ASTM D5934-96
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Modulus of Elasticity for Rigid and Semi-Rigid Plastic Specimens by Controlled Rate of Loading Using Three-Point Bending
Standard Test Method for Determination of Modulus of Elasticity for Rigid and Semi-Rigid Plastic Specimens by Controlled Rate of Loading Using Three-Point Bending
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the use of controlled rate of loading mechanical instrumentation for gathering and reporting the modulus of elasticity of thermoplastic and thermosetting resins and composite systems in the form of rectangular bars molded directly or cut from sheets, plates, or molded shapes. The data generated, using three-point bending techniques, may be used to identify the thermomechanical properties of a plastics material or composition using a controlled rate of loading mechanical instrument. Results obtained from this test method may or may not be comparable to results obtained using D 790.
1.2 This test method is intended to provide a means for determining the modulus of elasticity within the linear region of the stress-strain curve (see Fig 1). This test is conducted at standard temperature and pressure.
1.3 Apparent discrepancies may arise in results obtained under differing experimental conditions. These apparent differences from results observed in another study can usually be reconciled, without changing the observed data, by reporting in full (as described in this test method) the conditions under which the data were obtained.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values stated in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1—There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 5934 – 96
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Modulus of Elasticity for Rigid and Semi-
Rigid Plastic Specimens by Controlled Rate of Loading
Using Three-Point Bending
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5934; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the use of controlled rate of
loading mechanical instrumentation for gathering and reporting
the modulus of elasticity of thermoplastic and thermosetting
resins and composite systems in the form of rectangular bars
molded directly or cut from sheets, plates, or molded shapes.
The data generated, using three-point bending techniques, may
be used to identify the thermomechanical properties of a
plastics material or composition using a controlled rate of
loading mechanical instrument. Results obtained from this test
method may or may not be comparable to results obtained
using D 790.
1.2 This test method is intended to provide a means for
determining the modulus of elasticity within the linear region
of the stress-strain curve (see Fig. 1). This test is conducted at
standard temperature and pressure.
1.3 Apparent discrepancies may arise in results obtained
under differing experimental conditions. These apparent differ-
ences from results observed in another study can usually be
reconciled, without changing the observed data, by reporting in
full (as described in this test method) the conditions under
which the data were obtained.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values stated in parentheses are for information
FIG. 1 Stress-Strain Curve (Linear Region)
only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Insulating Materials for Testing
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
D 1999 Guide for the Selection of Specimens and Test
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Parameters for International Trade
D 4092 Terminology Relating to Dynamic Mechanical
NOTE 1—There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard.
Measurements on Plastics
2. Referenced Documents E 177 Practice for the Use of the Terms Precision and Bias
in ASTM Test Methods
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions: Definitions of terms applying to these test
methods appear in Terminologies D 883 and D 4092, and
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on Plastics
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.10 on Mechanical Properties.
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 1996. Published May 1997. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
2 4
This apparatus is available from the Perkin-Elmer Corporation, 761 Main Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
Avenue, Norwalk, CT 06859-0256. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 5934
Annex A1 and Annex A2 of Test Method D 638.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A specimen of rectangular cross section is tested in
flexure as a beam. The bar rests on two supports and is loaded
by means of a loading nose midway between the supports. The
test specimen of known geometry is placed under mechanical
linear displacement at isothermal conditions by using a con-
trolled rate of loading. The modulus of elasticity is measured
using three-point bending.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method provides a simple means of character-
izing the mechanical behavior of plastics materials using very
small amounts of material. The data obtained may be used for
Dimensions
quality control, research and development, and establishment
Dimen- Tolerance,6
of optimum processing conditions.
Description Symbol sion, ,
5.2 Mechanical testing provides a sensitive test method for
mm mm
determining mechanical characteristics by measuring the
Support span L 20.0 0.1
modulus of elasticity.
Loading nose ra- r 3.0 0.5
dius
NOTE 2—Materials that are suspected to be too anisotropic may not be
Support radius r 1.0 0.1
suitable for this test method.
FIG. 2 Loading Members
5.3 This test method can be used to assess:
5.3.1 The effects of processing treatment,
7.3.2 Nitrogen—Or other inert gas supply, for purging
5.3.2 Relative resin behavioral properties, including cure,
purposes.
