ASTM B23-00(2005)
(Specification)Standard Specification for White Metal Bearing Alloys (Known Commercially as "Babbitt Metal")
Standard Specification for White Metal Bearing Alloys (Known Commercially as "Babbitt Metal")
ABSTRACT
This specification deals with eight typical white metal bearing alloys, in bar or ingot form, known commercially as "Babbitt metal." Covered in this specification are tin-based alloys, namely, UNS-L13910 (alloy no. 1), UNS-L13890 (alloy no. 2), UNS-L13840 (alloy no. 3), and UNS-L13870 (alloy no. 11); and lead-based alloys, namely, UNS-L53585 (alloy no. 7), UNS-L53565 (alloy no. 8), UNS-L53346 (alloy no. 13), and UNS-L53620 (alloy no. 15). Materials shall be manufactured in accordance with such practice as to obtain the chemical composition, weight, and dimensions as prescribed herein.
SCOPE
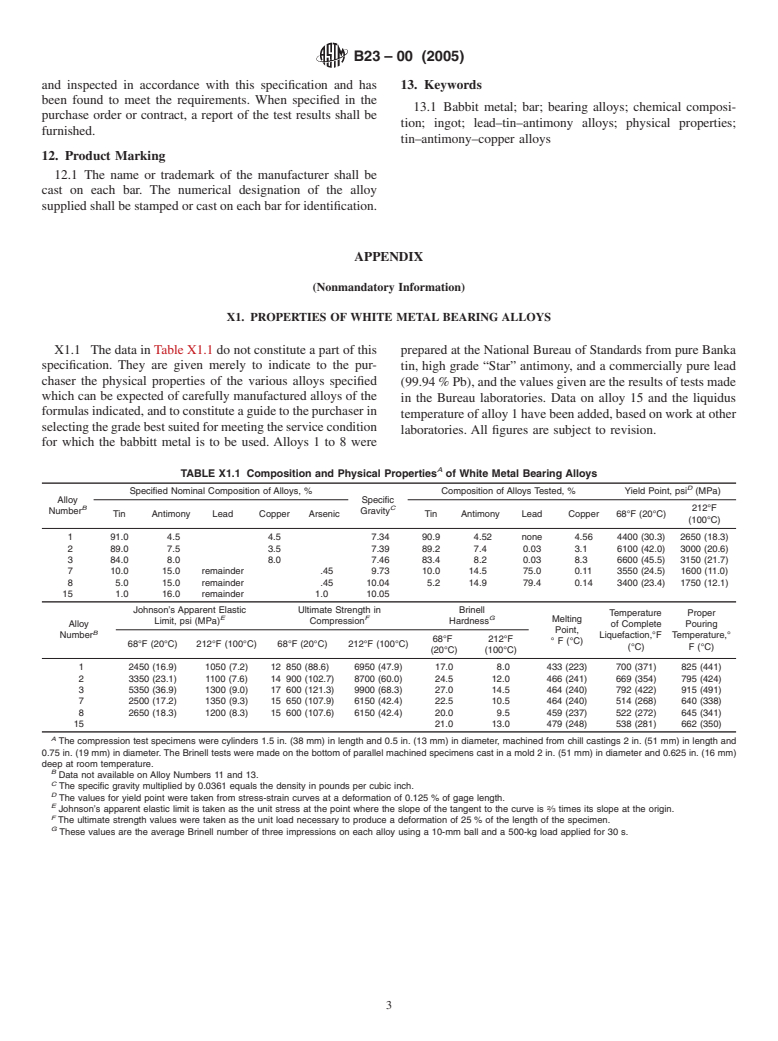
1.1 This specification covers eight typical white metal bearing alloys, in bar or ingot form, known commercially as "babbitt metal." The alloys are specified, covering the range commercially used, and are designated by the alloy numbers shown in .
1.2 &inch-pound-units;
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to become familiar with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for this product/material as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate safety and health practices, and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: B23 – 00 (Reapproved 2005)
Standard Specification for
White Metal Bearing Alloys
(Known Commercially as “Babbitt Metal”)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B23; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3.1.2 Form and nominal weight of individual bars,
3.1.3 Quantity,
1.1 This specification covers eight typical white metal
3.1.4 Alloy number,
bearing alloys, in bar or ingot form, known commercially as
3.1.5 Inspection required (Section 9),
“babbitt metal.” The alloys are specified, covering the range
3.1.6 Certification required (Section 10),
commercially used, and are designated by the alloy numbers
3.1.7 Marking required (Section 11), and
shown in Table 1.
