ASTM D6810-02
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measurement of Hindered Phenolic Antioxidant Content in HL Turbine Oils by Linear Sweep Voltammetry
Standard Test Method for Measurement of Hindered Phenolic Antioxidant Content in HL Turbine Oils by Linear Sweep Voltammetry
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the voltammetric determination of hindered phenol antioxidants in new or used Type HL turbine oils in concentrations from 0.0075 weight % up to concentrations found in new oils by measuring the amount of current flow at a specified voltage in the produced voltammogram.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation:D6810–02
Standard Test Method for
Measurement of Hindered Phenolic Antioxidant Content in
HL Turbine Oils by Linear Sweep Voltammetry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6810; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope shaken, the hindered phenol antioxidants and other solution
soluble oil components present in the sample are extracted into
1.1 This test method covers the voltammetric determination
the solution and the remaining droplets suspended in the
of hindered phenol antioxidants in new or used Type HL
solution are agglomerated by the sand. The sand/droplet
turbine oils in concentrations from 0.0075 weight % up to
suspension is allowed to settle out and the hindered phenol
concentrations found in new oils by measuring the amount of
antioxidants dissolved in the solution are quantified by volta-
current flow at a specified voltage in the produced voltammo-
mmetric analysis. The results are calculated and reported as
gram.
weight percent of antioxidant or as millimoles (mmol) of
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
antioxidant per litre of sample for prepared and fresh oils and
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
as a percent remaining antioxidant for used oils.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2 Voltammetric analysis is a technique that applies
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
electro-analytic methods when a sample to be analyzed is
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
mixed with an electrolyte and a solvent and placed within an
2. Referenced Documents electrolytic cell. Data is obtained by measuring the current
passing through the cell as a function of the potential applied,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
and test results are based upon current, voltage and time
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
relationships at the cell electrodes. The cell consists of a fluid
D 4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
container into which is mounted a small, easily polarized
Petroleum Products
working electrode, and a large nonpolarizable reference elec-
D 4378 Practice for In-Service Monitoring of Mineral Tur-
trode.Thereferenceelectrodeshouldbemassiverelativetothe
bine Oils for Steam and Gas Turbines
working electrode so that its behavior remains essentially
D 6224 Practice for In-Service Monitoring of Lubricating
constant with the passage of small current; that is, it remains
Oil for Auxiliary Power Plant Equipment
unpolarized during the analysis period. Additional electrodes,
D 6447 Test Method for Hydroperoxide Number of Avia-
auxiliary electrodes, can be added to the electrode system to
tion Turbine Fuels by Voltammetric Analysis
eliminate the effects of resistive drop for high resistance
2.2 ISO Standard:
solutions. In performing a voltammetric analysis, the potential
ISO 6743 Part 4—Lubricants, Industrial Oils, and Related
across the electrodes is varied linearly with time, and the
Products
resulting current is recorded as a function of the potential. As
3. Summary of Test Method
the increasing voltage is applied to the prepared sample within
the cell, the various additive species under investigation within
3.1 A measured quantity of sample is dispensed into a vial
the oil are caused to electrochemically oxidize. The data
containing a measured quantity of alcohol-based electrolyte
recorded during this oxidation reaction can then be used to
solution and containing a layer of sand. When the vial is
determine the remaining useful life of the oil type. A typical
current-potential curve produced during the practice of the
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
voltammetric test can be seen by reference to Fig. 1. Initially,
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
the applied potential produces an electrochemical reaction
D02.09 on Oxidation.
havingaratesoslowthatvirtuallynocurrentflowsthroughthe
Current edition approved June 10, 2002. Published September 2002.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01. cell. As the voltage is increased, as shown in Fig. 1, the
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02.
electro-active species (for example, substituted phenols) begin
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.03.
to oxidize at the working electrode surface, producing an
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.04.