5.3.3 The effects of substrate types and orientation (fabri-
8. Test Specimens
cation) on modulus, and
5.3.4 The effects of formulation additives that might affect
8.1 The specimens may be cut from sheets, plates, or
processability or performance.
molded shapes, or may be molded to the desired finished
dimensions. Specimens shall be long enough to allow over-
6. Interferences
hanging on each end of at least 10 % of the support span.
6.1 Since small test specimen geometries are used, it is
Overhang shall be sufficient to prevent the specimen from
essential that the specimens be representative of the polymeric
slipping through the supports. A typical rectangular test beam
material being tested.
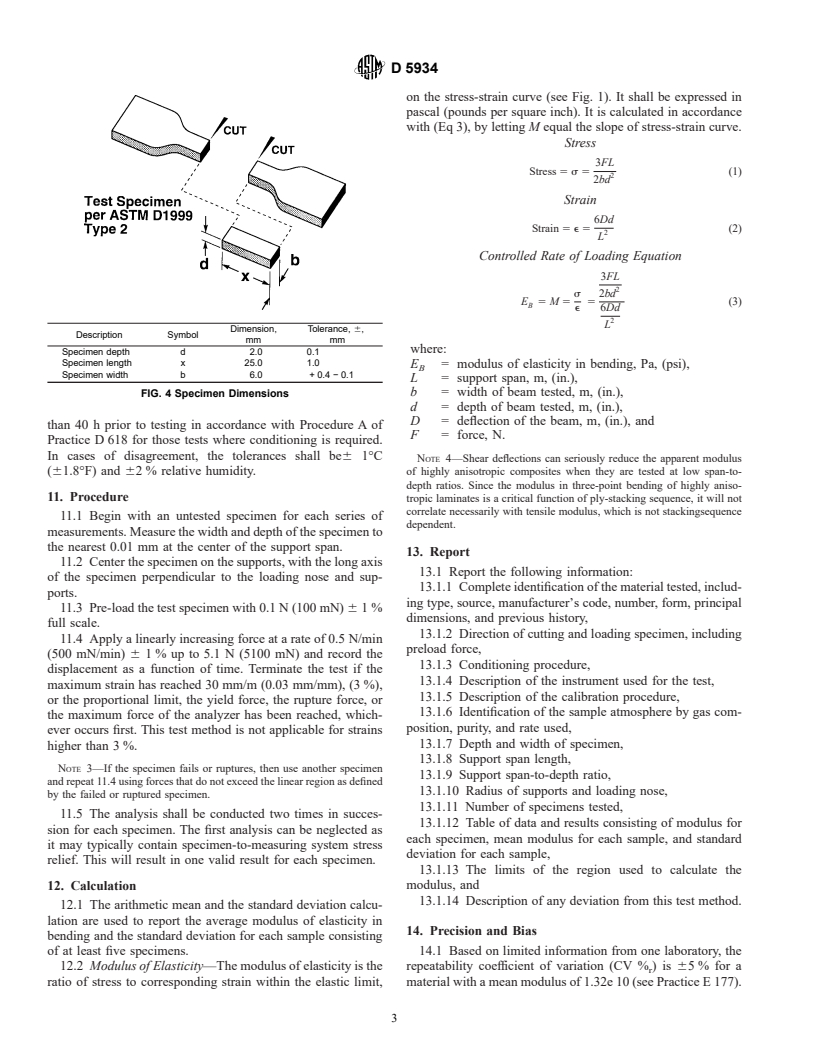
is tested flatwise on a support span (see Fig. 3 and Fig. 4).
8.2 At least five specimens shall be tested for each sample.
7. Apparatus
7.1 The function of the apparatus is to hold a rectangular
9. Calibration
test specimen of a polymeric material system so that the
9.1 Calibrate the instrument using procedures recommended
material acts as the elastic and dissipative element in a
by the manufacturer.
mechanically driven linear displacement system. Displace-
ments (deflections) are generated using a controlled loading
10. Conditioning
rate applied to a specimen in three-point bending configuration.
10.1 Conditioning—Condition the test specimens at 23 6
7.2 The apparatus shall consist of the following:
2°C (73.4 6 3.6°F) and 50 6 5 % relative humidity for not less
7.2.1 Loading Nose and Supports—The loading nose and
supports sha
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.