ASTM D6369-99
(Guide)Standard Guide for Design of Standard Flashing Details for EPDM Roof Membranes
Standard Guide for Design of Standard Flashing Details for EPDM Roof Membranes
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers the design of details for typical conditions encountered in new ballasted, mechanically attached or fully adhered ethylene propylene diene terpolymer (EPDM) sheet roof systems.
1.2 This guide illustrates general details for typical conditions that may be encountered on an EPDM sheet roofing system. The guide will assist the designer in preparing details for each specific condition that may occur on a project.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The conventional units given in parentheses are provided for information purposes only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D6369–99
Standard Guide for
Design of Standard Flashing Details for EPDM Roof
Membranes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6369; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Significance and Use
1.1 This guide covers the design of details for typical 4.1 This guide illustrates general details for typical condi-
conditions encountered in new ballasted, mechanically at- tions that may be encountered on an EPDM sheet roofing
tached or fully adhered ethylene propylene diene terpolymer system.
(EPDM) sheet roof systems. 4.2 This guide does not address all requirements associated
1.2 This guide illustrates general details for typical condi- with the installation of EPDM membrane flashing, such as
tions that may be encountered on an EPDM sheet roofing membrane cleaning and surface preparation, fastener spacing,
system. The guide will assist the designer in preparing details adhesive application and other seaming requirements which
for each specific condition that may occur on a project. may vary by membrane system supplier.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as 4.3 Insulation, fastener types, protection mats, stone ballast,
standard. The conventional units given in parentheses are pavers, and requirements for perimeter attachment are not
provided for information purposes only. covered by this guide. The designer shall review the project
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the requirementsandconsultthemembranesystemsupplier,build-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the ing insurer, and local building codes for specific requirements.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5. Drawings
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.1 This guide is not all-inclusive. The designer shall detail
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
all typical and special conditions on the project. Particular
2. Referenced Documents
attention shall be given to transitions in plane and intersection
2.1 ASTM Standards: of different details. The membrane system supplier or system
D1079 Terminology Relating to Roofing, Waterproofing applicator shall provide shop drawings of each condition to
and Bituminous Materials confirmfieldconditionsandtoverifytheirunderstandingofthe
design intent.
3. Terminology
5.2 Insulation, protection mats, stone ballast and pavers
3.1 Definitions— For definitions of terms used in this guide
have been omitted for clarity.
and not listed below, see Terminology D1079. 5.3 Treated wood blocking shall be installed to provide
3.2 ballasted sheet roofing, n—a system which incorporates
attachment for accessory items such as gravel stops, metal
alooselaidvulcanizedEPDMsheetoveranacceptedsubstrate sleeves, etc.
and is held in place with either stone ballast, pavers, or a
6. Penetrations
combination thereof.
3.3 fully adhered sheet roofing, n—a system which incor- 6.1 Flashing at penetrations shall accommodate differential
porates a vulcanized EPDM sheet fully adhered over a secured movement between the deck and penetration (that is, pipe,
and accepted substrate. conduit, column or drain).
3.4 mechanically attached sheet roofing, n—asystemwhich 6.1.1 Where “H” or “I” column sections occur, install
incorporates a mechanically fastened vulcanized EPDM sheet blocking between flanges to facilitate installation of flashing.
over a secured and accepted substrate. Weld sloping steel hoods to column. Extend vertical leg of
hood a minimum 100 mm (4 in.) over flashing.
6.1.2 Set cast iron drains with the top of the flange level
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D08 on Roofing,
with or slightly below the surrounding deck area. When
Waterproofing and Bituminous Materials and is the direct responsibility of Sub-
insulation is installed below the sheet membrane provide a
committee D08.18 on Nonbituminous Organic Roof Coverings.
Current edition approved Feb. 10, 1999. Published October 1999.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.04.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D6369
minimum 900 by 900 mm (36 by 36 in.) transition sump. Do 8.6 Expansion Joints—AsshowninFig.6,expansionjoints
not run field or factory seams within 600 mm (24 in.) of drain shall be raised above the roof membrane a minimum 200 mm
flange edge. (8 in.). A compressible tube or proprietary formed member is
used to permit the membrane to flex. An EPDM hammock is
7. Expansion Joints
installed to support the joint insulation and tube. If the
7.1 Expansion joints are designed to permit independent
expansion joint curb is constructed of wood blocking, then the
movement of structural elements on each side of the joint. top surfaces shall be beveled to provide a positive slope away
Expansion joint curbs and flashings shall be designed to
from the joint.An alternate method is to install a prefabricated
accommodate this movement. Expansion joints shall be raised ormetalexpansionjointcovertothetopoftheexpansionjoint.
a minimum 200 mm (8 in.) above the roof membrane.
