ASTM D3233-93(1998)
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Measurement of Extreme Pressure Properties of Fluid Lubricants (Falex Pin and Vee Block Methods)
Standard Test Methods for Measurement of Extreme Pressure Properties of Fluid Lubricants (Falex Pin and Vee Block Methods)
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover two procedures for making a preliminary evaluation of the load-carrying properties of fluid lubricants by means of the Falex Pin and Vee Block Test Machine. Note 1-Additional information can be found in Appendix X1 regarding coefficient of friction, load gage conversions, and load gage cablibration curve.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. Because the equipment used in these test methods is available only in inch-pound units, the SI units are omitted when referring to the equipment and the test specimens.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
An American National Standard
Designation: D 3233 – 93 (Reapproved 1998)
Standard Test Methods for
Measurement of Extreme Pressure Properties of Fluid
Lubricants (Falex Pin and Vee Block Methods)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3233; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope to a standard reference.
3.1.2 direct load, n—that which is applied linearly, bisect-
1.1 These test methods cover two procedures for making a
ing the angle of the vee block corrected to either the 800 or
preliminary evaluation of the load-carrying properties of fluid
3000-lbf gage reference.
lubricants by means of the Falex Pin and Vee Block Test
3.1.2.1 Discussion—This load is equivalent to the true load
Machine.
times the cos 42°.
NOTE 1—Additional information can be found in Appendix X1 regard-
3.1.3 true load, n—the sum of the applied forces normal to
ing coefficient of friction, load gage conversions, and load gage cablibra-
the tangents of contact between the faces of one vee block and
tion curve.
the journal pin corrected to the 4500 lbf gage reference line.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1.4 true load failure value, n—the true load at which the
standard. Because the equipment used in these test methods is
lubricant tested can no longer support the applied load resulting
available only in inch-pound units, the SI units are omitted
in either test pin or shear pin breakage, or inability to maintain
when referring to the equipment and the test specimens.
or increase load.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.4.1 Discussion—This value is also referred to as the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
limit of extreme pressure.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- 4. Summary of Test Methods
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.1 Both test methods consist of running a rotating steel
journal at 290 6 10 rpm against two stationary V-blocks
2. Referenced Documents
immersed in the lubricant sample. Load is applied to the
2.1 ASTM Standards:
V-blocks by a ratchet mechanism. In Test Method A (Note 1),
B 16 Specification for Free-Cutting Brass, Rod, Bar, and
increasing load is applied continuously. In Test Method B
Shapes for Use in Screw Machines
(Note 1), load is applied in 250-lbf (1112-N) increments with
D 2670 Test Method for Measuring Wear Properties of
load maintained constant for 1 min at each load increment. In
Fluid Lubricants (Falex Pen and Vee Block Method)
both methods the load-fail value obtained is the criteria for
D 2783 Test Method for Measurement of Extreme-Pressure
level of load-carrying properties. Both methods require cali-
Properties of Lubricating Fluids (Four-Ball Method)
bration of the load gage and reporting of test results as true
(corrected) loads rather than actual gage loads.
3. Terminology
NOTE 2—Test Method A is referred to as the Falex Run-Up Test. Test
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Method B is referred to as the Falex One-Minute Step Test.
3.1.1 actual gage load, n—the value obtained from the gage
while running the test and before any corrections are made.
5. Significance and Use
3.1.1.1 Discussion—This gage reading is irrespective of the
5.1 Evaluations by both test methods differentiate between
particular gage used, and corrections are made by comparison
fluids having low, medium, and high levels of extreme-pressure
properties. The user should establish any correlation between
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-2 on
results by either method and service performance.