anodic rise in the current.As the potential is further increased,
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1 rue de
Varembé, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D6810–02
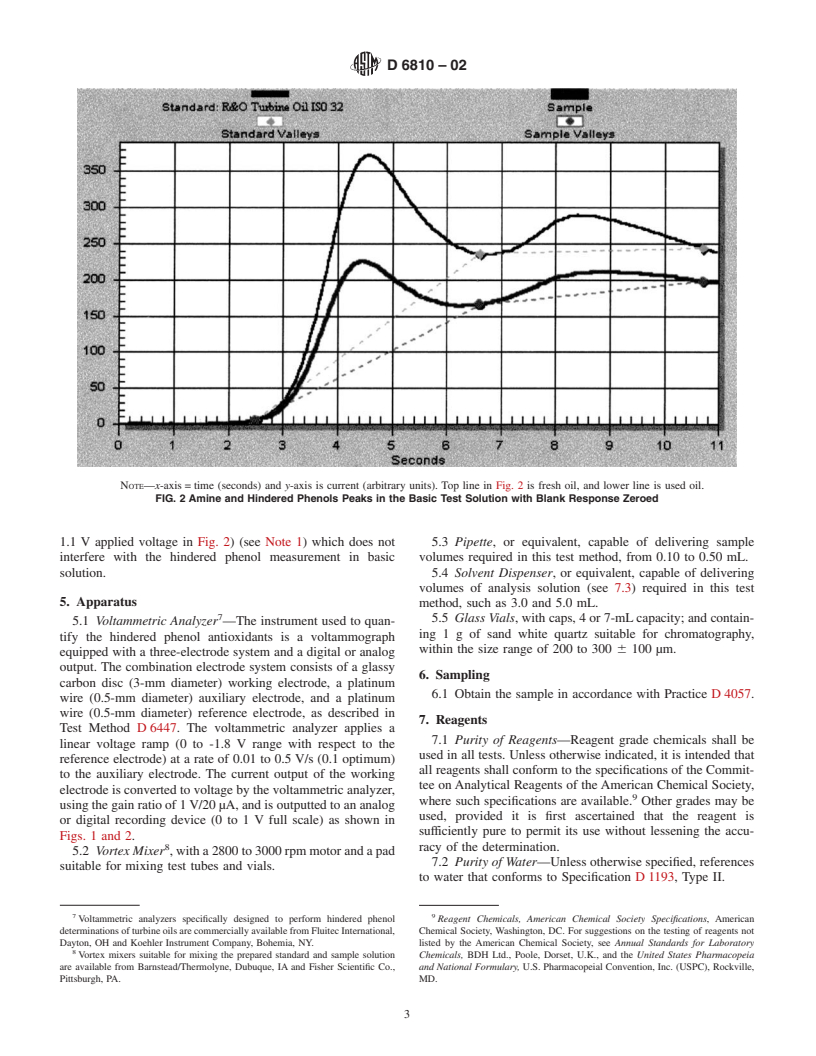
NOTE—x-axis = time (seconds) and y-axis is current (arbitrary units). Top line in Fig. 1 is voltammogram of a fresh R&O turbine oil showing valley
indicator before and after standard.
FIG. 1 Hinderd Phenol Voltammetric Response in Basic Test Solution with Blank Response Zeroed
the decrease in the electro-active species concentration at the 4.1.1 This test method is applicable to Type HL turbine oils
electrode surface and the exponential increase of the oxidation as defined by ISO 6743 Part 4, Table 1. These are refined
rate lead to a maximum in the current-potential curve shown in
mineral oils containing rust and oxidation inhibitors, but not
Fig. 1.
antiwear additives. This test method has not yet been estab-
lished with sufficient precision for antiwear oils.
