ISO 406:1982
(Main)Technical drawings — Linear and angular tolerancing — Indications on drawings
Technical drawings — Linear and angular tolerancing — Indications on drawings
Dessins techniques — Tolérancement linéaire et angulaire — Indications sur les dessins
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
International Standard @ 406
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDiZATiON.MEXflYHAPOflHAR OPïAHH3AUHR no CTAHflAPTH3AUMH.ORGANlSATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Technical drawings - Linear and angular tolerancing -
L
Indications on drawings
Dessins techniques - Tolérancernent linéaire et angulaire - Indications sur les dessins
First edition - 1982-10-01
UDC 744.43 : 621.753.1 : 003.62 Ref. No. IS0 406-1982 (E)
w
-
8 Descriptors : technical drawings, graphic symbols, tolerances, mechanics, dimensional tolerances, angular tolerances.
r!
U
v, Price based on 3 pages
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
Foreword
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of
national standards institutes (IS0 member bodies). The work of developing Inter-
national Standards is carried out through IS0 technical committees. Every member
body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been set up has the
right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental
and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the IS0 Council.
International Standard IS0 406 was developed by Technical Committee ISOiTC 10,
Technical drawings, and was circulated to the member bodies in August 1981.
I? has been approved by the member bodies of the following countries :
Australia
France Poland
Austria Germany, F. R. Romania
Belgium Hungary South Africa, Rep. of
Canada India
Spain
China Italy Sweden
Czechoslovakia Switzerland
Japan
Denmark Korea, Rep. of
USA
Egypt, Arab Rep. of New Zealand USSR
Finland Norway
The member body of the following country expressed disapproval of the document on
technical grounds :
United Kingdom
This International Standard cancels and replaces IS0 Recommendation R 406-1964, of
which it constitutes an updated version.
0 International Organization for Standardization, 1982 O
Printed in Switzerland
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD IS0 406-1982 (E)
Technical drawings - Linear and angular tolerancing -
Indications on drawings
1 Scope and field of application
This International Standard specifies the indications of linear and angular tolerances on technical drawings.
Indicating such tolerances does not necessarily imply the use of any particular method of production, measurement or gauging.
L 2 References
IS0 129, Technical drawings - Dimensioning - General principles, definitions, methods of execution and special indications. 1
IS0 28611, IS0 system of limits and fits - Part 1 : Bases of standard tolerances, fundamental deviations and fits.2)
IS0 6433, Technical drawings - Item references.
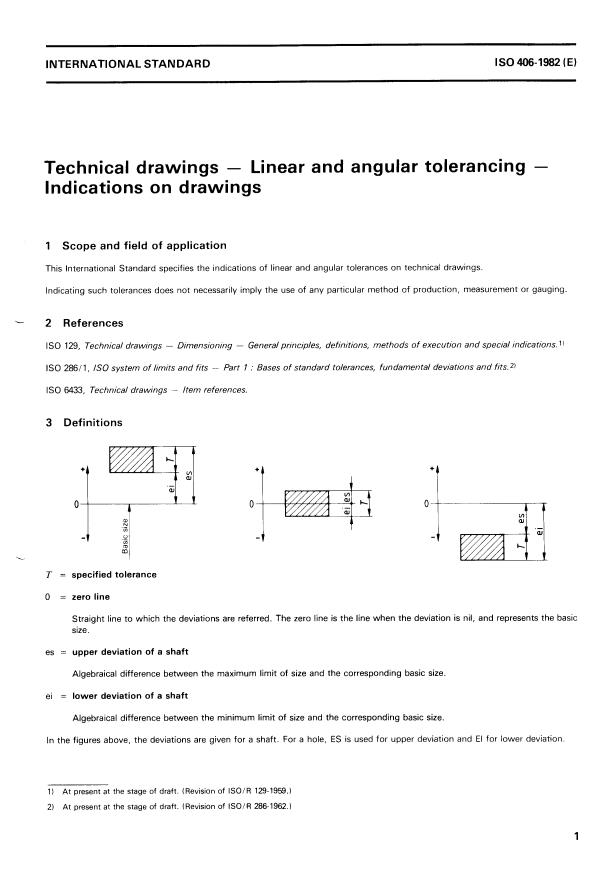
3 Definitions
+I
O
.-
-t -I
c-
.
f
T = specified tolerance
O = zero line
Straight line to which the deviations are referred. The zero line is the line when the deviation is nil, and represents the basic
size.
es = upper deviation of a shaft
Algebraical difference between the maximum limit of size and the corresponding basic size.
ei = lower deviation of a shaft
Algebraical difference between the minimum limit of size and the Corresponding basic size.
In the figures above, the deviations are given for a shaft.
...
Norme internationale @ 406
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION*MEX/lYHAPOLlHAR OPTAHHJAUHR no CTAH~APTU3A~klH@RGANISATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Dessins techniques - Tolérancement linéaire et
angulaire - Indications sur les dessins
Technical drawings - Linear and angular tolerancing - Indications on drawings
Première édition - 1982-10-01
CDU 744.43 : 621.753.1 : 003.62
Réf. no : IS0 406-1982 (FI
!k
Descripteurs : dessin industriel, symbole graphique, tolérance mécanique, tolérance de dimension, tolérance angulaire.
