ASTM B770-08
(Specification)Standard Specification for Copper-Beryllium Alloy Sand Castings for General Applications
Standard Specification for Copper-Beryllium Alloy Sand Castings for General Applications
ABSTRACT
This specification establishes requirements for copper-beryllium alloy sand castings for general applications and covers Copper Alloy UNS Nos. C81400, C82000, C82200, C82400, C82500, C82510, C82600, C82800, and C96700. The product shall be manufactured by casting and thermal treatment. Castings shall conform to the chemical composition requirements prescribed for copper, nickel, silicon, beryllium, cobalt, chromium, iron, zirconium, tin, and manganese. The standard temper designations include TF00 (cast, solution and precipitation heat treated) and M01 (as sand cast). Requirements for precipitation and solution heat-treatments of castings for the purpose of determining conformance to the specified mechanical properties including tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation are detailed. Special combinations of properties such as increased ductility, electrical conductivity, dimensional accuracy, and endurance life may be obtained by special precipitation heat-treatments. Tension tests shall also meet the mechanical property requirements.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes requirements for copper-beryllium alloy sand castings for general applications and nominal compositions alloys defined by this specification are shown in Table 1.
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the test methods described in this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory requirements prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B770 – 08
Standard Specification for
Copper-Beryllium Alloy Sand Castings for General
1
Applications
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B770; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* B601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper
and Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
1.1 This specification establishes requirements for copper-
B824 Specification for General Requirements for Copper
beryllium alloy sand castings for general applications and
Alloy Castings
nominal compositions alloys defined by this specification are
2
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
shown in Table 1.
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be
Unified Numbering System (UNS)
regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for
3. General Requirements
information only and are not considered standard.
3.1 The following sections of Specification B824 constitute
1.3 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the
a part of this specification:
test methods described in this specification: This standard does
3.1.1 Terminology,
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
3.1.2 Material and Manufacture,
associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthis
3.1.3 Chemical Composition,
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices
3.1.4 Dimensions and Permissible Variations,
and determine the applicability of regulatory requirements
3.1.5 Workmanship, Finish and Appearance,
prior to use.
3.1.6 Sampling,
2. Referenced Documents 3.1.7 Number of Tests and Retests,
3.1.8 Specimen Preparation,
2.1 The following documents in the current issue of the
3.1.9 Test Methods,
BookofStandardsformapartofthisspecificationtotheextent
3.1.10 Significance of of Numerical Limits,
referenced herein:
3 3.1.11 Inspection,
2.2 ASTM Standards:
3.1.12 Rejection and Rehearing,
B30 Specification for Copper Alloys in Ingot Form
3.1.13 Certification,
B208 Practice for Preparing Tension Test Specimens for
3.1.14 Mill Test Report, and
Copper Alloy Sand, Permanent Mold, Centrifugal, and
3.1.15 Packaging and Package Marking.
Continuous Castings
3.2 In addition, when a section with a title identical to that
referenced in 3.1 appears in this specification, it contains
additional requirements which supplement those appearing in
1
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB05onCopper
Specification B824.
and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.05 on
Castings and Ingots for Remelting.
4. Terminology
Current edition approved April 1, 2008. Published April 2008. Originally
approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as B770 – 05. DOI:
4.1 For definitions of terms relating to copper and copper
10.1520/B0770-08.
alloys, refer to Terminology B846.
2
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E527) is a simple
expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition
5. Ordering Information
of a prefix “C” and a suffix “00”. The suffix can be used to accommodate
composition variations of the base alloy.
5.1 Include the following information for orders for prod-
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
uct:
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
5.1.1 ASTM designation number, title, and year of issue,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. 5.1.2 Copper Alloy UNS Number designation,
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B770 – 08
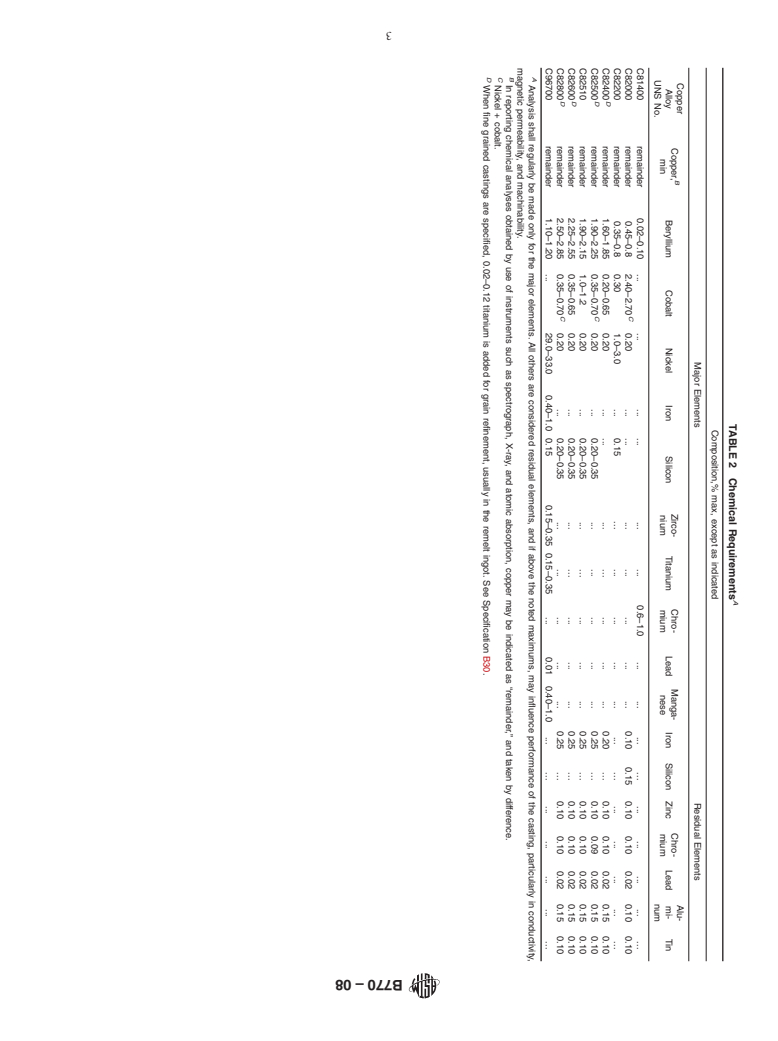
TABLE 1 Nominal Compositions
Copper Alloy Previous
Copper Nickel Silicon Beryllium Cobalt Chromium Iron Zirconium Tin Manganese
UNS No. Designation
C81400 70C 99.1 . . 0.06 . 0.8 . . . .
