ASTM D1518-14
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Thermal Resistance of Batting Systems Using a Hot Plate (Withdrawn 2023)
Standard Test Method for Thermal Resistance of Batting Systems Using a Hot Plate (Withdrawn 2023)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The thermal resistance of a batting or batting/fabric system is of considerable importance in determining its suitability for use in fabricating cold weather protective clothing, sleeping bags, and bedding systems. The thermal interchange between man and his environment is, however, an extremely complicated subject which involves many factors in addition to the insulation values of fabrics and battings. Therefore, measured thermal insulation values can only indicate relative merit of a particular material.
SCOPE
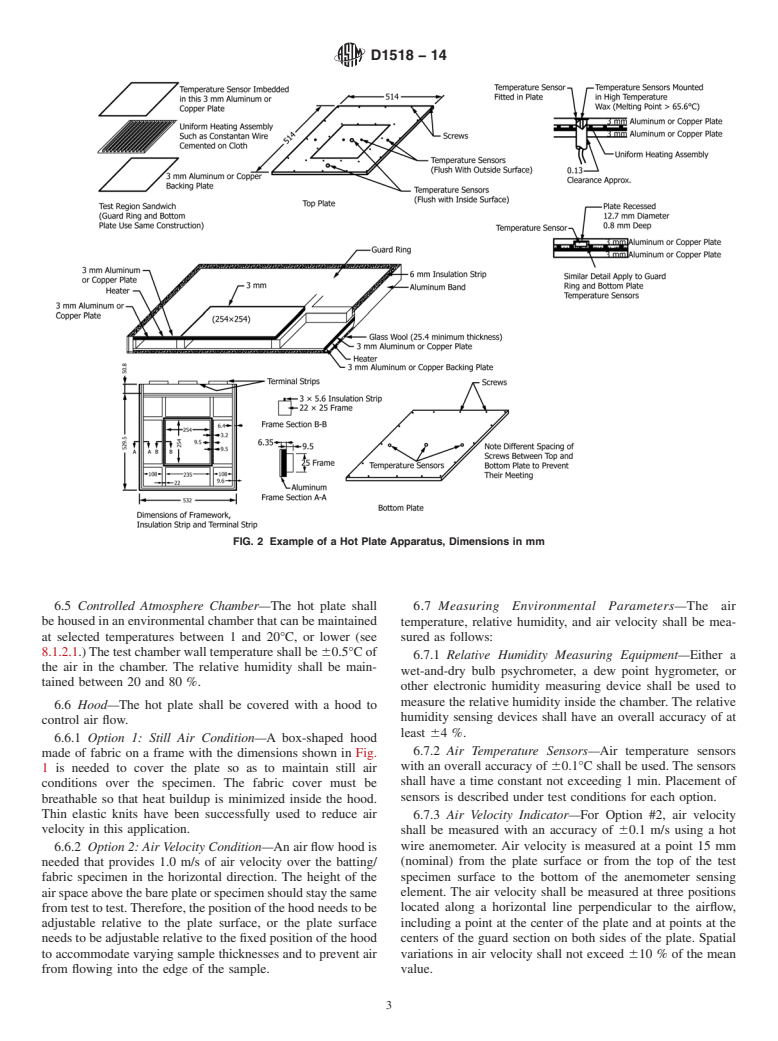
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the thermal resistance, under steady-state conditions, of battings and batting/fabric systems, and other materials within the limits specified in 1.2. It measures the heat transfer from a warm, dry, constant-temperature, horizontal flat-plate up through a layer of the test material to a cool atmosphere and calculates the resistance of the material. The measurements are made under still air conditions (Option #1) or with a horizontal air flow over the specimen (Option #2).
1.2 For practical purposes, this test method is limited to determinations on specimens of battings and layered batting/fabric assemblies having an intrinsic thermal resistance from 0.1 to 1.5 K·m2/W and thicknesses not in excess of 50 mm.
