ASTM E754-80(2022)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Pullout Resistance of Ties and Anchors Embedded in Masonry Mortar Joints
Standard Test Method for Pullout Resistance of Ties and Anchors Embedded in Masonry Mortar Joints
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is intended to provide a simple inexpensive means of generating conservative, comparative data on pullout strengths of various ties and anchors used with different types of masonry units and mortars. This test method is recommended for such use until economical, improved methods can be developed to simulate service conditions more inclusively.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method provides procedures for determining the ability of individual masonry ties and anchors to resist extraction from a masonry mortar joint.
1.2 Two laboratory testing procedures are provided for use with test specimens which consist of a masonry tie or anchor embedded in mortar between twin stack-bonded masonry units.
1.2.1 Procedure A—For use with small (brick-size) masonry units.
1.2.2 Procedure B—For use with large (block-size) masonry units.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E754 − 80 (Reapproved 2022)
Standard Test Method for
Pullout Resistance of Ties and Anchors Embedded in
Masonry Mortar Joints
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E754; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
The attachment of masonry walls to building exteriors has been based largely on experience and
professional judgment. Codes and standards requirements relating to the attachment of masonry
veneer and nonload-bearing masonry walls generally specify the size and spacing of the fasteners to
be provided (ties or anchors) rather than the forces to be resisted. In addition, there are very limited
data available on the structural performance of most types of fasteners currently used in masonry
construction.
This test method is recommended for determining conservative ultimate pullout values of masonry
fasteners under conditions that approach those usually found in the upper courses of masonry wall
construction, which experience little or practically no vertical load restraint. Its use is recommended
until more comprehensive methods are developed which can evaluate, economically, the capacity of
masonry ties and anchors to resist pullout loads, giving due consideration to service parameters such
as expanse of surrounding wall area and in-plane dead loads.
1. Scope 1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.1 This test method provides procedures for determining
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
the ability of individual masonry ties and anchors to resist
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
extraction from a masonry mortar joint.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.2 Two laboratory testing procedures are provided for use
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
with test specimens which consist of a masonry tie or anchor
embeddedinmortarbetweentwinstack-bondedmasonryunits.
2. Referenced Documents
1.2.1 Procedure A—For use with small (brick-size) masonry 2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
units.
C67/C67M Test Methods for Sampling and Testing Brick
1.2.2 Procedure B—For use with large (block-size) masonry
and Structural Clay Tile
units.
C109/C109M Test Method for Compressive Strength of
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50 mm] Cube
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
Specimens)
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only C140/C140M Test Methods for Sampling and Testing Con-
and are not considered standard.
crete Masonry Units and Related Units
C144 Specification for Aggregate for Masonry Mortar
1.4 This standard does not purport to address the safety
C270 Specification for Mortar for Unit Masonry
concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
E4 Practices for Force Calibration and Verification of Test-
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety,
ing Machines
health, and environmental practices and determine the appli-
E6 Terminology Relating to Methods of Mechanical Testing
cability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
E171/E171M Practice for Conditioning and Testing Flexible
Barrier Packaging
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.13
on Structural Performance of Connections in Building Construction. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2022. Published October 2022. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
ɛ1
approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as E754 – 80 (2014) . Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/E0754-80R22. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
E754 − 80 (2022)
E575 Practice for Reporting Data from Structural Tests of minimize apparatus deformation) and to maintain uniform
Building Constructions, Elements, Connections, and As- distribution of the axially applied test loads until failure of the
semblies specimen occurs.
6.2 Procedure B (Using Block-Size Masonry Units)—
3. Terminology
Apparatus for this procedure is shown in Fig. 3 and Fig. 4. Its
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test
special purpose is to avoid handling an unwieldy specimen in
method, refer to Terminology E6.
apparatus such as that used in ProcedureAby applying pullout
loads to the specimen placed on a convenient work surface.
4. Summary of Test Method
The apparatus shall be of sufficient strength and stiffness to
4.1 These procedures provide for a static pullout test of a tie minimize bending deformations that would tend to promote a
or anchor embedded in a hardened mortar joint between two
flexural bond failure of the mortar joint; and it shall have the
masonry units. capacity to develop the pullout failure load of the fastener
without yielding.
5. Significance and Use
6.3 For both Procedures A and B, the apparatus is made
5.1 This test method is intended to provide a simple
from common rolled metal sections and other stock items. The
inexpensive means of generating conservative, comparative
knockdown jig used for pulling the end of the fastener
data on pullout strengths of various ties and anchors used with
protruding from the masonry also serves as a reusable mold for
different types of masonry units and mortars. This test method
casting a gypsum head on that end of the fastener.The mold/jig
is recommended for such use until economical, improved
is reassembled around the gypsum pulling head when testing.
methods can be developed to simulate service conditions more
6.4 Instrumentation—Displacement of the fastener relative
inclusively.
to the masonry shall be measured by a dial gage or by an
electronic displacement transducer (for example, a linear
6. Apparatus
variable differential transformer (LVDT). The instrument used
6.1 Procedure A (Using Brick-Size Masonry Units):
shall be capable of reading 0.001 in. (0.025 mm) and be
6.1.1 The testing machine shall conform to the requirements
accurate to 1 %.
of Practices E4.
