ASTM A249/A249M-18a
(Specification)Standard Specification for Welded Austenitic Steel Boiler, Superheater, Heat-Exchanger, and Condenser Tubes
Standard Specification for Welded Austenitic Steel Boiler, Superheater, Heat-Exchanger, and Condenser Tubes
ABSTRACT
This guide specifies standard specification for nominal-wall-thickness welded tubes and heavily cold worked welded tubes made from the austenitic steels with various grades intended for such use as a boiler, superheater, heat exchanger, or condenser tubes. Heat and product analysis shall conform to the requirements as to chemical composition for carbon, manganese, phosphorous, sulfur, silicon, chromium, nickel, molybdenum, nitrogen, copper, and others. All materials shall be furnished in the heat-treated condition in accordance with the required solution temperature and quenching method. When the final heat treatment is in a continuous furnace, the number of tubes of the same size and from the same heat in a lot shall be determined from the prescribed size of the tubes. The material shall conform to the prescribed tensile and hardness properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, and Rockwell hardness number. The steel shall undergo mechanical tests such as tension test, flattening test, flange test, reverse-bend test, hardness test, and hydrostatic or nondestructive electric test. The grain size of different grades of steel shall be determined in accordance with the test methods.
SCOPE
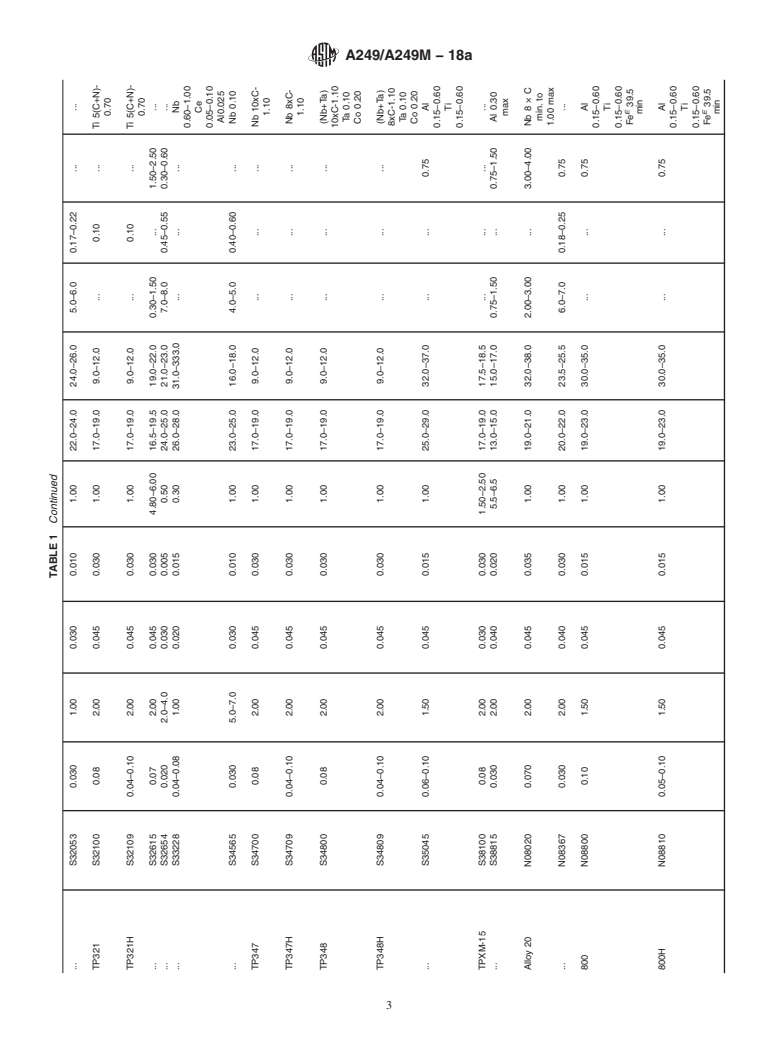
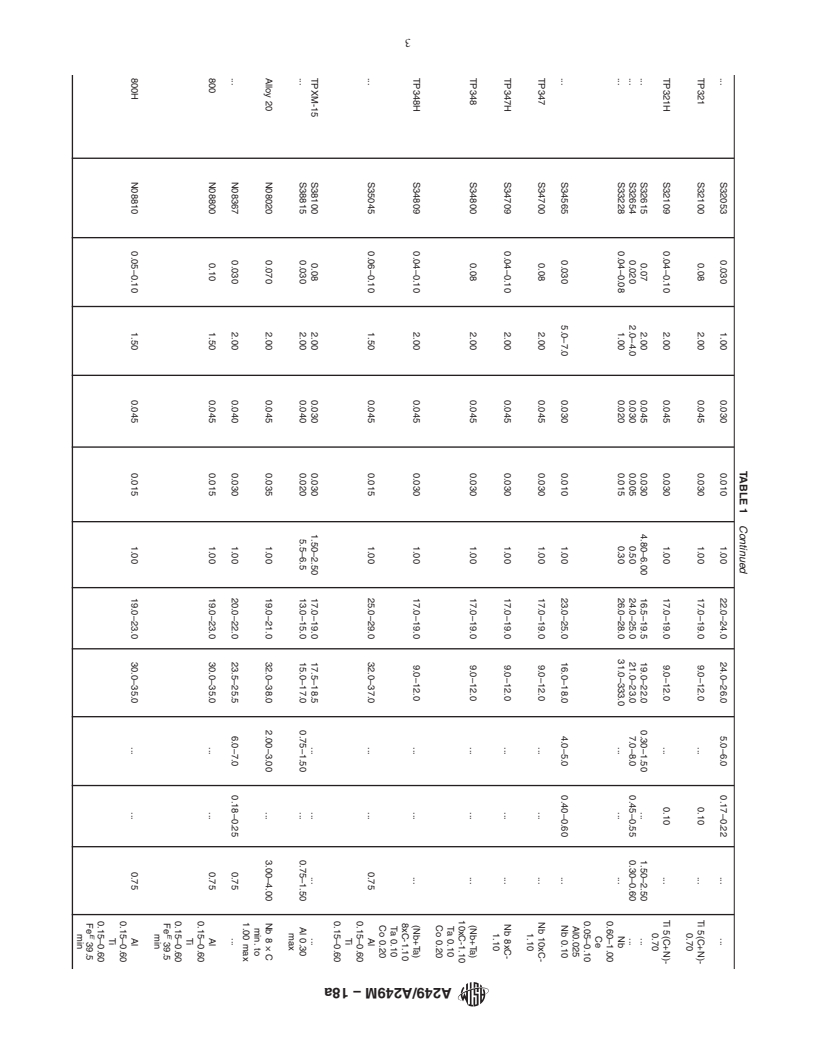
1.1 This specification2 covers nominal-wall-thickness welded tubes and heavily cold worked welded tubes made from the austenitic steels listed in Table 1, with various grades intended for such use as boiler, superheater, heat exchanger, or condenser tubes.
