ASTM C1517-16
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Metallic Impurities in Uranium Metal or Compounds by DC-Arc Emission Spectroscopy
Standard Test Method for Determination of Metallic Impurities in Uranium Metal or Compounds by DC-Arc Emission Spectroscopy
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is applicable to uranium metal, uranium oxides and compounds soluble in nitric or sulfuric acid, and uranium solutions which can be converted to uranium oxide (U3O8) in a muffle furnace. It may be used to determine the impurities in uranium compounds as listed in Specifications C753, C776, C788, and C967.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes the steps necessary for the preparation and determination of impurity metals in uranium metal and uranium compounds by DC arc emission spectroscopy.
1.2 The method is valid for those materials that can be dissolved in acid or converted to an oxide in a muffle furnace, or both (see Practice C1347).
1.3 This method uses the carrier distillation technique to selectively carry the impurities into the arc, leaving the uranium oxide in the electrode. If it is necessary to determine the carrier metal (usually a silver or strontium, or gallium compound) as an impurity, another technique must be chosen for that element.
1.4 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
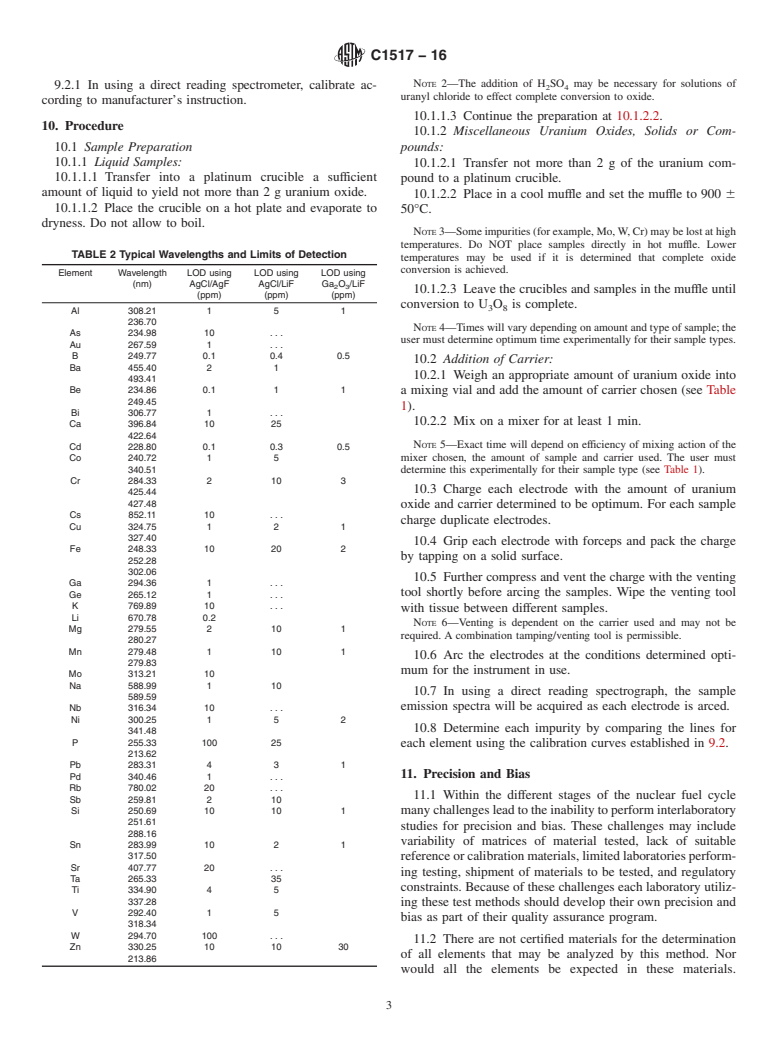
1.5 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C1517 − 16
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Metallic Impurities in Uranium Metal or
1
Compounds by DC-Arc Emission Spectroscopy
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1517; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope C776Specification for Sintered Uranium Dioxide Pellets
C788Specification for Nuclear-Grade Uranyl Nitrate Solu-
1.1 This test method describes the steps necessary for the
tion or Crystals
preparation and determination of impurity metals in uranium
C859Terminology Relating to Nuclear Materials
metal and uranium compounds by DC arc emission spectros-
C967Specification for Uranium Ore Concentrate
copy.
C1347Practice for Preparation and Dissolution of Uranium
1.2 The method is valid for those materials that can be
Materials for Analysis
dissolved in acid or converted to an oxide in a muffle furnace,
E130Practice for Designation of Shapes and Sizes of
or both (see Practice C1347). 3
Graphite Electrodes (Withdrawn 2013)
E135Terminology Relating to Analytical Chemistry for
1.3 This method uses the carrier distillation technique to
selectively carry the impurities into the arc, leaving the Metals, Ores, and Related Materials
uranium oxide in the electrode. If it is necessary to determine
3. Terminology
the carrier metal (usually a silver or strontium, or gallium
compound) as an impurity, another technique must be chosen
3.1 Except as otherwise defined herein, definitions of terms
for that element.
are as given in Terminologies C859 and E135.
