Systems of Butler, PA.
D 5329
free surface water and condition them according to their
respective material specification.
9.3.2 Take these blocks and mold the test specimen between
them as follows (see Fig. 1): Place four treated (see Note 1)
brass or TFE-fluorocarbon spacer strips, approximately ⁄4 in.
(6.4 mm) thick, on a treated metal plate base to enclose an open
space according to the width specified in the respective
material specification by 2 in. (50 mm) long. Place the blocks
on the spacer strips and space them the required width 6 0.005
in. (60.13 mm) apart by means of other treated brass or
TFE-fluorocarbon spacer strips, of the required width placed at
such distances from the ends that an opening is of the required
width 60.005 in. by 2.000 6 0.005 in. by 2.000 6 0.005 in.
(required width by 50.80 6 0.13 mm by 50.806 0.13 mm) is
formed between the blocks with a ⁄4-in. (6.4-mm) opening
below the blocks.
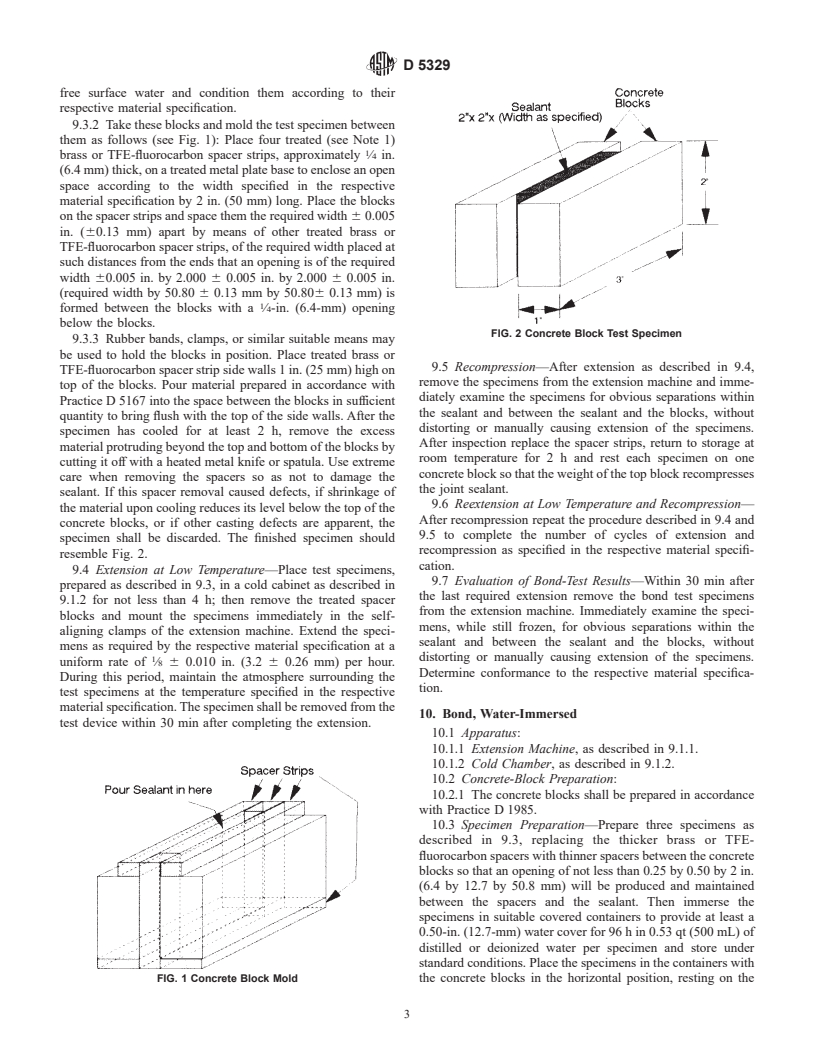
FIG. 2 Concrete Block Test Specimen
9.3.3 Rubber bands, clamps, or similar suitable means may
be used to hold the blocks in position. Place treated brass or
9.5 Recompression—After extension as described in 9.4,
TFE-fluorocarbon spacer strip side walls 1 in. (25 mm) high on
remove the specimens from the extension machine and imme-
top of the blocks. Pour material prepared in accordance with
diately examine the specimens for obvious separations within
Practice D 5167 into the space between the blocks in sufficient
the sealant and between the sealant and the blocks, without
quantity to bring flush with the top of the side walls. After the
distorting or manually causing extension of the specimens.
specimen has cooled for at least 2 h, remove the excess
After inspection replace the spacer strips, return to storage at
material protruding beyond the top and bottom of the blocks by
room temperature for 2 h and rest each specimen on one
cutting it off with a heated metal knife or spatula. Use extreme
concrete block so that the weight of the top block recompresses
care when removing the spacers so as not to damage the
the joint sealant.
sealant. If this spacer removal caused defects, if shrinkage of
9.6 Reextension at Low Temperature and Recompression—
the material upon cooling reduces its level below the top of the
After recompression repeat the procedure described in 9.4 and
concrete blocks, or if other casting defects are apparent, the
9.5 to complete the number of cycles of extension and
specimen shall be discarded. The finished specimen should
recompression as specified in the respective material specifi-
resemble Fig. 2.
cation.
9.4 Extension at Low Temperature—Place test specimens,
9.7 Evaluation of Bond-Test Results—Within 30 min after
prepared as described in 9.3, in a cold cabinet as described in
the last required extension remove the bond test specimens
9.1.2 for not less than 4 h; then remove the treated spacer
from the extension machine. Immediately examine the speci-
blocks and mount the specimens immediately in the self-
mens, while still frozen, for obvious separations within the
aligning clamps of the extension machine. Extend the speci-
sealant and between the sealant and the blocks, without
mens as required by the respective material specification at a
1 distorting or manually causing extension of the specimens.
uniform rate of ⁄8 6 0.010 in. (3.2 6 0.26 mm) per hour.
Determine conformance to the respective material specifica-
During this period, maintain the atmosphere surrounding the
tion.
test specimens at the temperature specified in the respective
material specification. The specimen shall be removed from the
10. Bond, Water-Immersed
test device within 30 min after completing the extension.
10.1 Apparatus:
10.1.1 Extension Machine, as described in 9.1.1.
10.1.2 Cold Chamber, as described in 9.1.2.
10.2 Concrete-Block Preparation:
10.2.1 The concrete blocks shall be prepared in accordance
with Practice D 1985.
10.3 Specimen Preparation—Prepare three specimens as
described in 9.3, replacing the thicker brass or TFE-
fluorocarbon spacers with thinner spacers between the concrete
blocks so that an opening of not less than 0.25 by 0.50 by 2 in.
(6.4 by 12.7 by 50.8 mm) will be produced and maintained
between the spacers and the sealant. Then immerse the
specimens in suitable covered containers to provide at least a
0.50-in. (12.7-mm) water cover for 96 h in 0.53 qt (500 mL) of
distilled or deionized water per specimen and store under
standard conditions. Place the specimens in the containers with
FIG. 1 Concrete Block Mold the concrete blocks in the horizontal position, resting on the
D 5329
block faces measuring 2 by 3 in. (50 by 76 mm). Three contact with the surfac
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.