8.7 Scuppers—Scuppers shall be fabricated from sheet
metal with soldered or sealed seams as shown in Fig. 7. The
8. Explanatory Notes
flanges shall be set in water seal and flashed. Seal the exterior
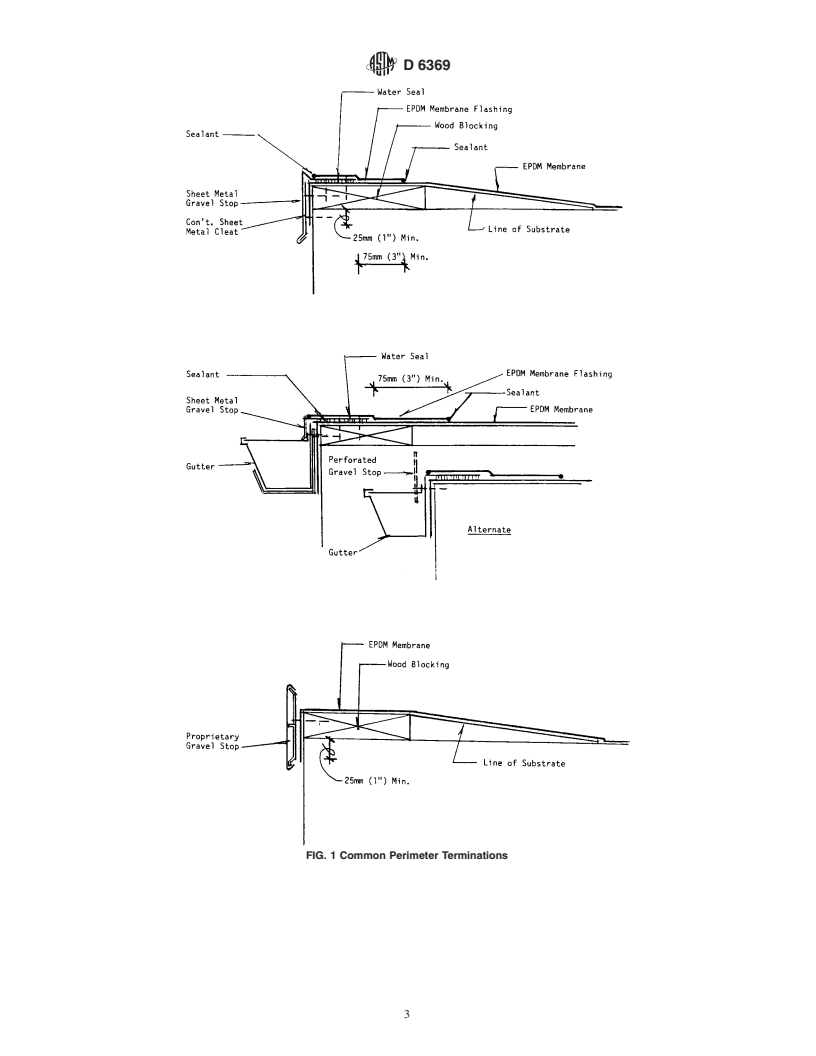
8.1 Perimeter Terminations—The most common perimeter
portion of the scupper to the vertical surfaces.
terminations are shown in Fig. 1. Extend sheet roofing mem-
8.8 Membrane Termination on Vertical Surface—Wherethe
brane down the building face covering the joint between the
membrane terminates on a vertical surface (see Fig. 8), it shall
wood blocking and exterior building finish a minimum 25 mm
be secured with fasteners a maximum 200 mm (8 in.) outside
(1 in.). Install the gravel stop as specified by the designer or
circumference or a metal termination bar that is fastened a
manufacturer. Where sheet metal gravel stops are installed,
maximum 200 mm (8 in.) outside circumference. Extend
surfaces of the metal shall be primed with the manufacturer’s
membrane under the cap flashing a minimum 75 mm (3 in.).
recommended primer prior to application of the EPDM flash-
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.