1.4 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
4. Summary of Test Method
as standard. The values given in parentheses are for informa-
4.1 Uranium metal, solutions and compounds are converted
tion only.
to uranium oxide (U O ) in a muffle furnace. A weighed
3 8
1.5 This standard may involve hazardous materials, opera-
amount of the oxide is mixed with an appropriate spectro-
tions and equipment. This standard does not purport to address
graphic carrier and loaded into a graphite electrode. The
all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is
electrode is excited in a DC arc and the light is dispersed by a
the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish
spectrograph or spectrometer. The resulting spectrum is mea-
appropriate safety and health practices and determine the
sured electronically using a CCD, CID, or CMOS camera
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
sensitive to the proper regions. The line intensities are com-
pared directly to calibration curves derived from the arced
2. Referenced Documents
standards.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C753Specification for Nuclear-Grade, Sinterable Uranium
5. Significance and Use
Dioxide Powder
5.1 This test method is applicable to uranium metal, ura-
C761Test Methods for Chemical, Mass Spectrometric,
nium oxides and compounds soluble in nitric or sulfuric acid,
Spectrochemical,Nuclear,andRadiochemicalAnalysisof
and uranium solutions which can be converted to uranium
Uranium Hexafluoride
oxide (U O ) in a muffle furnace. It may be used to determine
3 8
theimpuritiesinuraniumcompoundsaslistedinSpecifications
C753, C776, C788, and C967.
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC26onNuclear
Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.05 on Methods of
6. Apparatus
Test.
Current edition approved April 1, 2016. Published May 2016. Originally
6.1 Spectrograph or Spectrometer—A spectrograph with
approved in 2002. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as C1517–09. DOI:
sufficient resolving power and linear dispersion to separate the
10.1520/C1517-16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1517 − 16
TABLE 1 Carrier—Sample Combinations
analytical lines from other lines in the spectrum of the sample
in the spectral region of 230 to 855 nm is required. Some Carrier Carrier Wt, Oxide Wt, Electrode Mixing Time,
Material (mg) (mg) Charge, (mg) (s)
spectrographs may be able to access wavelengths
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1517 − 09 C1517 − 16
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Metallic Impurities in Uranium Metal or
1
Compounds by DC-Arc Emission Spectroscopy
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1517; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method describes the steps necessary for the preparation and determination of impurity metals in uranium metal
and uranium compounds by DC arc emission spectroscopy.
1.2 The method is valid for those materials that can be dissolved in acid and/oror converted to an oxide in a muffle furnace
furnace, or both (see Practice C1347).
1.3 This method uses the carrier distillation technique to selectively carry the impurities into the arc, leaving the uranium oxide
in the electrode. If it is necessary to determine the carrier metal(usually metal (usually a silver or strontium, or gallium compound)
as an impurity, another technique must be chosen for that element.
1.4 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all
of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate
safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C753 Specification for Nuclear-Grade, Sinterable Uranium Dioxide Powder
C761 Test Methods for Chemical, Mass Spectrometric, Spectrochemical, Nuclear, and Radiochemical Analysis of Uranium
Hexafluoride
C776 Specification for Sintered Uranium Dioxide Pellets
C788 Specification for Nuclear-Grade Uranyl Nitrate Solution or Crystals
C859 Terminology Relating to Nuclear Materials
C967 Specification for Uranium Ore Concentrate
C1347 Practice for Preparation and Dissolution of Uranium Materials for Analysis
3
E130 Practice for Designation of Shapes and Sizes of Graphite Electrodes (Withdrawn 2013)
E135 Terminology Relating to Analytical Chemistry for Metals, Ores, and Related Materials
3. Terminology
3.1 See definitions and terms Except as otherwise defined herein, definitions of terms are as given in Terminologies C859 and
E135.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Uranium metal, solutions and compounds are converted to uranium oxide (U O ) in a muffle furnace. A weighed amount
3 8
of the oxide is mixed with an appropriate spectrographic carrier and loaded into a graphite electrode. The electrode is excited in
a DC arc and the light is dispersed by a spectrograph or spectrometer. The resulting spectrum is measured electronically using a
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C26 on Nuclear Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.05 on Methods of Test.
Current edition approved June 1, 2009April 1, 2016. Published July 2009May 2016. Originally approved in 2002. Last previous edition approved in 20022009 as
C1517 – 02.C1517 – 09. DOI: 10.1520/C1517-09.10.1520/C1517-16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1517 − 16
CCD, CID, or CMOS camera or photographed on photographic plates or film sensitive to the proper regions. The line intensities
are compared directly to standard plates or to calibration curves derived from the arced standards.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method is applicable to uranium metal, uranium oxides and compounds soluble in nitric or sulfuric acid, and
uranium solutions which can be converted to uranium oxide (U O ) in a muffle furnace. It may be used to determine the impurities
3 8
in uranium compounds as listed in Specifications C753, C776, C788, and C967.
6. Apparatus
6.1 Spectrograph or Spectrometer—A spectrograph with sufficient resolving power and
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.