ASTM C633-13(2021)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Adhesion or Cohesion Strength of Thermal Spray Coatings
Standard Test Method for Adhesion or Cohesion Strength of Thermal Spray Coatings
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 This test method is recommended for quality control, acceptance testing; or it may help to develop or qualify a thermal spray operator's equipment and procedure or to aid in developing thermal spray coatings with improved adhesion and integrity.
3.2 This test method is useful for comparing adhesion or cohesion strengths of coatings of similar types of thermal spray materials. The test should not be considered to provide an intrinsic value for direct use in making calculations, such as to determine if a coating will withstand specific environmental stresses. Because of residual stresses in thermal spray coatings, actual strength depends upon the shape of the particular coated part. Also, in use, a coating may be stressed in a more complex manner than is practical for a standard test.
SCOPE
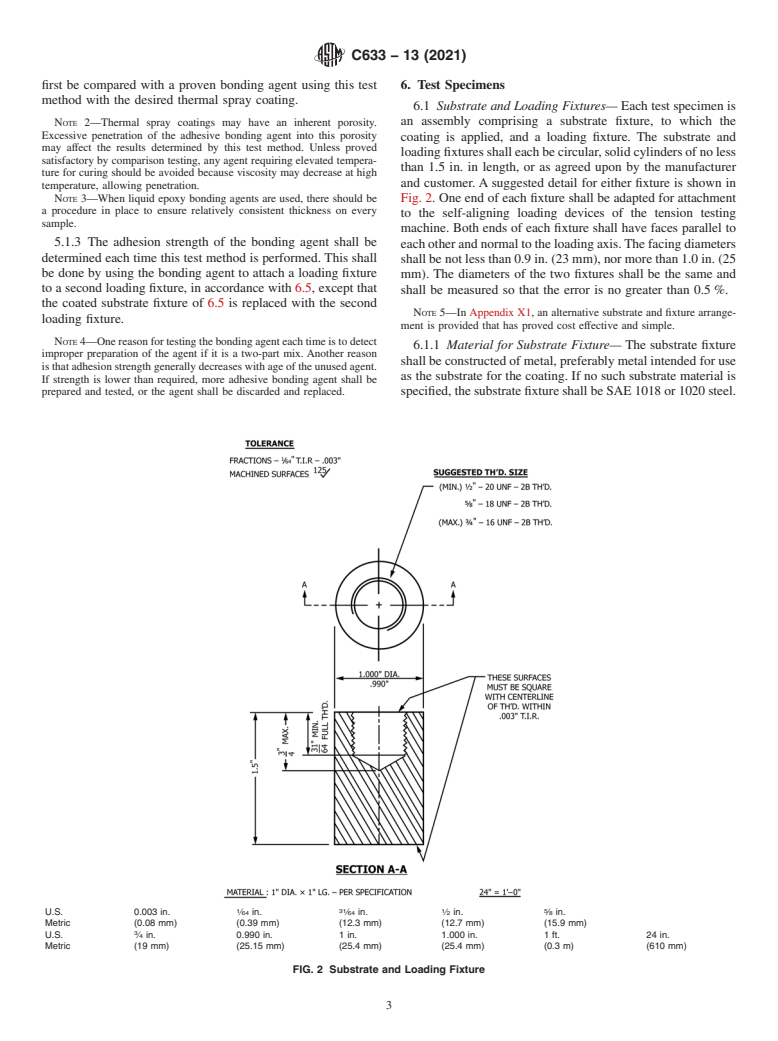
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the degree of adhesion (bonding strength) of a coating to a substrate or the cohesion strength of the coating in a tension normal to the surface. The test consists of coating one face of a substrate fixture, bonding this coating to the face of a loading fixture, and subjecting this assembly of coating and fixtures to a tensile load normal to the plane of the coating. It is adapted particularly for testing coatings applied by thermal spray, which is defined to include the combustion flame, plasma arc, two-wire arc, high-velocity oxygen fuel, and detonation processes for spraying feedstock, which may be in the form of, wire, rod, or powder.
