ASTM B865-96a
(Specification)Standard Specification for Precipitation Hardening Nickel-Copper-Aluminum Alloy (UNS N05500) Bar, Rod, Wire, Forgings, and Forging Stock
Standard Specification for Precipitation Hardening Nickel-Copper-Aluminum Alloy (UNS N05500) Bar, Rod, Wire, Forgings, and Forging Stock
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers nickel-copper-aluminum alloy (UNS N05500) in the form of rounds, squares, hexagons, or rectangles, and forgings and forging stock, manufactured either by hot working or cold working, and cold-worked wire.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: B 865 – 96a
Standard Specification for
Precipitation Hardening Nickel-Copper-Aluminum Alloy
(UNS N05500) Bar, Rod, Wire, Forgings, and Forging Stock
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 865; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope MIL-STD-271 Nondestructive Testing Requirements for
Metals
1.1 This specification covers nickel-copper-aluminum alloy
(UNS N05500) in the form of rounds, squares, hexagons, or
3. Terminology
rectangles, and forgings and forging stock, manufactured either
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
by hot working or cold working, and cold-worked wire.
3.1.1 bar, , n—material of rectangular (flats), hexagonal, or
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
square solid section up to and including 10 in. (254 mm) in
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
width and ⁄8 in. (3.2 mm) and over in thickness in straight
information only.
lengths.
2. Referenced Documents 3.1.2 rod, , n—material of round solid section furnished in
straight lengths.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.3 wire, , n—a cold-worked solid product of uniform
E 8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
round cross section along its whole length, supplied in coil
E 18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness and Rockwell
form.
Superficial Hardness of Metallic Materials
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
4. Ordering Information
Determine Conformance with Specifications
4.1 Orders for material to this specification should include
E 112 Test Methods for Determining the Average Grain
2 the following information:
Size
4.1.1 ASTM designation and year of issue,
E 140 Hardness Conversion Tables for Metals
4.1.2 Alloy name or UNS number (see Table 1),
E 602 Test Method for Sharp-Notch Tension Testing with
2 4.1.3 Shape—rod (round) or bar (square, hexagonal, or
Cylindrical Specimens
rectangular),
E 1473 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Nickel,
4 4.1.3.1 Forging (sketch or drawing),
Cobalt, and High-Temperature Alloys
4.1.4 Dimensions, including length, (see Tables 2 and 3),
2.2 Federal Standards:
4.1.5 Condition (see Table 4, Table 5, and Table 6),
Fed. Std. No. 102 Preservation, Packaging, and Packing
4.1.6 Forging stock—Specify if material is stock for reforg-
Levels
ing,
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
4.1.7 Finish,
Fed. Std. No. 182 Continuous Identification Marking of
4.1.8 Quantity—feet or number of pieces, and
Nickel and Nickel-Base Alloys
4.1.9 Certification—State if certification or a report of test
2.3 Military Standards:
results is required (Section 15),
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
4.1.10 Samples for product (check) analysis—State whether
samples for product (check) analysis should be furnished, and
4.1.11 Purchaser inspection—If purchaser wishes to witness
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B-2 on
tests or inspection of material at place of manufacture, the
Nonferrous Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
purchase order must so state indicating which test or inspec-
B02.07 on Refined Nickel and Cobalt, and Alloys Containing Nickel or Cobalt or
tions are to be witnessed.
Both as Principal Constituents.
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 1996. Published December 1996. Originally
published as B 865 – 95. Last previous edition B 865 – 96.