3.1.8 ASTM designation and year of issue.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
4. Materials and Manufacture
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
4.1 The bars or ingots shall be made in accordance with
and are not considered standard.
such practice as to obtain the chemical composition, weight,
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
and dimensions as prescribed in this specification.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.2 The bars or ingots shall be as uniform in quality as
responsibility of the user of this standard to become familiar
practicable.
with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for this product/material
5. Chemical Composition
as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate
5.1 Thealloyscoveredbythisspecificationshallconformto
safety and health practices, and determine the applicability of
the requirements for chemical composition prescribed in Table
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.
2. Referenced Documents 5.2 By agreement between manufacturer and purchaser,
2 analysis may be required and limits established for elements
2.1 ASTM Standards:
not specified in Table 1.
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
Determine Conformance with Specifications
6. Dimensions and Weights
E57 Methods for Chemical Analysis of White Metal Bear-
3 6.1 The babbitt shall be furnished in bars of a convenient
ing Alloys
weightandsizeforhandling.Unlessotherwiseagreedupon,no
3. Ordering Information unnotched bar shall exceed 10 lb (4.5 kg) in weight, nor
notched bar exceed 15 lb (6.8 kg).
3.1 Orders for materials under this specification shall in-
6.2 By mutual agreement, babbitt may be furnished in small
clude the following information:
round bars about 3.5 in. (90 mm) in diameter.
3.1.1 Name of material (white metal bearing alloy),
7. Sampling
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B02 on
7.1 Three bars shall be selected to represent a shipment of
Nonferrous Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
less than 1000 lb (450 kg), five bars to represent a shipment of
B02.02 on Refined Lead, Tin, Antimony, and Their Alloys.
1000 lb to 10 000 lb (4500 kg) inclusive, and ten bars to
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2005. Published November 2005. Originally
approved in 1926. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as B23 – 00. DOI: represent a shipment of over 10 000 lb to one carload.
10.1520/B0023-00R05.
7.2 Saw cuts shall be made at points in the bars as indicated
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
in Fig. 1. No lubricants shall be used for sawing. The sawings
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
shallbecarefullytreatedwithamagnettoremoveanyparticles
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
of steel introduced in taking the sample.
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
B23 – 00 (2005)
A
TABLE 1 Chemical Composition —wt% (range or maximum)
Alloy Number
Tin Base Lead Base
Chemical
Composition, %
1 2 3 11 7 8 13 15
UNS—L13910 UNS—L13890 UNS—L13840 UNS—L13870 UNS—L53585 UNS—L53565 UNS—L53346 UNS—L53620
B B B B
Tin remainder remainder remainder remainder 9.3–10.7 4.5–5.5 5.5–6.5 0.8–1.2
Antimony 4.0–5.0 7.0–8.0 7.5–8.5 6.0–7.5 14.0–16.0 14.0–16.0 9.5–10.5 14.5–17.5
B B B B
Lead 0.35 0.35 0.35 0.50 remainder remainder remainder remainder
Copper 4.0–5.0 3.0–4.0 7.5–8.5 5.0–6.5 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.6
Iron 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.10
Arsenic 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.30–0.60 0.30–0.60 0.25 0.8–1.4
Bismuth 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.10
Zinc 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005
Aluminum 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005
Cadmium 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05
Total named 99.80 99.80 99.80 99.80
elements,
min
A
Alloy Number 9 was discontinued in 1946 and numbers 4, 5, 6, 10, 11, 12, 16, and 19 were discontinued in 1959. A new number 11, similar to SAE Grade 11, was
added in 1966.
B
To be determined by difference.
NOTE 1—With notched bars the saw cuts shall be distributed along the bar in a similar manner, avoiding if possible, saw cuts directly through a notch.
FIG. 1 Method of Sampling Unnotched Bar
7.3 When babbitt is furnished in bars under 5 lb (2.3 kg) in 8.3 For purposes of compliance with the specified chemical
weight, three bars shall be considered the equivalent of one bar composition limits, the reported analysis shall be rounded to
(6.1) for sampling purposes. These may be remelted in a clean the nearest unit in the right hand place of figures used in
utensil at a temperature slightly above the liquidus point of the expressing the limiting value, in accordance with the rounding
alloy, mixed thoroughly, poured into a cold mold forming a method of Practice E29.
convenient size bar, and then handled in accordance with 6.2.
9. Inspection
7.4 Sawings,thoroughlymixed,shallbeseparatedintothree
equal portions, each of which shall be placed in a sealed 9.1 Inspection of the material shall be made as agreed upon
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.