Prix basé sur 3 Pages
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
Avant-propos
L'ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d'organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I'ISO). L'élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I'ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I'ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I'ISO.
La Norme internationale IS0 406 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 10,
Dessins techniques, et a été soumise aux comités membres en août 1981,
Les comités membres des pays suivants l'ont approuvée :
Afrique du Sud, Rép. d' Égypte, Rép. arabe d' Nouvelle-Zélande
R. F.
Allemagne, Espagne Pologne
Australie Finlande
Roumanie
Autriche France Suède
Belgique Hongrie
Suisse
Canada Inde Tchécoslovaquie
Chine
Italie URSS
Corée, Rép. de Japon
USA
Danemark Norvège
Le comité membre du pays suivant l'a désapprouvée pour des raisons techniques :
Royaume-Uni
Cette Norme internationale annule et remplace la Recommandation ISOiR 406-1964,
dont elle constitue une mise à jour.
O Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1982 O
IrnDrimé en Suisse
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
~ ~~~
IS0 406-1982 (FI
NORM E I NTE R NATIONALE
Dessins techniques - Tolérancement linéaire et
angulaire - Indications sur les dessins
1 Objet et domaine d'application
La présente Norme internationale spécifie les indications de tolérances linéaires et angulaires à porter sur les dessins techniques.
L'indication de telles tolérances ne nécessite pas nécessairement l'emploi d'une méthode particulière de fabrication, de mesurage ou
de contrôle.
L
2 Références
IS0 129, Dessins techniques - Cotation - Principes généraux, définitions, méthodes d'exécution et indications spéciales. 1)
IS0 28611, Système IS0 de tolérances et d'ajustements - Partie 1 : Généralités, tolérances et écarts.2)
IS0 6433, Dessins techniques - Repères des éléments.
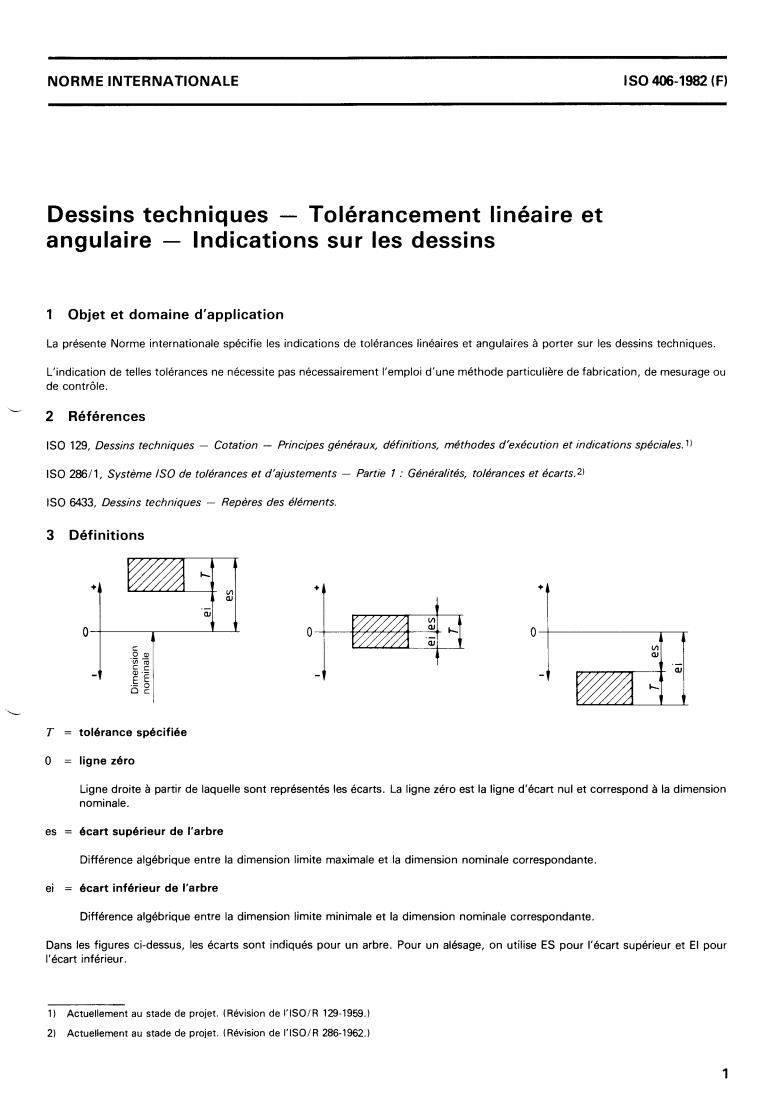
3 Définitions
O
-.+
T = tolérance spécifiée
O = ligne zéro
Ligne droite à partir de laquelle sont représentés les écarts. La ligne zéro est la ligne d'écart nul et correspond à la dimension
nominale.
es = écart supérieur de l'arbre
Différence algébrique entre la dimension limite maximale et la dimension nominale correspondante.
ei = écart inférieur de l'arbre
Différence algébrique entre la dimension limite minimale et la dimension nominale correspondante.
Dans les figures ci-dessus, les écarts sont indiqués pour un arbre. Pour un alésage, on utilise ES pour l'écart supérieur et El pour
l'écart inférieur.
1) Ac
...


Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.