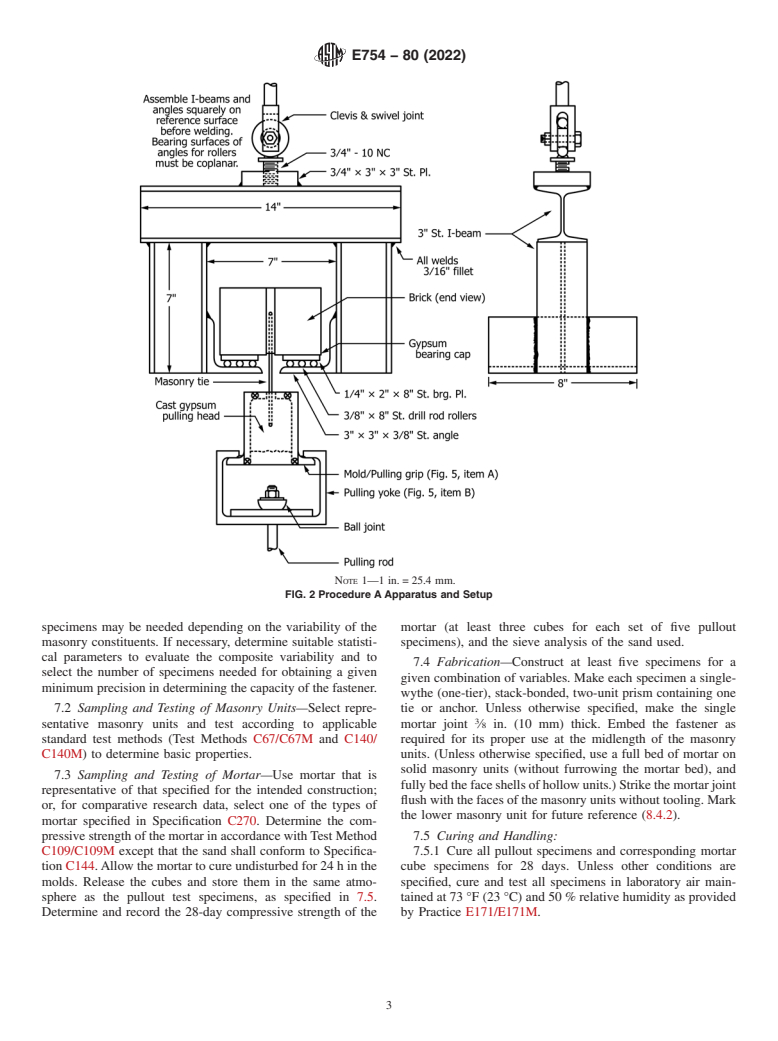
6.1.2 AuxiliarypullingapparatusisshowninFig.1andFig.
7. Test Specimen
2. These fixtures are provided with swivel joints and roller
bearings to eliminate lateral restraint and bending when apply- 7.1 Sampling of Fasteners (Masonry Ties or Anchors)—Test
ing the pullout loads. The apparatus shall be designed to have at least five specimens of a given type of fastener for each
enoughstrengthandstiffnesstopreventitsyielding(inorderto given combination of masonry constituent materials. More
FIG. 1 Procedure A Apparatus and Setup
E754 − 80 (2022)
NOTE 1—1 in. = 25.4 mm.
FIG. 2 Procedure A Apparatus and Setup
specimens may be needed depending on the variability of the mortar (at least three cubes for each set of five pullout
masonry constituents. If necessary, determine suitable statisti- specimens), and the sieve analysis of the sand used.
cal parameters to evaluate the composite variability and to
7.4 Fabrication—Construct at least five specimens for a
select the number of specimens needed for obtaining a given
given combination of variables. Make each specimen a single-
minimum precision in determining the capacity of the fastener.
wythe (one-tier), stack-bonded, two-unit prism containing one
7.2 Sampling and Testing of Masonry Units—Select repre- tie or anchor. Unless otherwise specified, make the single
sentative masonry units and test according to applicable mortar joint ⁄8 in. (10 mm) thick. Embed the fastener as
standard test methods (Test Methods C67/C67M and C140/ required for its proper use at the midlength of the masonry
C140M) to determine basic properties. units. (Unless otherwise specified, use a full bed of mortar on
solid masonry units (without furrowing the mortar bed), and
7.3 Sampling and Testing of Mortar—Use mortar that is
fullybedthefaceshellsofhollowunits.)Strikethemortarjoint
representative of that specified for the intended construction;
flush with the faces of the masonry units without tooling. Mark
or, for comparative research data, select one of the types of
the lower masonry unit for future reference (8.4.2).
mortar specified in Specification C270. Determine the com-
pressive strength of the mortar in accordance withTest Method 7.5 Curing and Handling:
C109/C109M except that the sand shall conform to Specifica- 7.5.1 Cure all pullout specimens and corresponding mortar
tion C144.Allow the mortar to cure undisturbed for 24 h in the cube specimens for 28 days. Unless other conditions are
molds. Release the cubes and store them in the same atmo- specified, cure and test all specimens in laboratory air main-
sphere as the pullout test specimens, as specified in 7.5. tained at 73 °F (23 °C) and 50 % relative humidity as provided
Determine and record the 28-day compressive s
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.