ASTM D5154-10
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Activity and Selectivity of Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Catalysts by Microactivity Test
Standard Test Method for Determining Activity and Selectivity of Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Catalysts by Microactivity Test
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The microactivity test provides data to assess the relative performance of FCC catalysts. Because results are affected by catalyst pretreatment, feedstock characteristics, test equipment, and operating parameters, adherence to this test method is a prerequisite for correct interpretation of results. Apparatus, test conditions, and analytical procedures actually used should closely resemble those described in this test method. Significant variations in apparatus, test conditions and/or analytical procedures may result in activity and selectivity data which do not correlate with data developed by other laboratories on identical catalyst/feedstock samples.
The standard method reaction temperature is 960°F (516°C). Other reaction temperatures can be used; however, catalyst selectivity data developed at temperatures other than 960°F (516°C) may not correlate with selectivity data developed at 960°F (516°C). Also, precision at other reaction temperatures may change compared to data obtained at 960°F (516°C).
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers determining the activity and selectivity of either equilibrium or laboratory deactivated fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts. The activity is evaluated on the basis of mass percent conversion of gas oil in a microactivity unit. The selectivities are evaluated on the basis of mass percent yields of specifically defined products resulting from the catalytic cracking of gas oil.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.2.1 Exception—SI units have been retained in some of the figures.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5154 − 10
Standard Test Method for
Determining Activity and Selectivity of Fluid Catalytic
1
Cracking (FCC) Catalysts by Microactivity Test