4. Significance and Use
4.2 This test method is also suitable for manufacturing
4.1 The quantitative determination of hindered phenol anti-
control and specification acceptance.
oxidants in a new turbine oil measures the amount of this
4.3 When a voltammetric analysis is obtained for a turbine
material that has been added to the oil as protection against
oilinhibitedwithatypicalhinderedphenolantioxidant,thereis
oxidation. Beside phenols, turbine oils can be formulated with
an increase in the current of the produced voltammogram
other antioxidants such as amines which can extend the oil life.
between 3-5 s (or 0.3 to 0.6 V applied voltage) (see Note 1)in
In used oil, the determination measures the amount of original
basic alcohol solution (Fig. 1—x-axis 1 second = 0.1 V).
(phenolic) antioxidant remaining after oxidation have reduced
Hindered phenol antioxidants detected by voltammetric analy-
its initial concentration. This test method is not designed or
sis include, but are not limited to, 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-
intended to detect all of the antioxidant intermediates formed
duringthethermalandoxidativestressingoftheoils,whichare methylphenol; 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol and 4,4’-
recognizedashavingsomecontributiontotheremaininguseful methylenebis(2,6-di-tert-butylphenol).
life of the used or in-service oil. Nor does it measure the
NOTE 1—Voltages listed with respect to reference electrode. The
overall stability of an oil, which is determined by the total
voltammograms shown in Figs. 1 and 2 were obtained with a platinum
contribution of all species present. Before making final judg-
reference electrode and a voltage scan rate of 0.1 V/s.
ment on the remaining useful life of the used oil, which might
result in the replacement of the oil reservoir, it is advised to 4.4 For turbine oils containing amine compounds (antioxi-
perform additional analytical techniques (in accordance with
dants and corrosion inhibitors), there is an increase in the
Practices D 6224 and D 4378), having the capability of mea-
current of the produced voltammogram between 7-11 s (0.7 to
suring remaining oxidative life of the used oil.
D6810–02
NOTE—x-axis = time (seconds) and y-axis is current (arbitrary units). Top line in Fig. 2 is fresh oil, and lower line is used oil.
FIG. 2 Amine and Hindered Phenols Peaks in the Basic Test Solution with Blank Response Zeroed
1.1 V applied voltage in Fig. 2) (see Note 1) which does not 5.3 Pipette, or equivalent, capable of delivering sample
interfere with the hindered phenol measurement in basic volumes required in this test method, from 0.10 to 0.50 mL.
solution. 5.4 Solvent Dispenser, or equivalent, capable of delivering
volumes of analysis solution (see 7.3) required in this test
5. Apparatus
method, such as 3.0 and 5.0 mL.
5.5 Glass Vials, with caps, 4 or 7-mLcapacity; and contain-
5.1 Voltammetric Analyzer —The instrument used to quan-
ing1gof sand white quartz suitable for chromatography,
tify the hindered phenol antioxidants is a voltammograph
within the size range of 200 to 300 6 100 µm.
equipped with a three-electrode system and a digital or analog
output. The combination electrode system consists of a glassy
6. Sampling
carbon disc (3-mm diameter) working electrode, a platinum
6.1 Obtain the sample in accordance with Practice D 4057.
wire (0.5-mm diameter) auxiliary electrode, and a platinum
wire (0.5-mm diameter) reference electrode, as described in
7. Reagents
Test Method D 6447. The voltammetric analyzer applies a
7.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
linear voltage ramp (0 to -1.8 V range with respect to the
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
reference electrode) at a rate of 0.01 to 0.5 V/s (0.1 optimum)
all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Commit-
to the auxiliary electrode. The current output of the working
tee onAnalytical Reagents of theAmerican Chemical Society,
electrode is converted to voltage by the voltammetric analyzer,
where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
using the gain ratio of 1V/20 µA, and is outputted to an analog
used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is
or digital recording device (0 to 1 V full scale) as shown in
sufficiently pure to permit its use without lessening the accu-
Figs. 1 and 2.
8 racy of the determination.
5.2 Vortex Mixer ,witha2800to3000rpmmotorandapad
7.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise specified, references
suitable for mixing test tubes and vials.
to water that conforms to Specification D 1193, Type II.
