ASTM B193-02
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Resistivity of Electrical Conductor Materials
Standard Test Method for Resistivity of Electrical Conductor Materials
ABSTRACT
This test method covers the determination of the electrical resistivity of metallic electrical conductor material. Weight resistivity accuracy may be adversely affected by possible inaccuracies in the assumed density of the conductor. The definition of resistivity and the equations for calculating volume resistivity and weight resistivity are given. Resistance shall be measured using an apparatus with a circuit configuration and instrumentation that has a resistance measurement capability of the prescribed accuracy. The test specimen requirements and the test procedure including: (1) determination of dimensions (such as length and cross-section), weight, and density, and (2) resistance measurement are detailed. The formula for calculating the corrected resistance, when the measurement is made at any temperature other than a reference temperature, is given. No statement of precision has been made and no work has been planned to develop such a statement. This test method has no bias because the value for resistivity is determined solely in terms of this test method.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the electrical resistivity of metallic electrical conductor material. It provides for an accuracy of ±0.30% on test specimens having a resistance of 0.00001 [omega] (10 µ[omega]) or more. Weight resistivity accuracy may be adversely affected by possible inaccuracies in the assumed density of the conductor.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:B 193–02
Standard Test Method for
1
Resistivity of Electrical Conductor Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 193; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
5
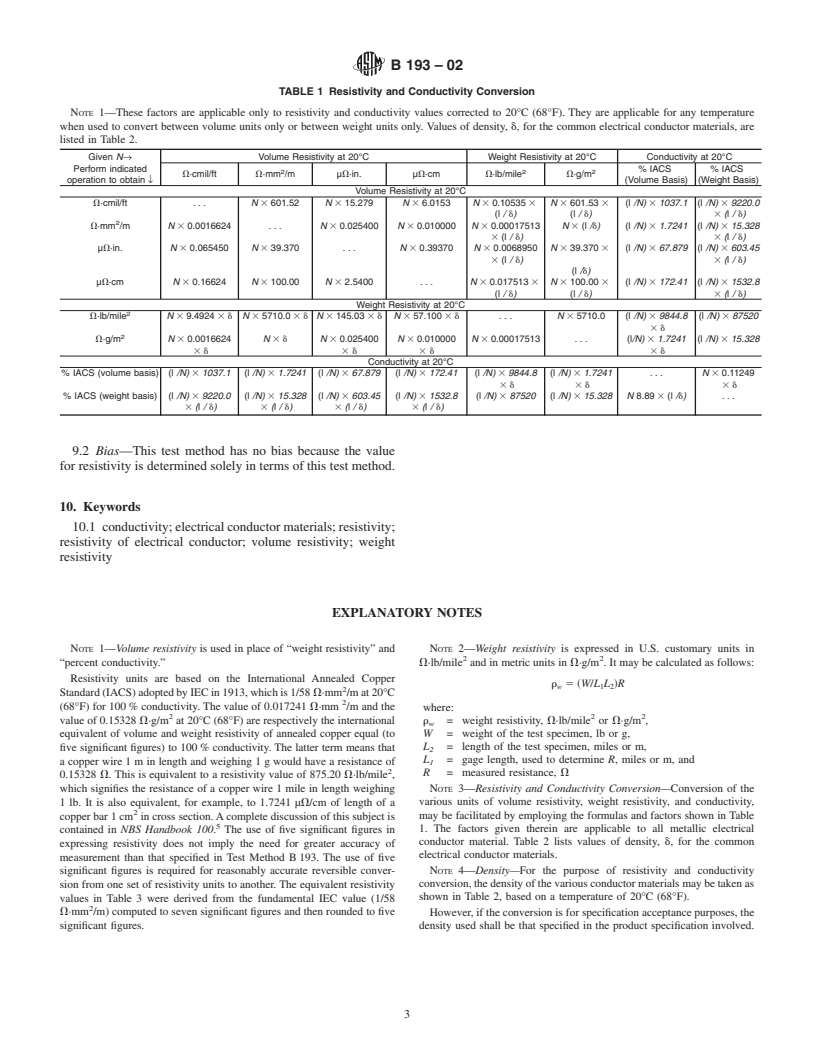
1. Scope NBS Handbook 100— Copper Wire Tables
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the elec-
3. Resistivity
trical resistivity of metallic electrical conductor material. It
3.1 Resistivity (Explanatory Note 1) is the electrical resis-
provides for an accuracy of 60.30 % on test specimens having
tance of a body of unit length, and unit cross-sectional area or
a resistance of 0.00001 V (10 µV) or more. Weight resistivity
unit weight.