5. Chemical Composition
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
3 5.1 The material shall conform to the composition limits
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.06. specified in Table 1.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
B 865 – 96a
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements TABLE 3 Permissible Variations in Straightness of Precision
Straightened Cold-Worked Shafting
Product (check) analysis
variations, under min or
Permissible Variations
Element Composition Limits, %
Standard Distance
over max, of the specified
Specified Dimension, Throw In One Revolution
Between Supports,
limit of element, %
in. (mm) From Straightness,
in. (mm)
in. (mm)
A
Nickel 63.0 min 0.45
1 15
Aluminum 2.30–3.15 0.20
⁄2 (12.7) to ⁄16 (23.8), 42 (1070) 0.005 (0.13)
Carbon 0.18 max 0.01
incl
15 15
Iron 2.0 max 0.05
Over ⁄16 (23.8) to 1 ⁄16 42 (1070) 0.006 (0.15)
Manganese 1.5 max 0.04 (49.2), incl
15 1
Silicon 0.50 max 0.03
Over 1 ⁄16 (49.2) to 2 ⁄2 42 (1070) 0.007 (0.18)
Titanium 0.35–0.85 0.03 min (63.5), incl
0.04 max
Over 2 ⁄2 (63.5) to 4 42 (1070) 0.008 (0.20)
Sulfur 0.010 max 0.003 (101.6), incl
3 15
Copper 27.0–33.0 0.15 min
⁄4 (19.0) to ⁄16 (23.8), Specified lengths of 3 to 100.004 (0.10) plus 0.0025
0.20 max incl ft (0.91 to 3.05 m) (0.064) for each foot, or
fraction thereof, in excess
A
The nickel content shall be determined arithmetically by difference.
of 3 ft (0.91 m)
Over ⁄16 (23.8) to 4 Specified lengths of 20 ft 0.005 (0.13) plus 0.0015
(101.6), incl (6.10 m) and less (0.038) for each foot, or
TABLE 2 Permissible Variations in Diameter or Distance
A
fraction thereof, in excess
Between Parallel Surfaces of Hot-Worked Rod and Bar
of 3 ft (0.91 m)
Permissible Variations from
B
Specified Dimensions, in. (mm)
Specified Dimension, in. (mm)
Plus Minus A
TABLE 4 Mechanical Properties—Unaged (Bar, Rod, Forgings)
Rod and bar, hot worked:
Hardness
1 (25.4) and under 0.016 (0.41) 0.016 (0.41)
Form Condition
Brinell
Over 1 (25.4) to 2 (50.8), incl 0.031 (0.79) 0.016 (0.41)
Rockwell, max
3000 kg, max
Over 2 (50.8) to 4 (101.6), incl 0.047 (1.19) 0.031 (0.79)
Over 4 (101.6) 0.125 (3.18) 0.063 (1.60)
B
Rounds, hexagons, Hot-worked 245 C23
Rod, rough-turned or ground:
squares, rectangles, and
Under 1 (25.4) 0.005 (0.13) 0.005 (0.13)
forgings
1 (25.4) and over 0.031 (0.79) 0
Hexagons Cold-worked 260 C26
Round rod, semi-smooth, machined:
Rounds:
Over 3 ⁄2 (88.9) 0.031 (0.79) 0
⁄4 (6.4 mm) to 1 in. Cold-worked 280 C29
Round rod, smooth finished, machined:
(25.4 mm), incl
Over 3 ⁄2 (88.9) 0 0.005 (0.13)
Over 1 (25.4 mm) to 3 Cold-worked 260 C26
Forging quality bolt stock (rounds only):
in. (76.2 mm), incl
1 5
⁄4 (6.4), ⁄16 (7.9) 0 0.0062 (0.16)
Over 3 (76.2 mm) to 4 Cold-worked 240 C22
3 7 1
⁄8 (9.5), ⁄16 (11.1), ⁄2 (12.7) 0 0.0066 (0.17)
in. (101.6 mm), incl
9 5 11 3
⁄16 (14.3), ⁄8 (7.9), ⁄16 (17.5), ⁄4 0 0.0082 (0.21)
Rounds, hexagons, Hot-worked or cold- 185 B90
13 7
(19.1), ⁄16 (20.6), ⁄8 (22.2)
squares, rectangles, and worked and annealed
⁄16 (7.9), 1 (25.4) 0 0.0098 (0.25)
forgings
1 1 1
1 ⁄16 to 1 ⁄2 (27.0 to 38.1), in ⁄16 (1.6) 0 0.0112 (0.28)
A
No tensile tests are required except as provided for in 9.2.3.
increments
B
Rounds over 4 ⁄4 in. (108.0 mm) in diameter shall have hardness of 260 BHN,
A
Not applicable to forging stock.
max.