1.2 Grades TP304H, TP309H, TP309HCb, TP310H, TP310HCb, TP316H, TP321H, TP347H, and TP348H are modifications of Grades TP304, TP309S, TP309Cb, TP310S, TP310Cb, TP316, TP321, TP347, and TP348, and are intended for high-temperature service such as for superheaters and reheaters.
1.3 The tubing sizes and thicknesses usually furnished to this specification are 1/8 in. [3.2 mm] in inside diameter to 12 in. [304.8 mm] in outside diameter and 0.015 to 0.320 in. [0.4 to 8.1 mm], inclusive, in wall thickness. Tubing having other dimensions may be furnished, provided such tubes comply with all other requirements of this specification.
1.4 Mechanical property requirements do not apply to tubing smaller than 1/8 in. [3.2 mm] in inside diameter or 0.015 in. [0.4 mm] in thickness.
1.5 Optional supplementary requirements are provided and, when one or more of these are desired, each shall be so stated in the order.
1.6 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard. The inch-pound units shall apply unless the “M” designation of this specification is specified in the order.
1.7 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method described in the Supplementary Requirements of this specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. A specific warning statement is given in Supplementary Requirement S7, Note S7.1.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A249/A249M − 18a Used in USDOE-NE Standards
Standard Specification for
Welded Austenitic Steel Boiler, Superheater, Heat-
1
Exchanger, and Condenser Tubes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A249/A249M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* standard. The inch-pound units shall apply unless the “M”
2 designation of this specification is specified in the order.