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5154; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.1 This test method covers determining the activity and
selectivity of either equilibrium or laboratory deactivated fluid
3. Terminology
catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts. The activity is evaluated on
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
the basis of mass percent conversion of gas oil in a microac-
3.1.1 activity—calculated as conversion divided by the dif-
tivity unit. The selectivities are evaluated on the basis of mass
ference of 100 minus conversion.
percent yields of specifically defined products resulting from
the catalytic cracking of gas oil.
3.1.2 ASTM reference catalysts—a set of equilibrium FCC
catalysts within the useful range of this test method is used to
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
improve the reproducibility of test results between different
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
laboratories. Each catalyst has a consensus mean conversion
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
value assigned to it by Committee D32. Samples of theASTM
and are not considered standard.
reference catalysts can be obtained through NIST.
1.2.1 Exception—SI units have been retained in some of the
figures.
3.1.3 ASTM standard feed—aspecificbatchofgasoilthatis
3
used as feedstock in the described test method.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 3.1.4 catalyst/oil (C/O) ratio—the mass of catalyst used in
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- the test divided by the mass of feed fed to the reactor. In
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- practice, the mass of catalyst is usually maintained at a
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. constant value and the total mass of feed is varied.
3.1.5 contact time—calculated as 3600/(WHSV· C/O).This
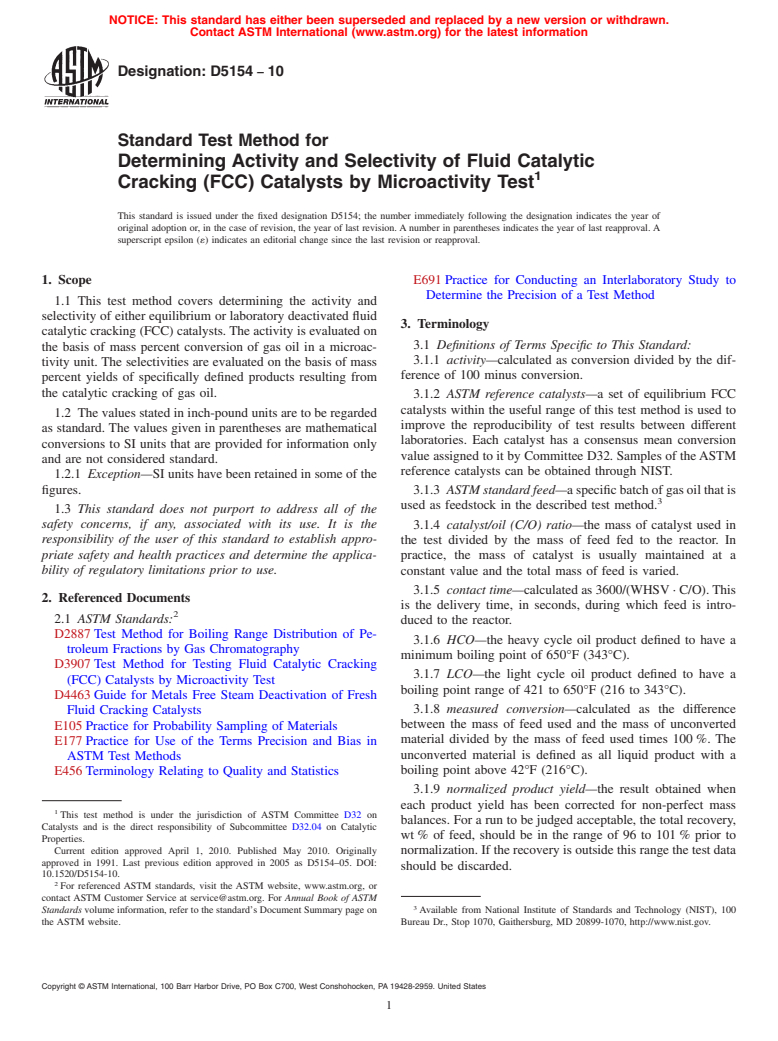
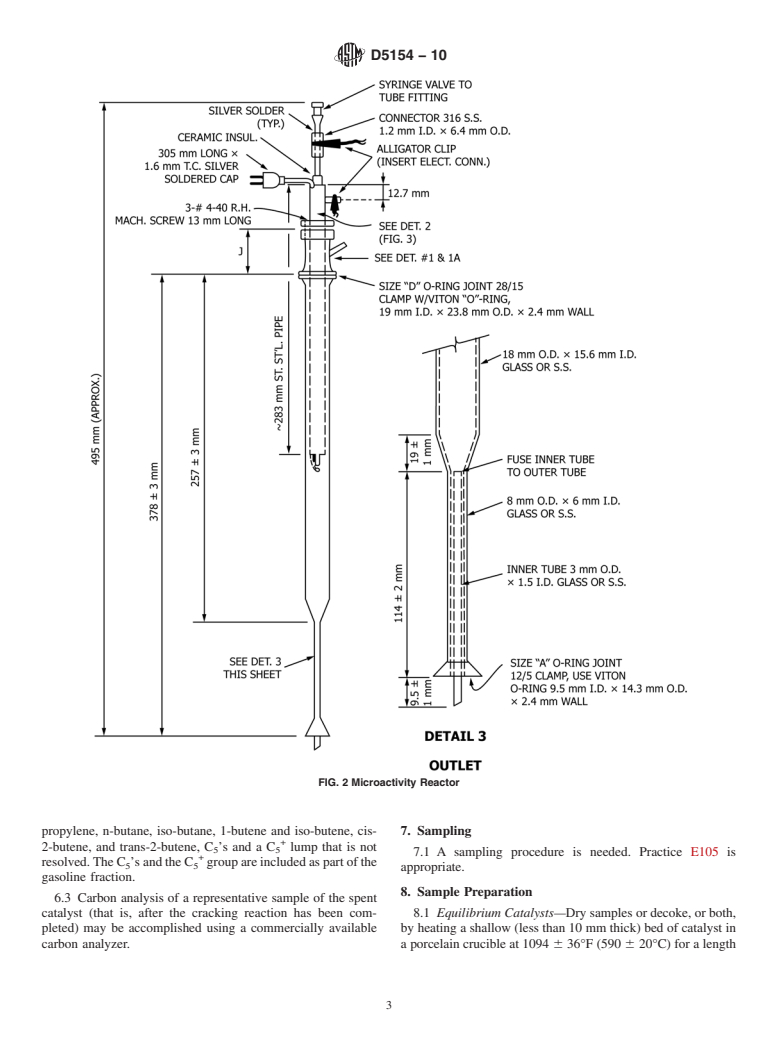
2. Referenced Documents
is the delivery time, in seconds, during which feed is intro-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
duced to the reactor.
