ASTM D6230-21
(Practice)Standard Practices for Monitoring Earth or Structural Movement Using Inclinometers
Standard Practices for Monitoring Earth or Structural Movement Using Inclinometers
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 An inclinometer is a deformation monitoring system, which uses a grooved pipe or casing with internal longitudinal grooves aligned with the anticipated direction of movement, installed in either a soil/rock mass or a geotechnical structural element. The inclinometer casing can be surveyed with a single traversing probe or with an array of in-place inclinometer (IPI) gauges connected to a data logger. The measurement and calculation of deformation normal to the axis of the inclinometer casing is done by passing a probe along the length of this pipe or placement of a sensor array, guided by the internal grooves. The probe or sensor array measures the inclination of the pipe, usually in two orthogonal directions 90 degrees apart (X- and Y direction) with respect to the axis of the casing (Z-direction, usually the line of gravity). Measurements are converted to distances using trigonometric functions. Successive surveys compared with an initial survey give differences in position and indicate deformation normal to the axis of the inclinometer casing. In most cases the inclinometer casing is installed in a near-vertical hole, and the measurements indicate subsurface horizontal deformation. In some cases, the inclinometer casing is installed horizontally, and the measurements indicate vertical deformation.
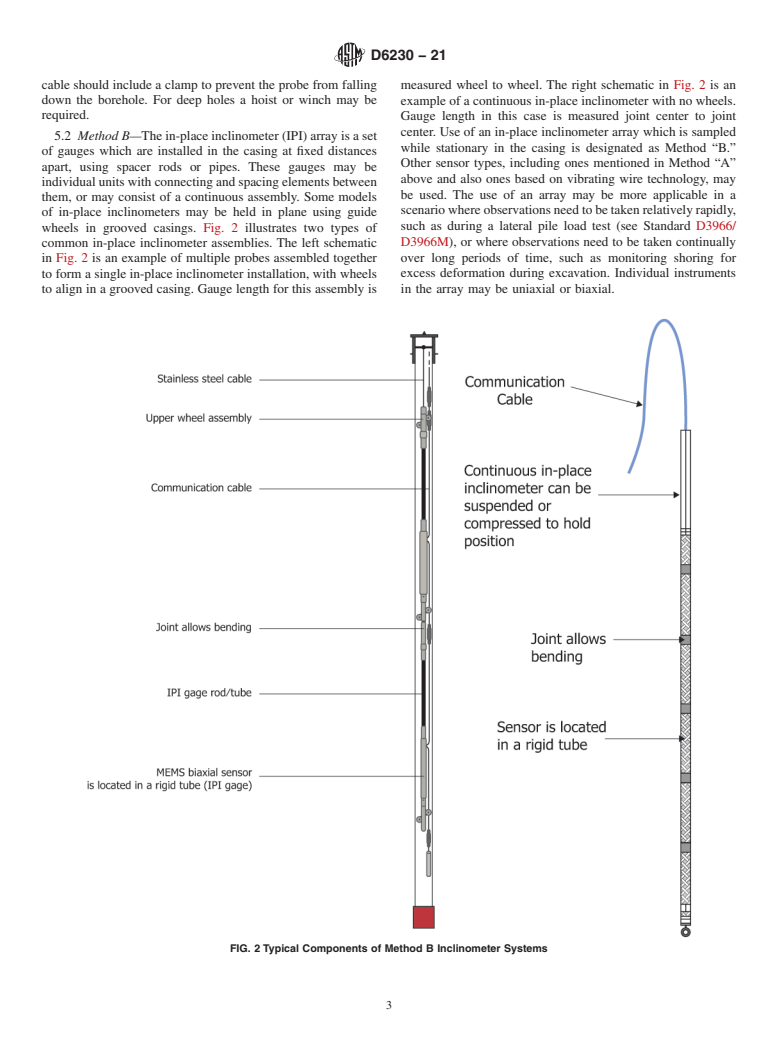
4.2 Inclinometers are also called slope inclinometers or slope indicators. Typical applications include measuring the rate and direction of landslide movement and locating the zone of shearing, monitoring the magnitude and rate of horizontal movements for embankments and excavations, monitoring the settlement and lateral spread beneath tanks and embankments, and monitoring the deflection of bulkheads, piles or structural walls.
Note 1: The precision of this standard is dependent on the competence of the personnel performing it and the suitability of the equipment and facilities used. Agencies that meet the criteria of Practice D3740 are generally considered cap...
SCOPE
1.1 This standard covers the use of inclinometers to monitor the internal movement of ground, or lateral movement of subsurface structures. The standard covers types of instruments, installation procedures, operating procedures, and maintenance requirements. The standard also provides formulae for data reduction.
1.2 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the guidelines for significant digits and rounding established in Practice D6026 unless superseded by this standard.
1.2.1 The procedures used to specify how data are collected, recorded or calculated in this standard are regarded as the industry standard. In addition, they are representative of the significant digits that generally should be retained. The procedures used do not consider material variation, purpose for obtaining the data, special purpose studies, or any considerations for the user’s objectives; it is common practice to increase or reduce significant digits of reported data to be commensurate with these considerations. It is beyond the scope of this standard to consider significant digits used in analytical methods for engineering design.
1.3 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for information only. Reporting of test results in units other than SI shall not be regarded as nonconformance with this standard.