C82000 10C 97 . . 0.5 2.5 . . . . .
C82200 3C, 14C 98 2.0 . 0.5 . . . . . .
A A
C82400 165C, 165CT 97.8 . . 1.7 0.5 . . . . .
A A
C82500 20C, 20CT 97.2 . 0.3 2.0 0.5 . . . . .
C82510 21C 96.6 . 0.3 2.0 1.1 . . . . .
A A
C82600 245C, 245CT 96.8 . 0.3 2.4 0.5 . . . . .
A A
C82800 275C, 275CT 96.6 . 0.3 2.6 0.5 . . . . .
C96700 72C 67.2 31.0 . 1.2 . . 0.6 0.3 0.3
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:B770–05 Designation: B 770 – 08
Standard Specification for
Copper-Beryllium Alloy Sand Castings for General
1
Applications
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 770; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification establishes requirements for copper-beryllium alloy sand castings for general applications and nominal
2
compositions alloys defined by this specification are shown in Table 1.
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
mathematical conversions to SI units, whichunits that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the test methods described in this specification: This standard does not
purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory requirements prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 The following documents in the current issue of the Book of Standards form a part of this specification to the extent
referenced herein:
3
2.2 ASTM Standards:
B 30 Specification for Copper Alloys in Ingot Form
B 208 Practice for Preparing Tension Test Specimens for Copper Alloy Sand, Permanent Mold, Centrifugal, and Continuous
Castings
B 601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper and Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
B 824 Specification for General Requirements for Copper Alloy Castings
B 846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
E 527Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS) Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering
System (UNS)
3. General Requirements
3.1 The following sections of Specification B 824 constitute a part of this specification:
3.1.1 Terminology,
3.1.2 Material and Manufacture,
3.1.3 Chemical Composition,
3.1.4 Dimensions and Permissible Variations,
3.1.5 Workmanship, Finish and Appearance,
3.1.6 Sampling,
3.1.7 Number of Tests and Retests,
3.1.8 Specimen Preparation,
3.1.9 Test Methods,
3.1.10 Significance of of Numerical Limits,
3.1.11 Inspection,
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee B05 on Copper and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.05 on Castings
and Ingots for Remelting.
Current edition approved MayApril 1, 2005.2008. Published May 2005.April 2008. Originally approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 20022005 as
B 770 – 025.
2
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E 527) is a simple expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition of
a prefix “C” and a suffix “00”. The suffix can be used to accommodate composition variations of the base alloy.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book ofASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B770–08
TABLE 1 Nominal Compositions
Copper Alloy Previous
Copper Nickel Silicon Beryllium Cobalt Chromium Iron Zirconium Tin Manganese
UNS No. Designation
C81400 70C 99.1 . . 0.06 . 0.8 . . . .
C82000 10C 97 . . 0.5 2.5 . . . . .
C82200 3C, 14C 98 2.0 . 0.5 . . . . . .
A A
C82400 165C, 165CT 97.8 . . 1.7 0.5 . . . . .
A A
C82500 20C, 20CT 97.2 . 0.3 2.0 0.5 . . . . .
C82510 21C 96.6 . 0.3 2.0 1.1 . . . . .
A A
C82600 245C, 245CT 96.8 . 0.3 2.4 0.5 . . . . .
A A
C82800 275C, 275CT 96.6 . 0.3 2.6 0.5 . . . . .
C96700 72C 67.2 31.0 . 1.2 . . 0.6 0.3 0.3 0.6
A
When fine-grained castings are specified, 0.02 to 0.12 titanium is added for grain refinement, usually in the remelt ingot. See Specification B 30.
3.1.12 Rejection and Rehearing,
3.1.13 Certification,
3.1.14 Mill Test Report,
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.