B
Dimensions apply to diameter of rods, to distance between parallel surfaces of
hexagons and squares, and separately to width and thickness of rectangles.
hot-worked rods ⁄2 in. (12.7 mm) in diameter and under, which
5.2 If a product (check) analysis is performed by the
may be cut-of-round by the total permissible variations in
purchaser, the material shall conform to the product (check)
diameter shown in Table 2. Cold-worked wire shall not be
analysis variations in Table 1.
out-of-round by more than one-half the total permissible
6. Mechanical Properties
variations in diameter shown in Table 7.
7.3 Edges—Square, rectangular, and hexagonal bar and rod
6.1 Mechanical Properties—The material in the unaged
shall have angles and corners consistent with commercial
condition shall conform to the mechanical properties specified
practice.
in Table 4. After aging the material shall conform to the
7.4 Machining Allowances for Hot-Worked Materials—
mechanical properties specified in Table 5 and Table 6.
When the surfaces of hot-worked products are to be machined,
7. Dimensions and Permissible Variations
the allowances prescribed in Table 8 are recommended for
normal machining operations.
7.1 Diameter, Thickness, or Width—The permissible varia-
7.5 Length—The permissible variations in length of cold-
tions from the specified dimensions as measured on the
worked and hot-worked rod and bar shall be as prescribed in
diameter or between parallel surfaces of cold-worked rod and
Table 9.
bar shall be as prescribed in Table 7; of hot-worked rod and bar
as prescribed in Table 2; and of wire as prescribed in Table 7. 7.5.1 Rods and bars ordered to random or nominal lengths
will be furnished with either cropped or saw-cut ends; material
7.2 Out-of-Round—Hot-worked rods and cold-worked rods
(except “forging quality”) of all sizes, in straight lengths, shall ordered to cut lengths will be furnished with square, saw-cut,
or machined ends.
not be out-of-round by more than one half the total permissible
variations in diameter shown in Table 2 and Table 7, except for 7.6 Straightness:
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
B 865 – 96a
