ASTM D2740-89
(Specification)Specification for Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Plastic Tubing (Withdrawn 1989)
Specification for Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Plastic Tubing (Withdrawn 1989)
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
ASTM D27L)û 87 m 0757530 0027034 7 =
/-----
([Tb Designation: D 2740 - 89
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
1916 Race St., Philadelphia, Pa. i9103
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Sfandards. Copyright ASTM
If not listed in the currentcombined index. will appear in the next edition.
Standard Specification for
Poly(Viny1 Chloride) (PWC) Plastic Tubing’
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2740; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parenthem indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
F 412 Definitions of Terms Relating to Plastic Piping
1. Scope
Systems3
1.1 This specification covers poly(viny1 chloride) (PVC)
2.2 NSF Standard:
tubing pressure rated for water (Appendix). Included are
Standard No. 14 for Plastic Piping Components and
criteria for classifying PVC plastic tubing materials and PVC
Related Materials4
plastic tubing, and requirements and test methods for
materials, workmanship, dimensions, sustained pressure, 3, Definitions
burst pressure, flattening, and extrusion quality. Methods of
3.1 General-Definitions are in accordance with Defini-
marking are also given.
tions D 883 or F 412 and abbreviations are in accordance
1.2 The values in parentheses are for information pur-
with Abbreviations D 1600, unless otherwise indicated. The
poses only.
abbreviation for poly(viny1 chloride) plastic is PVC.
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to
hydrostatic design stress-the estimated maximum
3.2
the test method portion, Section 7, of this specification. This
tensile stress in the wall of the tubing in the circumferential
standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and
orientation due to internal hydrostatic water pressure that
equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of
can be applied continuously with a high degree of certainty
the safety problems associated with its use. Il is the responsi-
that failure of the tubing will not occur.
bility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate
3.3 pressure rating (PR)-the estimated maximum pres-
safity and health practices and determine the applicability of
sure that water in the tubing can exert continuously with a
regulatory limitations prior to use.
high degree of certainty that failure of the tubing will not
occur,
3.4 relation bet ween dimensions, hydrostatic design stress,
and pressure rating-the following expression, commonly
2. Referenced Documents
known as the IS0 eq~ation,~ is used in this specification to
relate dimensions, hydrostatic design stress, and pressure
2.1 ASTM Standards:
rating:
D 6 18 Methods of Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
2SJP = (Ddî) - 1 ûì 2SJP = R - 1
Insulating Materials for Testing2
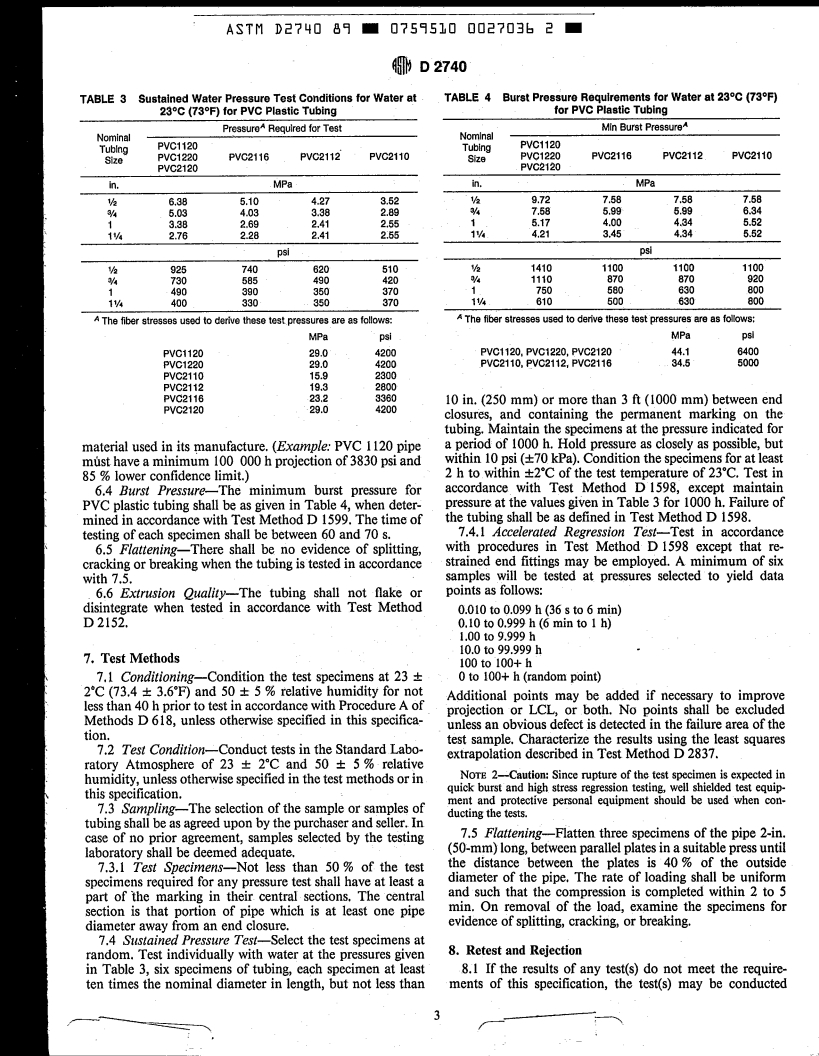
D 883 Definitions of Terms Relating to Plastics2i3
where:
D 1598 Test Method for Time-to-Failure of Plastic Pipe
S = hydrostatic design stress, MPa (or psi),
Under Constant Internal Pressure3
P = pressure rating, MPa (or psi),
D 1599 Test Method for Short-Time HydrauIic Failure
Do = average outside diameter, mm (or in.),
Pressure of Plastic Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings3
t = minimum wall thickness, mm (or in-), and
D i 600 Abbreviations of Terms Relating to
R = standard thermoplastic pipe dimension ratio (Do/t for
D 1784 Specification for Rigid Poly(Viny1 Chloride)
PVC tubing).
(PVC) Compounds and Chlorinated Poly(Viny1 Chlo-
3.5 standard dimension ratio (SDR)-the average outside
ride) (CPVC) Compounds3
diameter in inches divided by the minimum wall thickness in
D 2 122 Test Method of Determining Dimensions of Ther-
inches, rounded to the nearest 0.5
moplastic Pipe and Fittings’
3.6 standard thermoplastic tubing materials designation
D2152 Test Method for Degree of Fusion of Extruded
code-the tubing materials designation code shall consist of
Poly(Viny1 Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Molded Fittings
the abbreviation PVC for the type of plastic, followed by the
by Acetone Immersion3
ASTM type and grade in Arabic numerals and the hydro-
D 2837 Test Method for Obtaining Hydrostatic Design
static design stress in units of 100 psi with any decimal
Basis for Thermoplastic Pipe Materials3
figures dropped. Where the hydrostatic design code contains
less than two figures, a cipher shall be used before the
number. Thus a complete material code consists of three
I This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-17 on
Plastic Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.25 on
(Vinyl Based) Pipe.
4Available from the National Sanitation Foundation, P.O. Box 1468, Ann
Current edition approved Feb. 24, 1989. Published May 1989. Onginally
Arbor, MI 48106.
published as D 2740 - 68. Last previous edition D 2740 - 88.
See IS0 R161-1960, Pipes-of Plasti
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.