ASTM E488-96(2003)
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Strength of Anchors in Concrete and Masonry Elements
Standard Test Methods for Strength of Anchors in Concrete and Masonry Elements
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
These test methods are intended to provide data from which applicable design data and specifications are derivable for a given anchorage device used in a structural member of concrete, masonry and related products and for qualifying anchors or anchorage systems.
The test methods shall be followed to ensure reproducibility of the test data.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover procedures for determining the static, seismic, fatigue and shock, tensile and shear strengths of post-installed and cast-in-place anchorage systems in structural members made of concrete or structural members made of masonry. Only those tests required by the specifying authority need to be performed.
1.2 These test methods are intended for use with such anchorage devices designed to be installed perpendicular to a plane surface of the structural member.
1.3 Whereas combined tension and shear as well as torsion tests are performed under special conditions, such tests are not covered in the methods described herein.
1.4 While individual procedures are given for static, seismic, fatigue and shock testing, nothing herein shall preclude the use of combined testing conditions which incorporate two or more of these types of tests, (such as seismic, fatigue and shock tests in series), since the same equipment is used for each of these tests.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E488–96 (Reapproved 2003)
Standard Test Methods for
1
Strength of Anchors in Concrete and Masonry Elements
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E488; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope E575 Practice for Reporting Data from Structural Tests of
Building Constructions, Elements, Connections, and As-
1.1 These test methods cover procedures for determining
semblies
the static, seismic, fatigue and shock, tensile and shear
strengths of post-installed and cast-in-place anchorage systems
3. Terminology
in structural members made of concrete or structural members
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
made of masonry. Only those tests required by the specifying
3.1.1 adhesive anchor—a post-installed anchor that derives
authority need to be performed.
its holding strength from the chemical compound between the
1.2 These test methods are intended for use with such
wall of the hole and the anchor rods. The materials used
anchorage devices designed to be installed perpendicular to a
includeepoxy,cementitiousmaterial,polyesterresin,andother
plane surface of the structural member.
similar types.
1.3 Whereas combined tension and shear as well as torsion
3.1.2 anchor spacing—the distance between anchors mea-
tests are performed under special conditions, such tests are not
sured centerline to centerline, in mm (in.); also, the minimum
covered in the methods described herein.
distance between reaction points of the test frame.
1.4 While individual procedures are given for static, seis-
3.1.3 cast-in-place anchor—ananchorthatisinstalledprior
mic, fatigue and shock testing, nothing herein shall preclude
to the placement of concrete and derives its holding strength
the use of combined testing conditions which incorporate two
from plates, lugs, or other protrusions that are cast into the
or more of these types of tests, (such as seismic, fatigue and
concrete.
shock tests in series), since the same equipment is used for
3.1.4 displacement—movement of an anchor relative to the
each of these tests.
structural member. For tension tests, displacement is measured
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
along the axis of the anchor, and for shear tests, displacement
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
is measured perpendicular to the axis of the anchor, in mm
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
(in.).
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1.5 edge distance—side cover distance or the distance
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
from the centerline of an anchor to the nearest edge of a
2. Referenced Documents structural member, in mm (in.); also, minimum distance from
2
the centerline to the test frame.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.6 embedment depth—distance from the test member
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
surface to the installed end of the anchor, in mm (in.), prior to
E171 Specification for Atmospheres for Conditioning and
the setting of the anchor.
Testing Flexible Barrier Materials
3.1.7 expansion anchor—a post-installed anchor that de-
E468 Practice for Presentation of Constant Amplitude Fa-
rives its holding strength through a mechanically expanded
tigue Test Results for Metallic Materials
systemwhichexertsforcesagainstthesidesofthedrilledhole.
3.1.8 fatigue test—a laboratory test that applies repeated
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
load cycles to an anchorage system for the purpose of
Performance of Buildings and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.13
determining the fatigue life or fatigue strength of that system.
on Structural Performance of Connections in Building Construction.
3.1.9 LVDT—a linear variable differential transformer used
Current edition approved May 10, 2003. Published June 2003. Originally
approved in 1976. Last previous edition approved in 1996 as E488–96. DOI:
for measuring the displacement or movement of an anchor or
10.1520/E0488-96R03.
anchor system.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3.1.10 post-installed anchor—an anchor that is installed
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
after the placement and hardening of concrete.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA
...







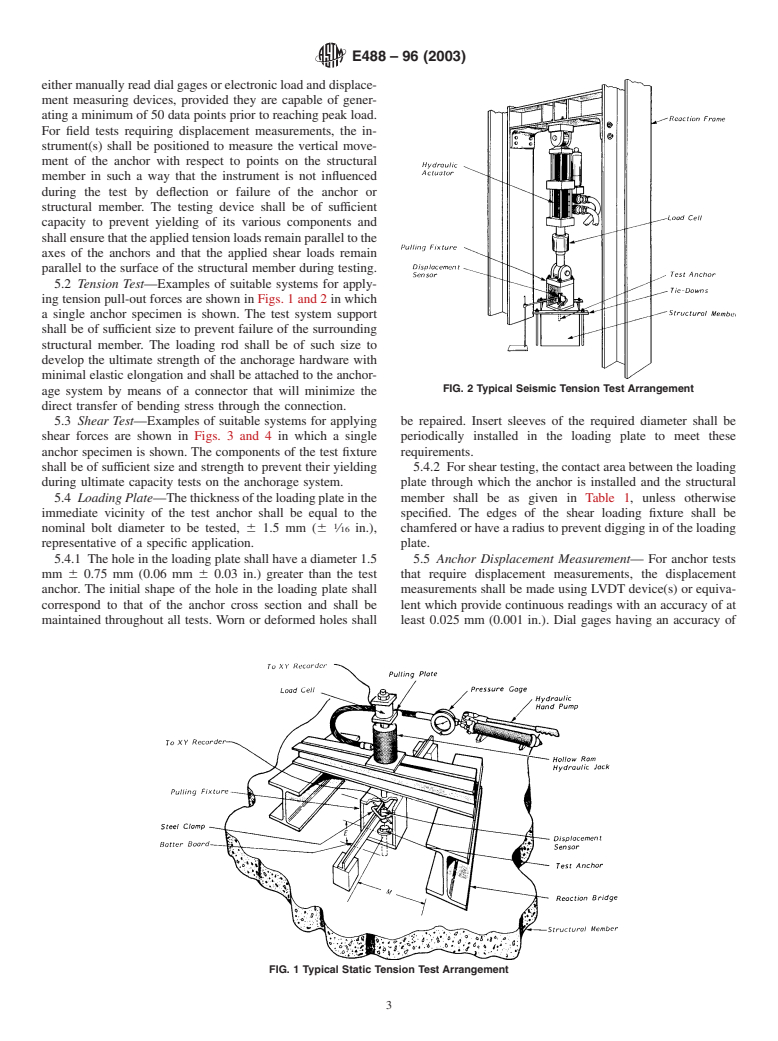
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.