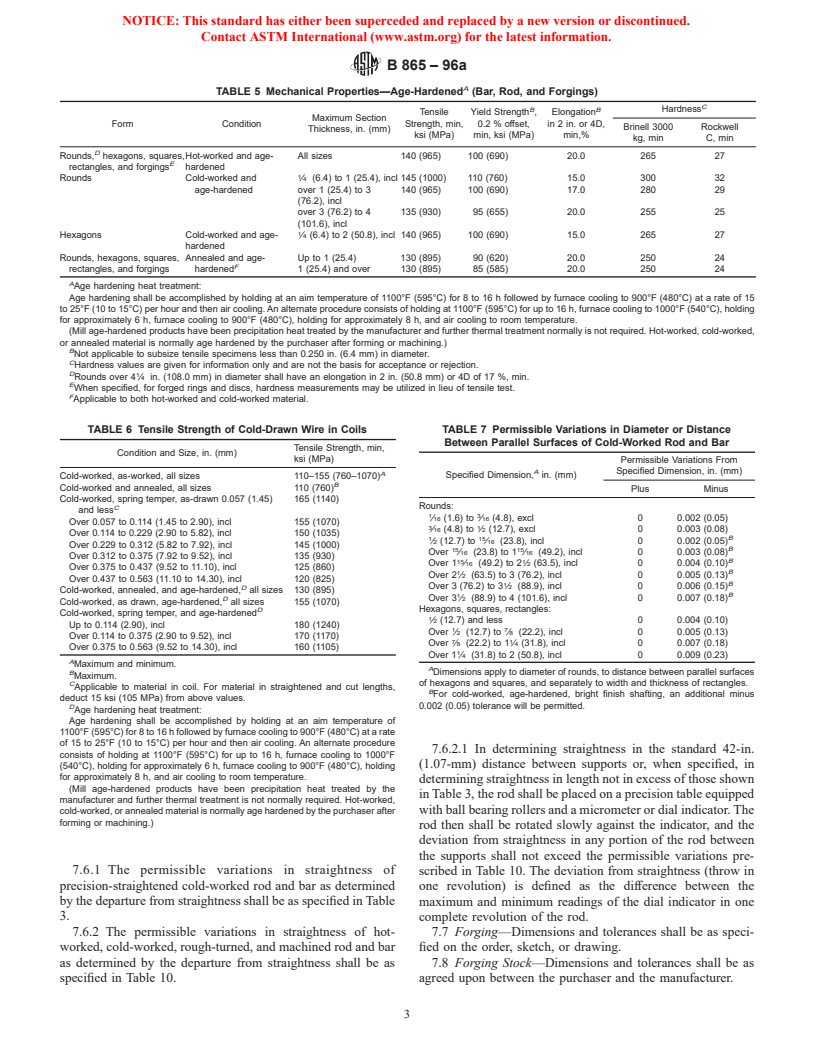
A
TABLE 5 Mechanical Properties—Age-Hardened (Bar, Rod, and Forgings)
C
B B
Hardness
Tensile Yield Strength , Elongation
Maximum Section
Form Condition Strength, min, 0.2 % offset, in 2 in. or 4D,
Brinell 3000 Rockwell
Thickness, in. (mm)
ksi (MPa) min, ksi (MPa) min,%
kg, min C, min
D
Rounds, hexagons, squares,Hot-worked and age- All sizes 140 (965) 100 (690) 20.0 265 27
E
rectangles, and forgings hardened
Rounds Cold-worked and ⁄4 (6.4) to 1 (25.4), incl 145 (1000) 110 (760) 15.0 300 32
age-hardened over 1 (25.4) to 3 140 (965) 100 (690) 17.0 280 29
(76.2), incl
over 3 (76.2) to 4 135 (930) 95 (655) 20.0 255 25
(101.6), incl
Hexagons Cold-worked and age- ⁄4 (6.4) to 2 (50.8), incl 140 (965) 100 (690) 15.0 265 27
hardened
Rounds, hexagons, squares, Annealed and age- Up to 1 (25.4) 130 (895) 90 (620) 20.0 250 24
F
rectangles, and forgings hardened 1 (25.4) and over 130 (895) 85 (585) 20.0 250 24
A
Age hardening heat treatment:
Age hardening shall be accomplished by holding at an aim temperature of 1100°F (595°C) for 8 to 16 h followed by furnace cooling to 900°F (480°C) at a rate of 15
to 25°F (10 to 15°C) per hour and then air cooling. An alternate procedure consists of holding at 1100°F (595°C) for up to 16 h, furnace cooling to 1000°F (540°C), holding
for approximately 6 h, furnace cooling to 900°F (480°C), holding for approximately 8 h, and air cooling to room temperature.
(Mill age-hardened products have been precipitation heat treated by the manufacturer and further thermal treatment normally is not required. Hot-worked, cold-worked,
or annealed material is normally age hardened by the purchaser after forming or machining.)
B
Not applicable to subsize tensile specimens less than 0.250 in. (6.4 mm) in diameter.
C
Hardness values are given for information only and are not the basis for acceptance or rejection.
D 1
Rounds over 4 ⁄4 in. (108.0 mm) in diameter shall have an elongation in 2 in. (50.8 mm) or 4D of 17 %, min.
E
When specified, for forged rings and discs, hardness measurements may be utilized in lieu of tensile test.
F
Applicable to both hot-worked and cold-worked material.