1.1 This specification covers nominal-wall-thickness
1.7 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
welded tubes and heavily cold worked welded tubes made from
test method described in the Supplementary Requirements of
the austenitic steels listed in Table 1, with various grades
this specification. This standard does not purport to address all
intended for such use as boiler, superheater, heat exchanger, or
of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
condenser tubes.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
1.2 Grades TP304H, TP309H, TP309HCb, TP310H,
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
TP310HCb, TP316H, TP321H, TP347H, and TP348H are
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. A
modifications of Grades TP304, TP309S, TP309Cb, TP310S,
specific warning statement is given in Supplementary Require-
TP310Cb, TP316, TP321, TP347, and TP348, and are intended
ment S7, Note S7.1.
for high-temperature service such as for superheaters and
1.8 This international standard was developed in accor-
reheaters.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.3 The tubing sizes and thicknesses usually furnished to
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
1
this specification are ⁄8 in. [3.2 mm] in inside diameter to 12 in.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
[304.8 mm] in outside diameter and 0.015 to 0.320 in. [0.4 to
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
8.1 mm], inclusive, in wall thickness. Tubing having other
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
dimensions may be furnished, provided such tubes comply
2. Referenced Documents
with all other requirements of this specification.
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.4 Mechanical property requirements do not apply to
1
A262 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular
tubing smaller than ⁄8 in. [3.2 mm] in inside diameter or 0.015
Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels
in. [0.4 mm] in thickness.
A480/A480M Specification for General Requirements for
1.5 Optional supplementary requirements are provided and,
Flat-Rolled Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Plate,
when one or more of these are desired, each shall be so stated
Sheet, and Strip
in the order.
A1016/A1016M Specification for General Requirements for
1.6 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
Ferritic Alloy Steel, Austenitic Alloy Steel, and Stainless
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
Steel Tubes
SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each
E112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system
E213 Practice for Ultrasonic Testing of Metal Pipe and
shall be used independently of the other. Combining values
Tubing
from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the
E273 Practice for Ultrasonic Testing of the Weld Zone of
Welded Pipe and Tubing
1
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
Unified Numbering System (UNS)
A01.10 on Stainless and Alloy Steel Tubular Products.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2018. Published January 2019. Originally
3
approved in 1941. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as A249/A249M – 18. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
DOI: 10.1520/A0249_A0249M-18A. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specifi- Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
cation SA-249 in Section II of that Code. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A249/A249M − 1
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A249/A249M − 18 A249/A249M − 18a Used in USDOE-NE Standards
Standard Specification for
Welded Austenitic Steel Boiler, Superheater, Heat-
1
Exchanger, and Condenser Tubes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A249/A249M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
2
1.1 This specification covers nominal-wall-thickness welded tubes and heavily cold worked welded tubes made from the
austenitic steels listed in Table 1, with various grades intended for such use as boiler, superheater, heat exchanger, or condenser
tubes.
1.2 Grades TP304H, TP309H, TP309HCb, TP310H, TP310HCb, TP316H, TP321H, TP347H, and TP348H are modifications
of Grades TP304, TP309S, TP309Cb, TP310S, TP310Cb, TP316, TP321, TP347, and TP348, and are intended for high-
temperature service such as for superheaters and reheaters.
1
1.3 The tubing sizes and thicknesses usually furnished to this specification are ⁄8 in. [3.2 mm] in inside diameter to 12 in. [304.8
mm] in outside diameter and 0.015 to 0.320 in. [0.4 to 8.1 mm], inclusive, in wall thickness. Tubing having other dimensions may
be furnished, provided such tubes comply with all other requirements of this specification.
1
1.4 Mechanical property requirements do not apply to tubing smaller than ⁄8 in. [3.2 mm] in inside diameter or 0.015 in. [0.4
mm] in thickness.
1.5 Optional supplementary requirements are provided and, when one or more of these are desired, each shall be so stated in
the order.
1.6 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units
are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used
independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard. The
inch-pound units shall apply unless the “M” designation of this specification is specified in the order.
1.7 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method described in the Supplementary Requirements of this
specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. A specific warning statement is given in Supplementary Requirement S7, Note
S7.1.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A262 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels
A480/A480M Specification for General Requirements for Flat-Rolled Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip
A1016/A1016M Specification for General Requirements for Ferritic Alloy Steel, Austenitic Alloy Steel, and Stainless Steel
Tubes
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A01.10
on Stainless and Alloy Steel Tubular Products.
Current edition approved July 1, 2018Dec. 1, 2018. Published August 2018January 2019. Originally approved in 1941. Last previous edition approved in 20162018 as
A249/A249M – 16a.A249/A249M – 18. DOI: 10.1520/A0249_A0249M-18.10.1520/A0249_A0249M-18A.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specification SA-249 in Section II of that Code.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
------------
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.