7 9
Voltammetric analyzers specifically designed to perform hindered phenol Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
determinationsofturbineoilsarecommerciallyavailablefromFluitecInternational, Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not
Dayton, OH and Koehler Instrument Company, Bohemia, NY. listed by the American Chemical Society, see Annual Standards for Laboratory
Vortex mixers suitable for mixing the prepared standard and sample solution Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
are available from Barnstead/Thermolyne, Dubuque, IA and Fisher Scientific Co., and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville,
Pittsburgh, PA. MD.
D6810–02
NOTE—Standard (top line) and sample used oil (lower line).
FIG. 3 Voltammetric Reading for a Used Oil Sample Comparing Hindered Phenols Peaks (in the Basic Test Solution)
7.3 Analysis Materials: 8.2.1.1 Definition—The blank reading (voltammetric num-
7.3.1 Alcohol Solution (Basic)—Proprietary yellow solu- ber) is a measurement of the analysis solution by itself. The
tion , ethanol solvent (1:10 distilled water/ethanol solution) blank measurement gives a reference number with no antioxi-
containing a dissolved base electrolyte. (Warning—Corrosive, dant present (the zero baseline).
poison, flammable, skin irritant; harmful if inhaled.) 8.2.2 Standard Reading—(30 to 150 mmol/L—weight %
7.3.2 Alcohol Cleansing Pads—70 % isopropyl alcohol dependent on density of fresh oil and molecular weight of
saturated cleansing pads. antioxidant).
8.2.2.1 Definition—The standard reading is a measurement
8. Procedure
of a fresh, unused oil (containing phenolic antioxidant) mixed
with an appropriate analysis solvent. This measurement gives
8.1 The voltammetric analyzer used in this test method
you a voltammetric reading (standard reading) that indicates
gives linear results between 2 to 50 mmol for hindered phenols
the voltammetric response for the concentration hindered
using an oil sample size of 0.40 and 5.0 mL of the analysis
phenol antioxidant being analyzed for the oil being tested.
solvent. The corresponding range of weight percents depends
8.2.3 Sample (Used Oil) Reading.
on the molecular weight of the hindered phenol and the density
8.2.3.1 Definition—Thesamplereadingisameasurementof
ofthebaseoil.Forinstance,theweight%rangeof0.044to1.1
afreshorusedoilmixedwiththesametypeofanalysissolvent
is equal to 2 to 50 mmol/L for a hindered phenol containing
as the standard. This measurement will provide voltammetric
one hydroxyl group and with a molecular weight of 220 g/mol
readings that normally range between the blank and standard
(2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol) and an oil density of 1
measurements,andreflecttheconcentrationofhinderedphenol
g/mL. Below 2 mmol, the noise to signal ratio becomes large
antioxidant present (fresh oil) or remaining (used oil) in the oil
decreasing the accuracy of the measurements. For measure-
sample. Voltammetric readings for used oils will decrease as
ments below 2 mmol or for fresh oils with high noise to signal
hindered phenol antioxidants are depleted.
ratios, the sample size should be increased to 0.60 mL and the
8.3 Voltammetric Reading—After the operator has selected
volume of analysis solvent decreased to 3.0 mL.
the valleys before and after the antioxidant peaks (as shown in
8.2 General Voltammetric Test Procedure—The test proce-
Fig.1),thesoftware(R-DMS )willautomaticallyidentifyand
dureforvoltammetricanalysiswillconsistoftheblankreading
calculate the area above the baseline between the 2 valley
(calibration), followed by a standard reading and finally the
indicators. This calculated area is then used for the sample
sample (used oil) reading.
reading (used oil), which will be established by comparing the
8.2.1 Blank Reading—(0 mmol/L = 0 weight %).
10 11
Voltammetric solutions are available from Fluitec International, Dayton, OH, R-DMS is a software package available from Fluitec International, Dayton,
and Koehler Instrument Company, Bohemia, NY. OH, and Koehler Instrument Company, Bohemia, NY.
D6810–02
used oil area to its standard (see Fig. 3) and make remaining between te
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.