ASTM D2647-10
(Specification)Standard Specification for Crosslinkable Ethylene Plastics
Standard Specification for Crosslinkable Ethylene Plastics
ABSTRACT
This specification covers a general classification system for crosslinkable ethylene plastics compounds. Two types of compounds are covered, namely, mechanical types in which mechanical strength properties are of prime importance in applications, and electrical types in which electrical insulating or conducting properties also are of prime importance in applications. These compounds shall be classified as: Type I; Type II; and Grade A. Tests shall be performed to determine the properties in accordance with the following test methods: conditioning; test conditions; ultimate elongation; elongation retention after aging; apparent modulus of rigidity; brittleness temperature; dielectric constant; dissipation factor; and degree of crosslinking.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers a general classification system for crosslinkable ethylene plastics compounds (Note 1). The requirements specified herein are not necessarily applicable for use as criteria in determining suitability for the end use of a fabricated product.
Note 1—It is to be noted that this specification describes materials that are available commercially in their uncrosslinked form. Therefore, they are crosslinkable compounds despite the fact that measurement of the parameters used for their classification and specification will usually be carried out after curing has been effected.
1.2 Two types of compounds are covered, namely, mechanical types in which mechanical strength properties are of prime importance in applications, and electrical types in which electrical insulating or conducting properties also are of prime importance in applications.
1.3 The parameters used to classify and specify the mechanical types are ultimate elongation, elongation retention after aging, apparent modulus of rigidity, and brittleness temperature.
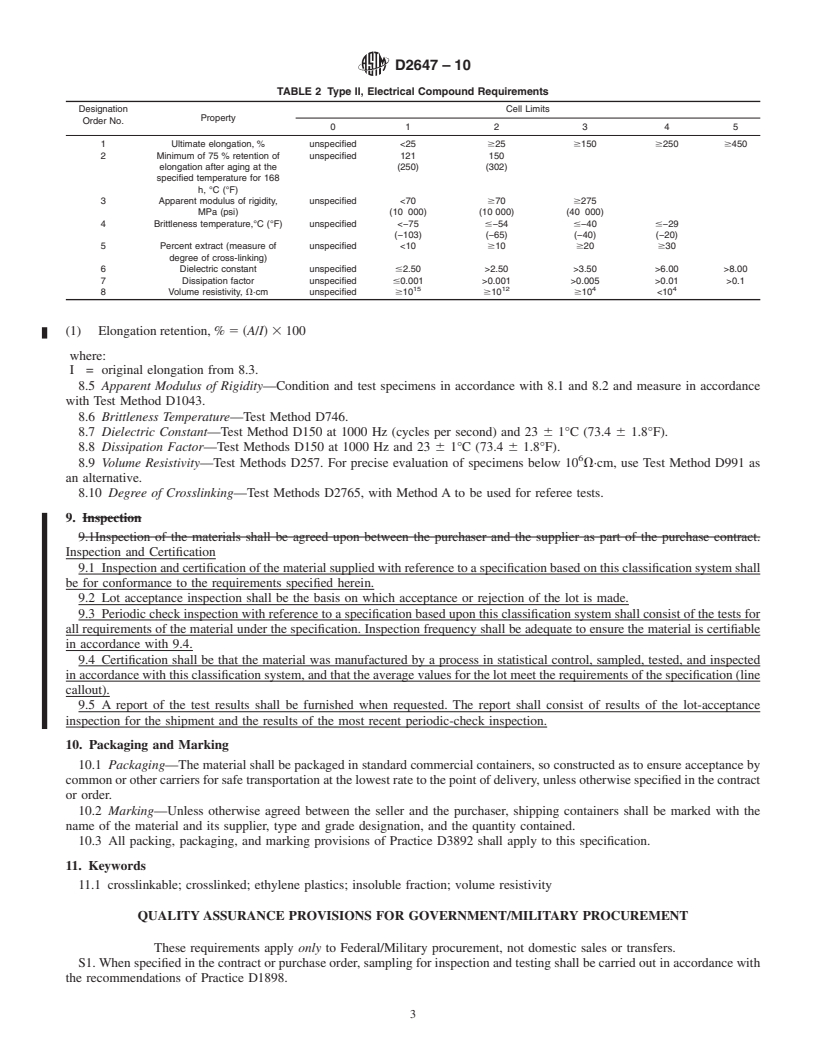
1.4 The parameters used to classify and specify the electrical types are ultimate elongation, elongation retention after aging, apparent modulus of rigidity, brittleness temperature, dielectric constant, dissipation factor, and volume resistivity.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 7, of this specification: This specification does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this specification to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 2—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D2647 −10
Standard Specification for
1
Crosslinkable Ethylene Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2647; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This specification covers a general classification system 2.1 ASTM Standards:
for crosslinkable ethylene plastics compounds (Note 1). The D150 Test Methods forAC Loss Characteristics and Permit-
requirements specified herein are not necessarily applicable for tivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulation
use as criteria in determining suitability for the end use of a D257 Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of
fabricated product. Insulating Materials
D573 Test Method for Rubber—Deterioration in an Air
NOTE 1—It is to be noted that this specification describes materials that
Oven
are available commercially in their uncrosslinked form. Therefore, they
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
are crosslinkable compounds despite the fact that measurement of the
parameters used for their classification and specification will usually be
D638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
carried out after curing has been effected.
