ASTM F2806-10
(Specification)Standard Specification for Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) Plastic Pipe (Metric SDR-PR)
Standard Specification for Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) Plastic Pipe (Metric SDR-PR)
ABSTRACT
This specification covers acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) pipe produced by single extrusion in standard thermoplastic pipe dimension ratios and pressure rated for water. Included are criteria for classifying ABS plastic pipe materials and ABS plastic pipe, a system of nomenclature for ABS plastic pipe, and requirements and test methods for materials, workmanship, dimensions, sustained pressure, burst pressure, and extrusion quality. Methods of marking are also given. The products covered by this specification are intended for use with the distribution of pressurized liquids, which are chemically compatible with the piping materials. Requirements cover workmanship, dimensions and tolerances (outside diameters and wall thickness), sustained pressure, burst pressure, and impact.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) pipe produced by single extrusion in standard thermoplastic pipe dimension ratios and pressure rated for water (see Appendix X1). Included are criteria for classifying ABS plastic pipe materials and ABS plastic pipe, a system of nomenclature for ABS plastic pipe, and requirements and test methods for materials, workmanship, dimensions, sustained pressure, burst pressure, and extrusion quality. Methods of marking are also given.
1.2 The products covered by this specification are intended for use with the distribution of pressurized liquids, which are chemically compatible with the piping materials. Consult with the manufacturer and local building codes before use in other applications. Due to inherent hazards associated with testing components and systems with compressed air or other compressed gases some manufacturers do not allow pneumatic testing of their products. Consult with specific product/component manufacturers for their specific testing procedures prior to pneumatic testing.
Note 1—Pressurized (compressed) air or other compressed gases contain large amounts of stored energy, which present serious safety hazards should a system fail for any reason.
Note 2—This specification addresses only pipe for use in above ground service. For buried service consult the manufacturer and local building codes.
Note 3—Exposure to ultraviolet radiation over a long period of time may affect the physical properties of ABS pipe. Consult the manufacturer for recommendations for handling, storage, and installations that are not protected by insulation.
1.3 Pipe meeting the requirements of this standard are not compatible with IPS sized DWV fittings. The ABS pipe covered in this standard is intended for pressure service and it shall be joined to pressure fittings. Non-pressure fittings, such as DWV fittings from any material (ABS, PVC, CPVC, etc.), are not acceptable for pressure applications.
1.4 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes, which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: F2806 – 10
Standard Specification for
Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) Plastic Pipe (Metric
SDR-PR)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2806; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.5 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes,
and appendixes, which provide explanatory material. These
1.1 This specification covers acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene
notesandfootnotes(excludingthoseintablesandfigures)shall
(ABS) pipe produced by single extrusion in standard thermo-
not be considered as requirements of the specification.
plastic pipe dimension ratios and pressure rated for water (see
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
AppendixX1).IncludedarecriteriaforclassifyingABSplastic
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
pipe materials andABS plastic pipe, a system of nomenclature
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
for ABS plastic pipe, and requirements and test methods for
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
materials, workmanship, dimensions, sustained pressure, burst
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
pressure, and extrusion quality. Methods of marking are also
given.
2. Referenced Documents
1.2 The products covered by this specification are intended
2.1 ASTM Standards:
for use with the distribution of pressurized liquids, which are
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
chemically compatible with the piping materials. Consult with
D1598 Test Method for Time-to-Failure of Plastic Pipe
the manufacturer and local building codes before use in other
Under Constant Internal Pressure
applications. Due to inherent hazards associated with testing
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
components and systems with compressed air or other com-
Plastics
pressed gases some manufacturers do not allow pneumatic
D2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
testing of their products. Consult with specific product/
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
component manufacturers for their specific testing procedures
D2837 TestMethodforObtainingHydrostaticDesignBasis
prior to pneumatic testing.
forThermoplastic Pipe Materials or Pressure Design Basis
NOTE 1—Pressurized (compressed) air or other compressed gases
for Thermoplastic Pipe Products
contain large amounts of stored energy, which present serious safety
D3965 Specification for Rigid Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-
hazards should a system fail for any reason.
Styrene (ABS) Materials for Pipe and Fittings
NOTE 2—Thisspecificationaddressesonlypipeforuseinaboveground
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
service. For buried service consult the manufacturer and local building
2.2 Federal Standard:
codes.
NOTE 3—Exposure to ultraviolet radiation over a long period of time
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
may affect the physical properties ofABS pipe. Consult the manufacturer
2.3 Military Standard:
for recommendations for handling, storage, and installations that are not
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
protected by insulation.
2.4 NSF/ANSI Standard:
1.3 Pipe meeting the requirements of this standard are not
Standard No. 14 for Plastic Piping Components and Related
compatible with IPS sized DWV fittings. The ABS pipe
Materials
covered in this standard is intended for pressure service and it
Standard No. 61 Drinking Water System Components -
shall be joined to pressure fittings. Non-pressure fittings, such
Health Effects
as DWV fittings from any material (ABS, PVC, CPVC, etc.),
are not acceptable for pressure applications.