accuracy may be adversely affected by possible inaccuracies in
3.2 Volume Resistivity is commonly expressed in ohms for
the assumed density of the conductor.
a theoretical conductor of unit length and cross-sectional area;
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
in inch-pound units in V·cmil/ft and in acceptable metric units
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
2
in V·mm /m. It may be calculated by the following equation:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- r 5 ~A/L!R
v
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
where:
2
r = volume resistivity, V·cmil/ft or V·mm /m,
2. Referenced Documents v
2
A = cross-sectional area, cmil or mm ,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
L = gage length, used to determine R,ftorm,and
A 111 Specification for Zinc-Coated (Galvanized) “Iron”
R = measured resistance, V.
2
Telephone and Telegraph Line Wire
3.3 WeightResistivity is commonly expressed in ohms for a
A 326 Specification for Zinc-Coated (Galvanized) High
theoretical conductor of unit length and weight. The method
3
Tensile Steel Telephone and Telegraph Line Wire
for calculating weight resistivity, based on resistance, length,
4
B 9 Specification for Bronze Trolley Wire
and weight measurements, of a test specimen is given in
B 105 Specification for Hard-Drawn Copper Alloy Wires
Explanatory Note 2.
4
for Electric Conductors
B 298 Specification for Silver-Coated Soft or Annealed
4. Apparatus
4
Copper Wire
4.1 Resistance shall be measured with a circuit configura-
B 355 Specification for Nickel-Coated Soft or Annealed
tion and instrumentation that has a resistance measurement
4
Copper Wire
capability of 60.15 % accuracy.
B 415 Specification for Hard-Drawn Aluminum-Clad Steel
4
Wire
5. Test Specimen
4
B 566 Specification for Copper-Clad Aluminum Wire
5.1 The test specimen may be in the form of a wire, strip,
B 800 Specification for 8000 Series Aluminum Alloy Wire
rod, bar, tube, or shape. It shall be of uniform cross section
for Electrical Purposes—Annealed and Intermediate Tem-
throughout its length within 60.75 % of the cross-sectional
4
pers
area. Wherever possible it shall be the full cross section of the
2.2 NIST Document:
material it represents, if the full cross section is such that the
uniformity of the cross-sectional area can be accurately deter-
1
mined.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B01 on
Electrical Conductors and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B01.02 on 5.2 The test specimen shall have the following characteris-
Methods of Test and Sampling Procedure.
tics:
Current edition approved Apr. 10, 2002. Published April 2002. Originally
published as B 193 – 44 T. Last previous edition B 193 – 01.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.06.
3 5
Discontinued; see 1989 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.06. Available from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST),
4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.03. Gaithersburg, MD 20899.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B193–02
5.2.1 A resistance of at least 0.00001 V (10 µV) in the test detected with the galvanometer. To eliminate errors due to
length between potential contacts, contact potential, take two readings, one direct and one with
5.2.2 A test length of at least 1 ft or 300 mm, current reversed, in direct succession. Check tests are recom-
5.2.3 A diameter, thickness, width, or other dimension mended whereby the specimen is turned end for end, and the
suitable to the limitations of the resistance measuring instru- test repeated. Surface cleaning of the specimen at current and
ment, potential contact points may be necessary to obtain
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.