D746 Test Method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastics
1.2 Two types of compounds are covered, namely, mechani- and Elastomers by Impact
cal types in which mechanical strength properties are of prime D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
importance in applications, and electrical types in which D991 Test Method for Rubber Property—Volume Resistiv-
electrical insulating or conducting properties also are of prime ity Of Electrically Conductive and Antistatic Products
importance in applications. D1043 Test Method for Stiffness Properties of Plastics as a
Function of Temperature by Means of a Torsion Test
1.3 The parameters used to classify and specify the me-
D2765 Test Methods for Determination of Gel Content and
chanical types are ultimate elongation, elongation retention
Swell Ratio of Crosslinked Ethylene Plastics
after aging, apparent modulus of rigidity, and brittleness
D3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
temperature.
IEEE/ASTM SI-10 Standard for Use of the International
1.4 The parameters used to classify and specify the electri-
System of Units (SI): (The Modernized Metric System)
cal types are ultimate elongation, elongation retention after
2.2 Military Standard:
aging, apparent modulus of rigidity, brittleness temperature,
MIL-STD-105 Sampling Procedures and Tables for Inspec-
dielectric constant, dissipation factor, and volume resistivity. 3
tion by Attributes (Obsolete 1995)
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3. Terminology
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only.
3.1 Definitions: For definitions of plastics terms used in this
specification, see Terminology D883.
1.6 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
test methods portion, Section 7, of this specification:This
3.2 Abbreviations: Units, Symbols, andAbbreviations—For
specification does not purport to address all of the safety
units, symbols, and abbreviations used in this specification see
concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
IEEE/ASTM SI-10.
of the user of this specification to establish appropriate safety
4. Classification
and health practices and determine the applicability of regu-
latory limitations prior to use.
4.1 Classification System—Table 1 and Table 2 provide a
classification system for these compounds so that the relations
NOTE 2—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
among them can be delineated and those that are commercially
1 2
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Materials. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published May 2010. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1967. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D2647 - 05A. DOI: AvailablefromDefenseAutomationandProductionService,Bldg.4SectionD,
10.1520/D2647-10. 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ---
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D2647–09 Designation: D2647 – 10
Standard Specification for
1
Crosslinkable Ethylene Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2647; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers a general classification system for crosslinkable ethylene plastics compounds (Note 1). The
requirements specified herein are not necessarily applicable for use as criteria in determining suitability for the end use of a
fabricated product.
NOTE 1—It is to be noted that this specification describes materials that are available commercially in their uncrosslinked form. Therefore, they are
crosslinkablecompoundsdespitethefactthatmeasurementoftheparametersusedfortheirclassificationandspecificationwillusuallybecarriedoutafter
curing has been effected.
1.2 Two types of compounds are covered, namely, mechanical types in which mechanical strength properties are of prime
importanceinapplications,andelectricaltypesinwhichelectricalinsulatingorconductingpropertiesalsoareofprimeimportance
in applications.
1.3 The parameters used to classify and specify the mechanical types are ultimate elongation, elongation retention after aging,
apparent modulus of rigidity, and brittleness temperature.
1.4 The parameters used to classify and specify the electrical types are ultimate elongation, elongation retention after aging,
apparent modulus of rigidity, brittleness temperature, dielectric constant, dissipation factor, and volume resistivity.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 7, of this specification: This
specification does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the
user of this specification to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
NOTE 2—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D150 Test Methods for AC Loss Characteristics and Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulation
D257 Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials
D573 Test Method for RubberDeterioration in an Air Oven
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
D746 Test Method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastics and Elastomers by Impact
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D991 Test Method for Rubber PropertyVolume Resistivity Of Electrically Conductive and Antistatic Products
D1043 Test Method for Stiffness Properties of Plastics as a Function of Temperature by Means of a Torsion Test
D2765 Test Methods for Determination of Gel Content and Swell Ratio of Crosslinked Ethylene Plastics
D3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
IEEE/ASTM SI-10 Standard for Use of the International System of Units (SI): (The Modernized Metric System)
2.2 Military Standard:
3
MIL-STD-105 Sampling Procedures and Tables for Inspection by Attributes (Obsolete 1995)
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic Materials.
Current edition approved Dec.April 1, 2009.2010. Published December 2009.May 2010. Originally approved in 1967. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as
D2647 - 05aA. DOI: 10.1520/D2647-109.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Defense Automation and Production Service, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2647 – 10
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions: For definitions of plastics terms used in this specification, see Terminology D883.
3.2 Abbreviations
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.