1.3 This test method also provides a method for determining the bulk density of the material, the insulation per unit thickness, and the insulation per unit weight.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address the safety concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility of whoever uses this standard to consult and establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This test method covers the measurement of the thermal resistance, under steady-state conditions, of battings and batting/fabric systems, and other materials within the limits specified in 1.2. It measures the heat transfer from a warm, dry, constant-temperature, horizontal flat-plate up through a layer of the test material to a cool atmosphere and calculates the resistance of the material. The measurements are made under still air conditions (Option #1) or with a horizontal air flow over the specimen (Option #2).
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee D13 on Textiles, this test method was withdrawn in January 2023 in accordance with section 10.6.3 of the Regulations Governing ASTM Technical Committees, which requires that standards shall be updated by the end of the eighth year since the last approval date.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D1518 − 14
Standard Test Method for
1
Thermal Resistance of Batting Systems Using a Hot Plate
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1518; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
This standard replaces D1518-85, Thermal Transmittance of Textile Materials. This standard
provides a method for measuring the thermal resistance (insulation) provided by battings and
batting/fabric systems under still air conditions or an air flow condition. Other hot plate standards
F1868 and ISO 11092 provide a method for measuring the thermal resistance and evaporative
resistance of fabrics and fabric systems.The method for measuring fabric insulation in these standards
is comparable to Option 2:Air Velocity Condition in D1518. These standards can be used to compare
the thermal properties of textile materials. Manikin standards F1291 and F2370 can be used to
measure and compare the thermal resistance and evaporative resistance of clothing systems,
respectively. Manikin standard F1720 can be used to measure the insulation provided by sleeping bag
systems.
1. Scope ate safety and health practices and determine the applicability
of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the thermal
resistance, under steady-state conditions, of battings and
2. Referenced Documents
batting/fabric systems, and other materials within the limits
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
specified in 1.2. It measures the heat transfer from a warm, dry,
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
constant-temperature, horizontal flat-plate up through a layer
D3776 Test Methods for Mass Per Unit Area (Weight) of
of the test material to a cool atmosphere and calculates the
Fabric
resistance of the material. The measurements are made under
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
still air conditions (Option #1) or with a horizontal air flow
ASTM Test Methods
over the specimen (Option #2).
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
1.2 For practical purposes, this test method is limited to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
determinations on specimens of battings and layered batting/
F1291 Test Method for Measuring the Thermal Insulation of
fabric assemblies having an intrinsic thermal resistance from
Clothing Using a Heated Manikin
2
0.1 to 1.5 K·m /W and thicknesses not in excess of 50 mm.
F1494 Terminology Relating to Protective Clothing
F1720 Test Method for Measuring Thermal Insulation of
1.3 Thistestmethodalsoprovidesamethodfordetermining
Sleeping Bags Using a Heated Manikin
the bulk density of the material, the insulation per unit
F1868 Test Method for Thermal and Evaporative Resistance
thickness, and the insulation per unit weight.
of Clothing Materials Using a Sweating Hot Plate
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
F2370 Test Method for Measuring the Evaporative Resis-
standard.
tance of Clothing Using a Sweating Manikin
3
1.5 This standard does not purport to address the safety 2.2 ISO Standards:
concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility of ISO 11092 Textiles–Physiological Effects–Measurement of
whoever uses this standard to consult and establish appropri- Thermal and Water-Vapour Resistance Under Steady-
State Conditions (Sweating Guarded-Hotplate Test)
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 on Textiles For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.51 on Conditioning and, contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Chemical and Thermal Properties. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved July 1, 2014. Published August 2014. Originally the ASTM website.
3
published as D1518 – 57 T. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as D1518 – 11a. Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
DOI: 10.1520/D1518-14. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1518 − 14
final design of equipment, including dimensions of component parts,
ISO 9073-2 Textile—Test Methods for Nonwovens—Part 2:
selection of electrical components and selection of sensors, shall be in
Determination of Thickness
conformance with the specifications set forth in the body of this standard.
3. Terminology
6.1 HotPlate—Aguardedflatplatecompose
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.