1.4 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
standard.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.61 on Water. dodssp.daps.dla.mil.
Current edition approved June 1, 2010. Published July 2010. DOI: 10.1520/ Available from NSF International, P.O. Box 130140, 789 N. Dixboro Rd.,Ann
F2806–10. Arbor, MI 48113-0140, http://www.nsf.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F2806 – 10
2.5 ISO Standard: is carried out in accordance with Test Method D1598 to find
ISO 1167 Thermoplastic pipes, fittings and assemblies for the HDB value. The HDB shall be a minimum of 17.2 MPa.
the conveyance of fluids—Determination of the resistance 4.4 Compound—TheABS plastic extrusion compound shall
to internal pressure—Part 1: General method meet the requirements ofABS Classes 42222, 20643, or 30444
ISO 3127 Thermoplastic pipes—Determination of resis- as described in Specification D3965.
tance to external blows—Round-the-clock method 4.5 Rework Material—The manufacturers shall use only
their own clean rework pipe material and the pipe produced
3. Terminology
shall meet all the requirements of this specification.
3.1 General—Definitions are in accordance with Terminol-
5. Pipe Classification
ogy F412. Abbreviations are in accordance with Terminology
5.1 General—This specification coversABS pipe produced
D1600, unless otherwise indicated. The abbreviation for
by single extrusion.
acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene plastic is ABS.
5.2 Standard Dimension Ratios (SDR)—This specification
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
coversABS pipe in eight standard dimension ratios. These are
3.3 acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) pipe and fitting
SDR 9, 11, 13.5, 17, 21, 26, 32.5, and SDR 41. The pressure
plastics—plastics containing polymers or blends of polymers,
rating is uniform for all nominal pipe sizes for a given ABS
or both, in which the minimum butadiene content is 6 %, the
pipe material and SDR.
minimum acrylonitrile content is 15 %, the minimum styrene
or substituted styrene content, or both, is 15 %, and the 6. Requirements
maximum content of all other monomers is not more than 5 %,
6.1 Workmanship—The pipe shall be homogeneous
and lubricants, stabilizers, and colorants.
throughout and free of visible cracks, holes, foreign inclusions,
3.4 mominal outside diameter (d )—specified outside di-
n
or other defects. The pipe shall be as uniform as commercially
ameter of a component, which is identical to the minimum
practicable in color, opacity, density, and other physical prop-
mean outside diameter, in millimeters
erties.
3.5 pressure rating (PR)—numerical designation used for
6.2 Dimensions and Tolerances:
reference purposes and related to the mechanical characteris-
6.2.1 Outside Diameters—The outside diameters and toler-
tics of the components of a piping system.
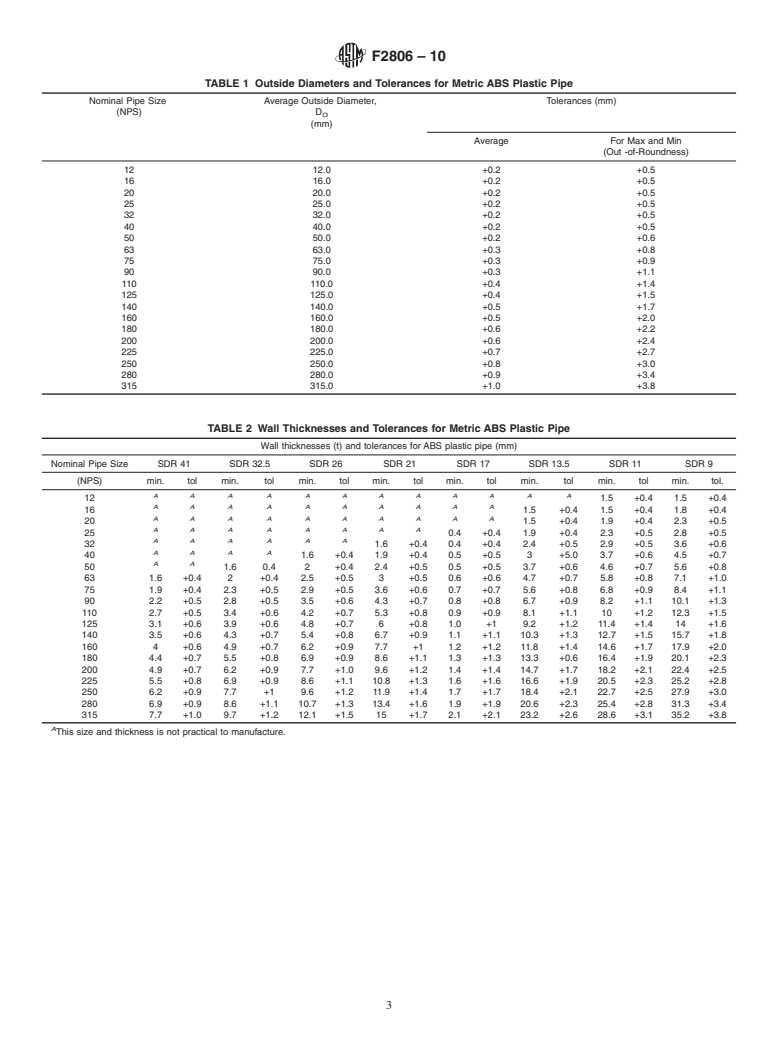
ances and out-of-roundness shall be as shown in Table 1 when
3.6 relation between standard dimension ratio, hydrostatic
measured in accordance with 7.4 and 7.4.1.