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and are the direct responsibility of Subcommit-
tee D02.0L on Industrial Lubricants. NOTE 3—Relative ratings by both test methods on the reference fluids
Current edition approved Aug. 15, 1993. Published October 1993. Originally
covered in Table 1 and Table 2 are in good general agreement with
published as D 3233 – 86. Last previous edition D 3233 – 92.
four-ball weld-point relative ratings obtained on these same reference
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.01.
fluids, covered in Test Method D 2783.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 3233
A
TABLE 1 Results of Cooperative Tests on Reference Fluids L-XI-1-2-A, B, C, D, E TEST METHOD A
L-XI-1-2-A L-XI-1-2-B L-XI-1-2-C L-XI-1-2-D L-XI-1-2-E
Labora-
Fail Load, lbf Fail Load, lbf Fail Load, lbf Fail Load, lbf Fail Load, lbf
Test
tory
Gage True Gage True Gage True Gage True Gage True
A1 1200 840 1200 840 4500 + 4100 + 4300 3950 2600 2100
2 1275 920 1275 920 4500 + 4100 + 4500 + 4100 + 2400 1925
B1 800 860 1000 1050 4500 + 4250 + 4100 3900 2050 2050
2 850 900 950 1025 4500 + 4250 + 4300 4100 1950 1950
C1 725 990 775 1020 4500 + 3200 + 3950 2900 1350 1460
2 650 910 750 980 4500 + 3200 + 4100 3000 1300 1430
D1 1400 1050 1100 770 4500 + 3500 + 4500 + 3500 + 2900 2150
2 1400 1050 1250 900 4500 + 3500 + 4500 + 3500 + 2650 1975
E1 825 900 1000 1060 4450 4500 + 4100 4475 1825 1970
2 750 820 925 1000 4450 4500 + 4150 4500 1825 1970
B B
F1 1000 920 1000 800 4500 + 4500 + 3500 4500 1850 1900
B B
2 990 910 1050 850 4500 + 4500 + 2900 3510 1720 1720
G1 800 900 690 800 4000 4275 3325 3625 1430 1600
2 700 800 660 750 3750 4000 3150 3450 1500 1675
H1 700 700 1000 1000 4500 + 4500 + 3750 3750 1900 1900
2 700 700 1000 1000 4500 + 4500 + 4000 4000 1650 1650
I1 750 600 1250 1000 4500 + 3750 + 4500 + 3750 + 1750 1450
2 750 600 1000 800 4500 + 3750 + 4500 + 3750 + 1750 1450
C
Min Avg 600 775 2950 1445
C
Max Avg 1050 1037 4488 2063
C
Grand Avg 854 920 3809 1796
Repeatability Reproducibility
s = 0.0624 S = 0.140
D D
r = 0.179 (TL) R = 0.402 (TL)
A
Reference fluids used and described in Test Method D 2783.
B
Calibration curves shifted.
C
Six laboratories.
D
TL = average true load, lbf, of sample tested.
6. Apparatus to 91 on a ground flat surface, surface finish 5 to 10 μin.
−7 −7
(1.3 3 10 to 2.5 3 10 m) rms.
6.1 Falex Pin and Vee Block Test Machine, illustrated in
7.3 Locking Pins, ⁄2H brass, conforming to Specification
Fig. 1, Fig. 2, and Fig. 3, fitted with 4500-lbf (20 000-N) gage
B 16.
or 3000-lbf (13 350-N) gage.
7.4 Solvent, safe, nonfilming, nonchlorinated.
6.2 Required for Calibration:
6.2.1 Allen Screw, with attached 10-mm Brinnell ball.
NOTE 4—Petroleum distillate and benzene, formerly used as solvents in
6.2.2 Back-Up Plug.
this method, have been eliminated due to possible toxic effects. Each user
6.2.3 Standard Test Coupon, soft, annealed copper, Hb should select a solvent that can meet applicable safety standards and still
thoroughly clean the parts.
37–39.
