ASTM B740-96
(Specification)Standard Specification for Copper-Nickel-Tin Spinodal Alloy Strip
Standard Specification for Copper-Nickel-Tin Spinodal Alloy Strip
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers copper-nickel-tin alloy strip. The following alloys are covered: Nominal Composition Weight % Copper Alloy UNS No. 2 Copper Nickel Tin C72700 85 9 6 C72900 77 15 8 C72650 87.5 7.5 5
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
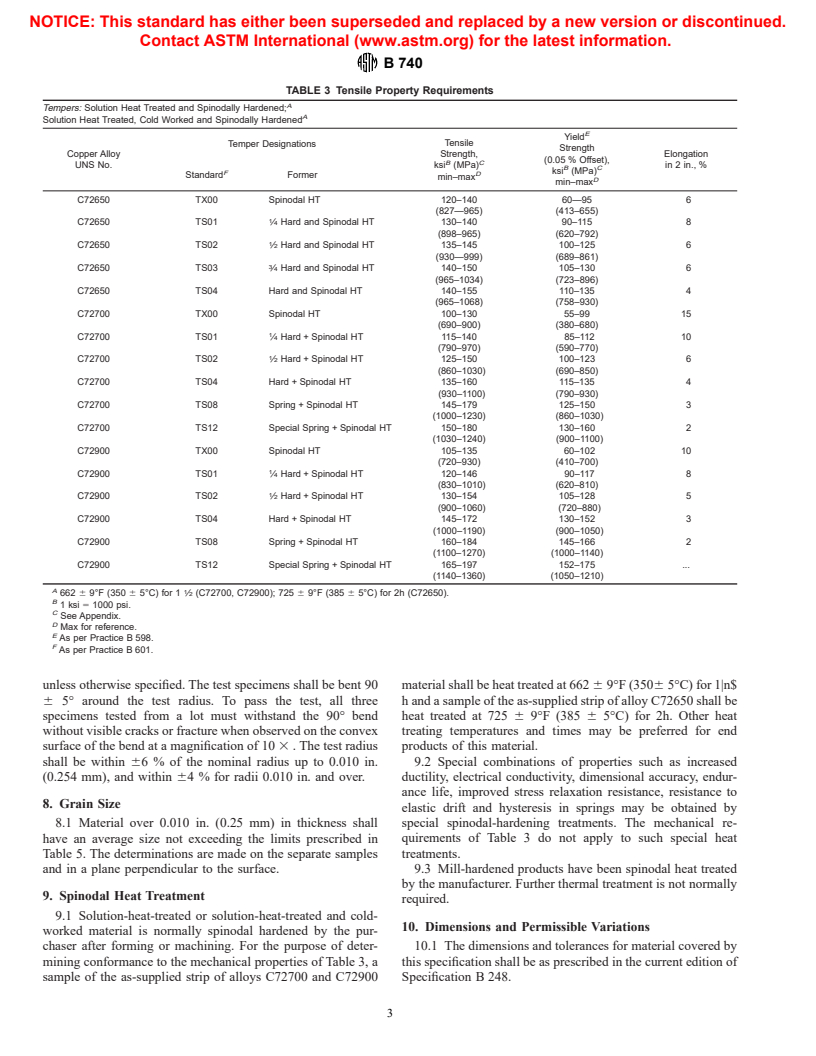
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: B 740 – 96
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Specification for
Copper-Nickel-Tin Spinodal Alloy Strip
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 740; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3.1.2 Copper Alloy UNS number (see 1.1),
3.1.3 Form of material: strip,
1.1 This specification covers copper-nickel-tin alloy strip.
2 3.1.4 Temper (see 5.1),
The following alloys are covered:
3.1.5 Dimensions: thickness and width, and length if appli-
Nominal Composition Weight %
Copper Alloy UNS No.
cable,
Copper Nickel Tin
C72700 85 9 6
3.1.6 How furnished: rolls or coils, stock lengths with or
C72900 77 15 8
without ends, specific lengths with or without ends,
C72650 87.5 7.5 5
3.1.7 Type of edge other than slit, for example, rounded
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
corners, rounded edges, or full-rounded edges (see Section 10).
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
3.1.8 Width and straightness tolerances, if different from
information only.
those required in Specification B 248 (see Section 10).
3.1.9 Special thickness tolerances if required (see Section
2. Referenced Documents
10),
2.1 The following documents of the issue in effect on date
3.1.10 Certification if required,
of material purchase form a part of this specification to the
3.1.11 Mill test report if required,
extent referenced herein:
3.1.12 Specification number and date, and
2.2 ASTM Standards:
3.1.13 Special tests or exceptions, if any.
B 248 Specification for General Requirements for Wrought
3.2 When material is purchased for agencies of the U.S.
Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled
Government, this shall be specified in the contract or purchase
Bar
order, and the material shall conform to the Supplementary
B 598 Practice for Determining Offset Yield Strength in
Requirements as defined in the current issue of Specification
Tension for Copper Alloys
B 248.
B 601 Practice for Temper Designations for Copper and
Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
4. Chemical Composition
E 3 Methods of Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
4.1 The material shall conform to the requirements specified
E 8 Test Methods of Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
in Table 1.
E 290 Test Method for Semi-Guided Bend Test for Ductility
4.2 These specification limits do not preclude the presence
of Metallic Materials
of other elements. Limits for unnamed elements may be
E 527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS)
established by agreement between manufacturer or supplier
and purchaser. Copper may be given as remainder and taken as
3. Ordering Information
the difference between the sum of all elements analyzed and
3.1 Orders for materials under this specification should
100 %. When all the elements in the table including copper are
include the following information:
analyzed, their sum shall be 99.7 % min.