Note 1: Thermal spray coating materials include ceramics, such as metal oxides or carbides, and metals. In some cases, a coating is formed of different spray materials, such as an oxide layer sprayed onto a sprayed metal-bonding layer. The substrate generally is a metal, but may be a ceramic, such as an oxide or graphite.
1.2 Usually this test method is performed at ambient temperature. Higher temperature testing is restricted by the need for a suitable adhesive bonding agent. For certain fundamental investigations, it is suggested that very low (cryogenic) temperature be used.
1.3 This test method is limited to testing thermal spray coatings that can be applied in thickness greater than 0.015 in. (0.38 mm). The limitation is imposed because an adhesive bonding agent is used in the test. Those bonding agents established so far for this method tend to penetrate thermal spray coatings and may invalidate results unless the coatings are thick enough to prevent penetration through the coating. Further development may establish that thin layers of certain types of especially dense coatings may be tested satisfactorily. Alternatively, new adhesive bonding agents that would allow reduction of the minimum thickness limitation may become available.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C633 − 13 (Reapproved 2021)
Standard Test Method for
1
Adhesion or Cohesion Strength of Thermal Spray Coatings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C633; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 1.4 Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegarded
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the degree
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
ofadhesion(bondingstrength)ofacoatingtoasubstrateorthe
and are not considered standard.
cohesion strength of the coating in a tension normal to the
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
surface. The test consists of coating one face of a substrate
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
fixture,bondingthiscoatingtothefaceofaloadingfixture,and
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
subjecting this assembly of coating and fixtures to a tensile
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
load normal to the plane of the coating. It is adapted particu-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
larly for testing coatings applied by thermal spray, which is
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
defined to include the combustion flame, plasma arc, two-wire
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
arc, high-velocity oxygen fuel, and detonation processes for
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
spraying feedstock, which may be in the form of, wire, rod, or
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
powder.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
NOTE 1—Thermal spray coating materials include ceramics, such as
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
metal oxides or carbides, and metals. In some cases, a coating is formed
ofdifferentspraymaterials,suchasanoxidelayersprayedontoasprayed
metal-bonding layer. The substrate generally is a metal, but may be a 2. Referenced Documents
ceramic, such as an oxide or graphite.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.2 Usually this test method is performed at ambient tem-
E4Practices for Force Calibration and Verification of Test-
perature. Higher temperature testing is restricted by the need
ing Machines
for a suitable adhesive bonding agent. For certain fundamental
investigations, it is suggested that very low (cryogenic) tem-
3. Significance and Use
perature be used.
3.1 This test method is recommended for quality control,
1.3 This test method is limited to testing thermal spray
acceptance testing; or it may help to develop or qualify a
coatings that can be applied in thickness greater than 0.015 in.
thermal spray operator’s equipment and procedure or to aid in
(0.38 mm). The limitation is imposed because an adhesive
developingthermalspraycoatingswithimprovedadhesionand
bonding agent is used in the test. Those bonding agents
integrity.
established so far for this method tend to penetrate thermal
3.2 This test method is useful for comparing adhesion or
spray coatings and may invalidate results unless the coatings
cohesionstrengthsofcoatingsofsimilartypesofthermalspray
are thick enough to prevent penetration through the coating.
materials. The test should not be considered to provide an
Further development may establish that thin layers of certain
intrinsic value for direct use in making calculations, such as to
types of especially dense coatings may be tested satisfactorily.
determine if a coating will withstand specific environmental
Alternatively, new adhesive bonding agents that would allow
stresses.Becauseofresidualstressesinthermalspraycoatings,
reduction of the minimum thickness limitation may become
actualstrengthdependsupontheshapeoftheparticularcoated
available.
part.Also,inuse,acoatingmaybestressedinamorecomplex
manner than is practical for a standard test.
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB08onMetallic
and Inorganic Coatings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B08.12 on
2
Materials for Porcelain Enamel and Ceramic-Metal Systems. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2021. Published November 2021. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approvedin196
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.