1.4 This standard offers an organized collection of information or a series of options and does not recommend a specific course of action. This document cannot replace education or experience and should be used in conjunction with professional judgment. Not all aspects of this standard may be applicable in all circumstances. This ASTM standard is not intended to represent or replace the standard of care by which the adequacy of a given professional service must be judged, nor should this document be applied without consideration of a project’s man...
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6230 − 21
Standard Practices for
Monitoring Earth or Structural Movement Using
1
Inclinometers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6230; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* unique aspects. The word “Standard” in the title of this
document means only that the document has been approved
1.1 This standard covers the use of inclinometers to monitor
through the ASTM consensus process.
the internal movement of ground, or lateral movement of
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
subsurface structures. The standard covers types of
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
instruments, installation procedures, operating procedures, and
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
maintenance requirements. The standard also provides formu-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
lae for data reduction.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.2 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
guidelines for significant digits and rounding established in
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
Practice D6026 unless superseded by this standard.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
1.2.1 Theproceduresusedtospecifyhowdataarecollected,
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
recorded or calculated in this standard are regarded as the
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
industry standard. In addition, they are representative of the
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
significant digits that generally should be retained. The proce-
dures used do not consider material variation, purpose for
2. Referenced Documents
obtaining the data, special purpose studies, or any consider-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ations for the user’s objectives; it is common practice to
D653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
increase or reduce significant digits of reported data to be
Fluids
commensuratewiththeseconsiderations.Itisbeyondthescope
D3740 Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies
of this standard to consider significant digits used in analytical
Engaged in Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock as
methods for engineering design.
Used in Engineering Design and Construction
1.3 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
D3966/D3966M Test Methods for Deep Foundations Under
as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are
Lateral Load
for information only. Reporting of test results in units other
D6026 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Geotechnical
than SI shall not be regarded as nonconformance with this
Data
standard.
D7299 Practice for Verifying Performance of a Vertical
1.4 This standard offers an organized collection of informa-
Inclinometer Probe
tion or a series of options and does not recommend a specific
course of action. This document cannot replace education or
3. Terminology
experienceandshouldbeusedinconjunctionwithprofessional
3.1 For definitions of common technical terms used in this
judgment. Not all aspects of this standard may be applicable in
standard, refer to Terminology D653.
all circumstances. This ASTM standard is not intended to
3.2
representorreplacethestandardofcarebywhichtheadequacy
3.3 inclinometer casing, n—a (typically segmented) pipe or
of a given professional service must be judged, nor should this
casing with grooves specific for the type of inclinometer being
document be applied without consideration of a project’s many
used.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D18 on Soil and
Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.23 on Field Instrumen-
2
tation. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved June 1, 2021. Published June 2021. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as D6230 – 13. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D6230-21. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6230 − 21
3.3.1 Discussion—Casing is typically made of plastic, alu- installed in a near-vertical hole, and the measurements indicat
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6230 − 13 D6230 − 21
Standard Test Method Practices for
Monitoring Ground Earth or Structural Movement Using
1
Probe-Type Inclinometers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6230; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the use of inclinometers to monitor the internal movement of ground. The test method covers types
of instruments, installation procedures, operating procedures, and maintenance requirements. It also provides formulae for data
reduction.
1.2 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the guidelines for significant digits and rounding established in Practice
D6026 unless superseded by this test method.
1.2.1 The procedures used to specify how data are collected, recorded or calculated in this test method are regarded as the industry
standard. In addition, they are representative of the significant digits that generally should be retained. The procedures used do not
consider material variation, purpose for obtaining the data, special purpose studies, or any considerations for the user’s objectives;
it is common practice to increase or reduce significant digits of reported data to be commensurate with these considerations. It is
beyond the scope of this test method to consider significant digits used in analytical methods for engineering design.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for information
only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate health and safety practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained Fluids
D3740 Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies Engaged in Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock as Used in
Engineering Design and Construction
D6026 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Geotechnical Data
D7299 Practice for Verifying Performance of a Vertical Inclinometer Probe
1
This test method practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D18 on Soil and Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.23 on Field
Instrumentation.
Current edition approved Jan. 15, 2013June 1, 2021. Published February 2013June 2021. Originally approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 20052013 as
D6230 – 98 (2005).D6230 – 13. DOI: 10.1520/D6230-13. 10.1520/D6230-21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6230 − 21
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of general terms, see Terminology D653.
3.1.2 Definitions of terms specific to this test method are included in Section 5.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 An inclinometer is a device for measuring deformation normal to the axis of a pipe by passing a probe along the pipe and
measuring the inclination of the probe with respect to the line of gravity. Measurements are converted to distances using
trigonometric functions. Distances are summed to find the position of the pipe. Successive measurements give differences in
position of the pipe and indicate deformation normal to the axis of the pipe. In most cases the pipe is installed in a near-vertical
hole. Measurements indicate subsurface horizontal deformation. In some cases the pipe is installed horizontally and the
measurements indicate vertical deformation.
4.2 Inclinometers are also called slope inclinometers or slope indicators. Typical applications include measuring the rate of
landslide movement and locating the zone of shearing, monitoring the magnitude and rate of horizontal movements for
embankments and excavations, monitoring the settlement and lateral spread beneath tanks and embankments, and mo
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.