3.1.1 Quantity,
5. Temper
This specification is under the ASTM Committee B-5 on Copper and Copper 5.1 The standard tempers of material are as designated in
Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.01 on Plate, Sheet, and
Table 2, Table 3, and Table 4. Tempers are as follows: TB00
Strip.
(solution heat treated), or with varying additional degrees of
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 1996. Published November 1996. Originally
cold rolling TD01 to TD12 (solution heat treated with varying
published as B 740 – 84. Last previous edition B 740 – 95.
The UNS system for copper alloys (see Practice E 527) is a simple expansion
degrees of cold rolling); spinodal hardened from these appro-
of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition of a prefix
priate tempers TX00 or TS01 to TS12 (spinodal hardened from
“C” and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate composition
the appropriate solution heat treated or solution heat treated
variations of the base alloy.
and cold rolled temper); or: Mill Hardened TM00 to TM08
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
(mill hardened).
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.01.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
B 740
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Composition, %
Copper Copper, Nickel, Manga- Nio- Magne-
A A A
Previous Lead , Iron , Zinc ,
A A A
Alloy UNS incl incl Tin nese , bium , sium ,
Designation max max max
No. Silver Cobalt max max max
C72650 Cu-7.5Ni-5Sn remainder 0.01 0.50 0.20 7.0–8.0 4.5–5.5 0.10 . .
C72700 Cu-9Ni-6Sn remainder 0.02 0.50 0.50 8.5–9.5 5.5–6.5 0.30 0.10 0.15
C72900 Cu-15Ni-8Sn remainder 0.02 0.50 0.50 14.5–15.5 7.5–8.5 0.30 0.10 0.15
A
The total of the elements Pb, Fe, Zn, Mn, Cb, and Mg not to exceed 0.7 %.
TABLE 2 Tensile Property Requirements
Tempers: Solution Heat-Treated
Solution Heat-Treated and Cold Worked
D
Yield
Tensile
Temper Designations
Strength
Copper Alloy Strength, Elongation
(0.05 % Offset),
A B
UNS No. ksi (MPa) in 2 in., %
A B
ksi (MPa)
E
C
Standard Former
min–max
C
min–max
C72650 TB00 Solution HT 55–70 21—32 32
(379—482) (145–220)
C72650 TD01 ⁄4 Hard 60–75 45–60 18
(413–517) (310–413)
C72650 TD02 ⁄2 Hard 75—85 55–75 5
(517—586) (379–516)
C72650 TD03 ⁄4 Hard 80–90 68–82 4
(551–620) (468–565)
C72650 TD04 Hard 85–95 77–90 2
(586–655) (530–620)
C72700 TB00 Solution HT 60–80 23–33 30
(410–550) (160–230)
C72700 TD01 ⁄4 Hard 72–95 48–64 12
(500–660) (330–440)
C72700 TD02 ⁄2 Hard 82–108 57–80 6
(570–740) (390–550)
C72700 TD04 Hard 97–125 77–100 3
(670–860) (530–690)
C72700 TD08 Spring 110–140 95–115 2
(760–970) (660–790)
C72700 TD12 Special Spring 115–150 105–125 .
(790–1030) (720–860)
C72900 TB00 Solution HT 64–85 24–40 32
(440–590) (170–280)
C72900 TD01 ⁄4 Hard 74–100 50–66 18
(510–690) (340–460)
C72900 TD02 ⁄2 Hard 85–110 65–84 8
(590–760) (450–580)
C72900 TD04 Hard 100–130 85–108 .
(690–900) (590–740)
C72900 TD08 Spring 122–145 100–125 .
(840–1000) (690–860)
C72900 TD12 Special Spring 135–155 110–130 .
(930–1070) (760–900)
A
1 ksi 5 1000 psi.
B
See Appendix.
C
Max for reference.
D
As per Practice B 598.
E
As per Practice B 601.
5.2 Special or nonstandard tempers are available and are 7. Bend Test Requirements
subject to agreement between supplier or manufacturer and
7.1 The bend test is a method for evaluating the ductility of
purchaser.
mill-hardened copper-nickel-tin spinodal alloy strip in thick-
nesses of 0.004 to 0.020 in. (0.102 to 0.508 mm), inclusive.
6. Tensile Property Requirements
7.1.1 Material in tempers TM00, TM02, TM04, and TM06
6.1 The solution heat-treated or solution heat-treated and
shall conform to the bend test requirements specified in Table
cold-worked material shall conform to the tensile property
4 when tested in accordance with 7.2.
requirements specified in Table 2.
1 1
6.2 The spinodal heat-treated material shall conform to the 7.2 Three specimens, ⁄2 6 ⁄16 in. (12.706 1.59 mm) in
tensile property requirements specified in Table 3. Spinodal width of any convenient length, with the rolling direction
heat-treatment parameters are given in 9.1. perpendicular to the ⁄2 in. dimension shall be prepared and
6.3 The mill-hardened material shall conform to the tensile tested in accordance with Test Method E 290. The axis of the
property requirements specified in Table 4. bend shall be at an angle of 90° to the direction of rolling
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
B 740
TABLE 3 Tensile Property Requirements
A
Tempers: Solution Heat Treated and Spinodally Hardened;
A
Solution Heat Treated, Cold Worked and Spinodally Hardened
E
Yiel
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.