ASTM D8393-21
(Guide)Standard Guide for Determination of Pore Volume of Powdered Catalysts and Catalyst Carriers by Water Adsorption
Standard Guide for Determination of Pore Volume of Powdered Catalysts and Catalyst Carriers by Water Adsorption
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This guide is intended to determine meso- and macropore volume which affects heavy oil cracking performance of a catalyst. The information is useful for materials specification, manufacturing control, and research and development in the evaluation of catalytic materials.
5.2 It has been reported in literature the existence of a correlation between the pore volume obtained from this guide and that from Test Method D4284.3
SCOPE
1.1 This guide measures pore volume of powdered catalysts and catalyst carriers by titration with water. The water does not react with material. The range of pore volume is 0.25 mL/g to 0.46 mL/g.
1.2 This guide is suitable for fine catalysts such as fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts (fresh or equilibrium), catalyst additives and spray dried catalyst carriers or finished catalysts, or a combination thereof, and is typically applicable to powders with the majority of particles (above 90 %) in the distribution range between 20 and 150 µm equivalent spherical diameter (determined by Test Method D4464) and with an average particle size between 60 and 100 µm.
Note 1: This technique is capable of measuring particles below and above this range (for example, from 1 to 300 µm) but no precision data is available.
1.3 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D8393 − 21
Standard Guide for
Determination of Pore Volume of Powdered Catalysts and
1
Catalyst Carriers by Water Adsorption
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D8393; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This guide measures pore volume of powdered catalysts
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
and catalyst carriers by titration with water.The water does not
D4284 Test Method for Determining Pore Volume Distribu-
react with material. The range of pore volume is 0.25 mL/g to
tion of Catalysts and Catalyst Carriers by Mercury Intru-
0.46 mL/g.
sion Porosimetry
1.2 This guide is suitable for fine catalysts such as fluid
D4464 Test Method for Particle Size Distribution of Cata-
catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts (fresh or equilibrium),
lytic Materials by Laser Light Scattering
catalyst additives and spray dried catalyst carriers or finished
E105 Guide for Probability Sampling of Materials
catalysts, or a combination thereof, and is typically applicable E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
to powders with the majority of particles (above 90 %) in the ASTM Test Methods
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
distribution range between 20 and 150 µm equivalent spherical
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
diameter (determined by Test Method D4464) and with an
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
average particle size between 60 and 100 µm.
3. Terminology
NOTE 1—This technique is capable of measuring particles below and
above this range (for example, from 1 to 300 µm) but no precision data is
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
available.
3.1.1 capillary action, n—the ability of a liquid to flow in
1.3 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded narrowspaces as inducedby the intermolecular forcesbetween
as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this the liquid and surrounding solid surfaces.
standard.
3.1.2 macropore, n—pore with internal width greater than
50 nm.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 3.1.3 mesopore, n—pore with internal width between 2 nm
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- and 50 nm.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3.1.4 surface tension, n—the attractive force exerted upon
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
the surface molecules of a liquid by the molecules beneath that
tends to draw the surface molecules into the bulk of the liquid
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
and makes the liquid assume the shape having the least surface
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
area.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4. Summary of Guide
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.1 This guide is intended to provide mesopore and mac-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
ropore volume information of powdered catalysts and catalyst
carriers.Ithelpsuserstojudgetheendpointduringthetitration
of catalytic material with water.
4.2 The added water is drawn by capillarity action into the
catalytic material’s mesopores and macropores. When the end
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D32 on Catalysts and
2
is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D32.01 on Physical-Chemical Proper- For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
ties. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Current edition approved June 1, 2021. Published August 2021. DOI: 10.1520/ Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
D8393-21. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D8393 − 21
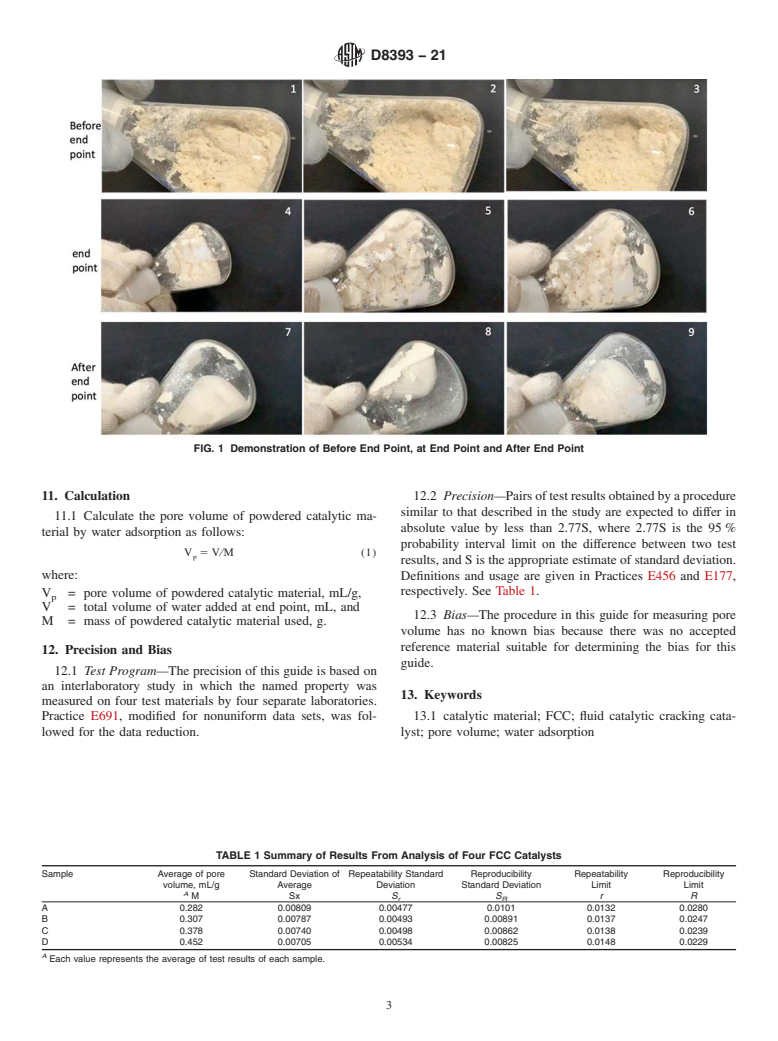
point of the titration is reached, water overflows and forms a 10.2 Drop deionized water from a 25 mL burette into the
film on the surface of the water-saturated particles. The conical flask. For the first time, 4.0–4.5 mLof water (less than
particles stick together by surface tension. They adhere to the 80 % of the total amount) can be delivered.
interna
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.