TABLE 6 Tensile Strength of Cold-Drawn Wire in Coils TABLE 7 Permissible Variations in Diameter or Distance
Between Parallel Surfaces of Cold-Worked Rod and Bar
Tensile Strength, min,
Condition and Size, in. (mm)
ksi (MPa)
Permissible Variations From
A Specified Dimension, in. (mm)
A
Specified Dimension, in. (mm)
Cold-worked, as-worked, all sizes 110–155 (760–1070)
B
Cold-worked and annealed, all sizes 110 (760)
Plus Minus
Cold-worked, spring temper, as-drawn 0.057 (1.45) 165 (1140)
Rounds:
C
and less
1 3
⁄16 (1.6) to ⁄16 (4.8), excl 0 0.002 (0.05)
Over 0.057 to 0.114 (1.45 to 2.90), incl 155 (1070)
3 1
⁄16 (4.8) to ⁄2 (12.7), excl 0 0.003 (0.08)
Over 0.114 to 0.229 (2.90 to 5.82), incl 150 (1035)
B
1 15
⁄2 (12.7) to ⁄16 (23.8), incl 0 0.002 (0.05)
Over 0.229 to 0.312 (5.82 to 7.92), incl 145 (1000)
B
15 15
Over ⁄16 (23.8) to 1 ⁄16 (49.2), incl 0 0.003 (0.08)
Over 0.312 to 0.375 (7.92 to 9.52), incl 135 (930)
15 1 B
Over 1 ⁄16 (49.2) to 2 ⁄2 (63.5), incl 0 0.004 (0.10)
Over 0.375 to 0.437 (9.52 to 11.10), incl 125 (860)
B
Over 2 ⁄2 (63.5) to 3 (76.2), incl 0 0.005 (0.13)
Over 0.437 to 0.563 (11.10 to 14.30), incl 120 (825)
B
Over 3 (76.2) to 3 ⁄2 (88.9), incl 0 0.006 (0.15)
D
Cold-worked, annealed, and age-hardened, all sizes 130 (895)
B
D Over 3 ⁄2 (88.9) to 4 (101.6), incl 0 0.007 (0.18)
Cold-worked, as drawn, age-hardened, all sizes 155 (1070)
Hexagons, squares, rectangles:
D
Cold-worked, spring temper, and age-hardened
⁄2 (12.7) and less 0 0.004 (0.10)
Up to 0.114 (2.90), incl 180 (1240)
1 7
Over ⁄2 (12.7) to ⁄8 (22.2), incl 0 0.005 (0.13)
Over 0.114 to 0.375 (2.90 to 9.52), incl 170 (1170)
7 1
Over ⁄8 (22.2) to 1 ⁄4 (31.8), incl 0 0.007 (0.18)
Over 0.375 to 0.563 (9.52 to 14.30), incl 160 (1105)
Over 1 ⁄4 (31.8) to 2 (50.8), incl 0 0.009 (0.23)
A
Maximum and minimum.
A
Dimensions apply to diameter of rounds, to distance between parallel surfaces
B
Maximum.
C of hexagons and squares, and separately to width and thickness of rectangles.
Applicable to material in coil. For material in straightened and cut lengths,
B
For cold-worked, age-hardened, bright finish shafting, an additional minus
deduct 15 ksi (105 MPa) from above values.
D 0.002 (0.05) tolerance will be permitted.
Age hardening heat treatment:
Age hardening shall be accomplished by holding at an aim temperature of
1100°F (595°C) for 8 to 16 h followed by furnace cooling to 900°F (480°C) at a rate
of 15 to 25°F (10 to 15°C) per hour and then air cooling. An alternate procedure
7.6.2.1 In determining straightness in the standard 42-in.
consists of holding at 1100°F (595°C) for up to 16 h, furnace cooling to 1000°F
(1.07-mm) distance between supports or, when specified, in
(540°C), holding for approximately 6 h, furnace cooling to 900°F (480°C), holding
for approximately 8 h, and air cooling to room temperature.
determining straightness in length not in excess of those shown
(Mill age-hardened products have been precipitation heat treated by the
in Table 3, the rod shall be placed on a precision table equipped
manufacturer and further thermal treatment is not normally required.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.