design basis (HDB), and pressure rating (PR)——the follow-
6.2.2 Wall Thickness—The wall thicknesses and tolerances
ing expression is used in this specification to relate standard
shall be as shown in Table 2 when measured in accordance
dimension ratio, hydrostatic design basis, and pressure rating:
with 7.4 and 7.4.2.
PR5 2 HDB/~SDR21! or PR52 HDB/~~D /t!21! (1) 6.3 Sustained Pressure—The pipe shall not fail, balloon,
O
burst, or weep as defined in ISO 1167 at the test pressures
where:
given in Table 3 when tested in accordance with 7.5.
6.4 Burst Pressure—The minimum burst pressures forABS
HDB = Hydrostatic design basis, MPa
plastic pipe shall be the pressure rating (PR) multiplied by a
PR = Pressure rating, MPa
factor of 3.2, when determined in accordance with 7.6.
DO = average outside diameter, mm
6.5 Impact —The pipe shall meet the impact requirements
t = minimum wall thickness mm, and
when tested in accordance with 7.7.
SDR = standard dimension ratio (D /t)
O
7. Test Methods
4. Materials 7.1 Conditioning—Condition the test specimens at 23 6
2°Cand50 65%relativehumidityfornotlessthan40hprior
4.1 General—Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene plastics used
to test in accordance with Procedure A of Practice D618 for
to make pipe meeting the requirements of this specification are
those tests where conditioning is required.
categorized by means of two criteria namely (1) short-term
7.2 Test Conditions—Conduct the tests in the Standard
tests and (2) long-term strength tests.
Laboratory Atmosphere of 23 6 2°C and 50 6 5 % relative
4.2 Basic Materials—The material properties of the grade
humidity, unless otherwise specified in the test methods or in
of ABS plastic are characterized using short-term tests as
this specification.
defined in Specification D3965.
7.3 Test Specimens—Not less than 50 % of the test speci-
4.3 Hydrostatic Design Basis (HDB)—This specification
mens required for any pressure test shall have at least a part of
covers pipe made from material, which has been evaluated in
the marking in their central sections. The central section is that
accordance with Test Method D2837 where a pressure testing
portion of pipe, which is at least one pipe diameter away from
an end closure.
7.4 Dimensions and Tolerances—Use any length of pipe to
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de
determine the dimensions. Measure in accordance with Test
la Voie-Creuse, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://
www.iso.ch. Method D2122.
F2806 – 10
TABLE 1 Outside Diameters and Tolerances for Metric ABS Plastic Pipe
Nominal Pipe Size Average Outside Diameter, Tolerances (mm)
(NPS) D
O
(mm)
Average For Max and Min
(Out -of-Roundness)
12 12.0 +0.2 +0.5
16 16.0 +0.2 +0.5
20 20.0 +0.2 +0.5
25 25.0 +0.2 +0.5
32 32.0 +0.2 +0.5
40 40.0 +0.2 +0.5
50 50.0 +0.2 +0.6
63 63.0 +0.3 +0.8
75 75.0 +0.3 +0.9
90 90.0 +0.3 +1.1
110 110.0 +0.4 +1.4
125 125.0 +0.4 +1.5
140 140.0 +0.5 +1.7
160 160.0 +0.5 +2.0
180 180.0 +0.6 +2.2
200 200.0 +0.6 +2.4
225 225.0 +0.7 +2.7
250 250.0 +0.8 +3.0
280 280.0 +0.9 +3.4
315 315.0 +1.0 +3.8
TABLE 2 Wall Thicknesses and Tolerances for Metric ABS Plastic Pipe
Wall thicknesses (t) and tolerances for ABS plastic pipe (mm)
Nominal Pipe Size SDR 41 SDR 32.5 SDR 26 SDR 21 SDR 17 SDR 13.5 SDR 11 SDR 9
(NPS) min. tol min. tol min. tol min. tol min. tol min. tol min. tol min. to
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.