D2887 Test Method for Boiling Range Distribution of Pe-
3.1.6 HCO—the heavy cycle oil product defined to have a
troleum Fractions by Gas Chromatography
minimum boiling point of 650°F (343°C).
D3907 Test Method for Testing Fluid Catalytic Cracking
3.1.7 LCO—the light cycle oil product defined to have a
(FCC) Catalysts by Microactivity Test
boiling point range of 421 to 650°F (216 to 343°C).
D4463 Guide for Metals Free Steam Deactivation of Fresh
3.1.8 measured conversion—calculated as the difference
Fluid Cracking Catalysts
between the mass of feed used and the mass of unconverted
E105 Practice for Probability Sampling of Materials
material divided by the mass of feed used times 100 %. The
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
unconverted material is defined as all liquid product with a
ASTM Test Methods
boiling point above 42°F (216°C).
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
3.1.9 normalized product yield—the result obtained when
each product yield has been corrected for non-perfect mass
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D32 on
balances. For a run to be judged acceptable, the total recovery,
Catalysts and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D32.04 on Catalytic
wt % of feed, should be in the range of 96 to 101 % prior to
Properties.
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published May 2010. Originally
normalization. If the recovery is outside this range the test data
approved in 1991. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D5154–05. DOI:
should be discarded.
10.1520/D5154-10.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), 100
the ASTM website. Bureau Dr., Stop 1070, Gaithersburg, MD 20899-1070, http://www.nist.gov.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5154 − 10
3.1.10 product yield—one hundred times the mass
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D5154–05 Designation:D5154–10
Standard Test Method for
Determining Activity and Selectivity of Fluid Catalytic
1
Cracking (FCC) Catalysts by Microactivity Test
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5154; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversdeterminingtheactivityandselectivityofeitherequilibriumorlaboratorydeactivatedfluidcatalytic
cracking (FCC) catalysts. The activity is evaluated on the basis of mass percent conversion of gas oil in a microactivity unit. The
selectivities are evaluated on the basis of mass percent yields of specifically defined products resulting from the catalytic cracking
of gas oil.
1.2The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information
only.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.2.1 Exception—SI units have been retained in some of the figures.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D2887 Test Method for Boiling Range Distribution of Petroleum Fractions by Gas Chromatography
D3907 Test Method for Testing Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Catalysts by Microactivity Test
D4463 Guide for Metals Free Steam Deactivation of Fresh Fluid Cracking Catalysts
E105 Practice for Probability Sampling of Materials
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D32 on Catalysts and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D32.04 on Catalytic Properties.
Current edition approved Oct.April 1, 2005.2010. Published November 2005.May 2010. Originally approved in 1991. Last previous edition approved in 20032005 as
D5154–03.D5154–05. DOI: 10.1520/D5154-105.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5154–10
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 activity—calculated as conversion divided by the difference of 100 minus conversion.
3.1.2 ASTM reference catalysts—a set of equilibrium FCC catalysts within the useful range of this test method is used to
improve the reproducibility of test results between different laboratories. Each catalyst has a consensus mean conversion value
assigned to it by Committee D32. Samples of the ASTM reference catalysts can be obtained through NIST.
3
3.1.3 ASTM standard feed—a specific batch of gas oil that is used as feedstock in the described test method.
3.1.4 catalyst/oil (C/O) ratio—the mass of catalyst used in the test divided by the mass of feed fed to the reactor. In practice,
the mass of catalyst is usually maintained at a constant value and the total mass of feed is varied.
3.1.5 contact time—calculated as 3600/(WHSV · C/O). This is the delivery time, in seconds, during which feed is introduced
to the reactor.
3.1.6 HCO—the heavy cycle oil product defined to have a minimum boiling point of 343°C (650°F). 650°F (343°C).
3.1.7 LCO—the light cycle oil product defined to have a boiling point range of 216421 to 343°C (421650°F (216 to 650°F).
343°C).
3.1.8 measured conversion—calculated as the difference between the mass of feed used and the mass of unconverted material
divided by the mass of feed used times 100 %.The unconverted material is defined as all liquid product with a boiling point above
216°C (42°F). 42°F (216°C).
3.1.9 normalized product yield—the resu
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.