6.2.4 Brinnell Microscope, or equivalent.
8. Preparation of Apparatus
6.2.5 Timer, graduated in seconds and minutes.
6.2.6 Rule, steel, 6-in. (approximately 150-mm) long. 8.1 Cleaning:
8.1.1 Thoroughly clean the V-blocks, test journals, lubricant
7. Reagents and Materials
cup, and supports for V-blocks and test journals by washing,
7.1 Standard Coined-Blocks, 96 6 1° angle, AISI C-1137
successively, with solvent selected in 7.4. Dry the V-blocks,
−7
steel, HRC 20 to 24, surface finish 5 to 10 μin. (1.3 3 10 to
test journals, lubricant cup, and supports, by allowing the final
−7
2.5 3 10 m), rms.
solvent to evaporate in air.
7.2 Standard Test Journals, ⁄4 in. (6.35 mm) outside
8.1.2 After cleaning, handle the test pieces with care to
diameter by 1 ⁄4 in. (31.75 mm) long, AISI 3135 steel, HRB 87
prevent contamination. Particularly, avoid contact of fingers
with mating surfaces of V-blocks and test journals.
8.2 Assembly:
The Falex Pin and Vee Block Test Machine, available from the Falex Corp.,
1020 Airpark Dr., Sugar Grove, IL 60554 has been found satisfactory for this
8.2.1 Insert the test journal into the test shaft and secure
purpose. A new model of this machine has been available since 1983. Certain
with a new brass locking pin, as shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 3.
operating procedures are different for this new model. Consult instruction manual of
8.2.2 Insert the V-blocks into the recesses of the loading
machine for this information.
Available from Falex Corp., 1020 Airpark Dr., Sugar Grove, IL 60554. device and swing the V-blocks inward to contact the journal so
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 3233
A
TABLE 2 Results of Cooperative Tests on Reference Fluids L-XI-1-2-A, B, C, D, E TEST METHOD B
L-XI-1-2-A L-XI-1-2-B L-XI-1-2-C L-XI-1-2-D L-XI-1-2-E
Fail Load, lbf Fail Load, lbf Fail Load, lbf Fail Load, lbf Fail Load, lbf
Labora-
Test
tory
Gage True Gage True Gage True Gage True Gage True
A1 1100 750 1400 1000 4150 3750 4350 4000 2750 2250
2 1100 750 1400 1000 4350 4000 4150 3750 2200 1750
B1 670 750 940 1000 4200 4000 3900 3750 2000 2000
2 670 750 670 750 3900 3750 4200 4000 1750 1750
C1 520 750 520 750 4100 + 3000 + 4100 3000 1750 1750
2 520 750 790 1000 4100 + 3000 + 4100 + 3000 + 1750 1750
D1 1600 1250 1080 750 4500 + 3500 + 4500 + 3500 + 3000 2250
2 1600 1250 1080 750 4500 + 3500 + 4500 + 3500 + 3300 2500
E1 700 750 925 1000 3850 4250 3850 4250 1380 1500
2 700 750 925 1000 4150 4500 3650 4000 1850 2000
B B
F1 1075 1000 950 750 3350 4250 3350 4250 1925 2000
B B
2 1075 1000 950 750 3500 4500 3050 3750 1560 1500
G1 660 750 660 750 3500 3750 3000 3250 1550 1750
2 660 750 800 1000 3200 3500 2800 3000 1350 1500
H1 750 750 1000 1000 3500 3500 4250 4250 1500 1500
2 750 750 1000 1000 4000 4000 4000 4000 1750 1750
I1 930 750 910 750 4400 3750 4400 + 3750 + 1800 1500
2 930 750 910 750 4400 3750 4400 + 3750 + 1800 1500
C D
Min Avg 750 750 3625 3125 1500
C D
Max Avg 1250 1000 4375 4125 2375
C D
Grand Avg 833 875 3932 3837 1846
Repeatability Reproducibility
s = 0.0624 S = 0.137
E E
r = 0.179 (TL) R = 0.391 (TL)
A
Reference fluids used and described in Test Method D 2783.
B
Calibration curves shifted.
C
Seven laboratories.
D
Six laboratories.
E
TL = average true load, lbf, of sample tested.
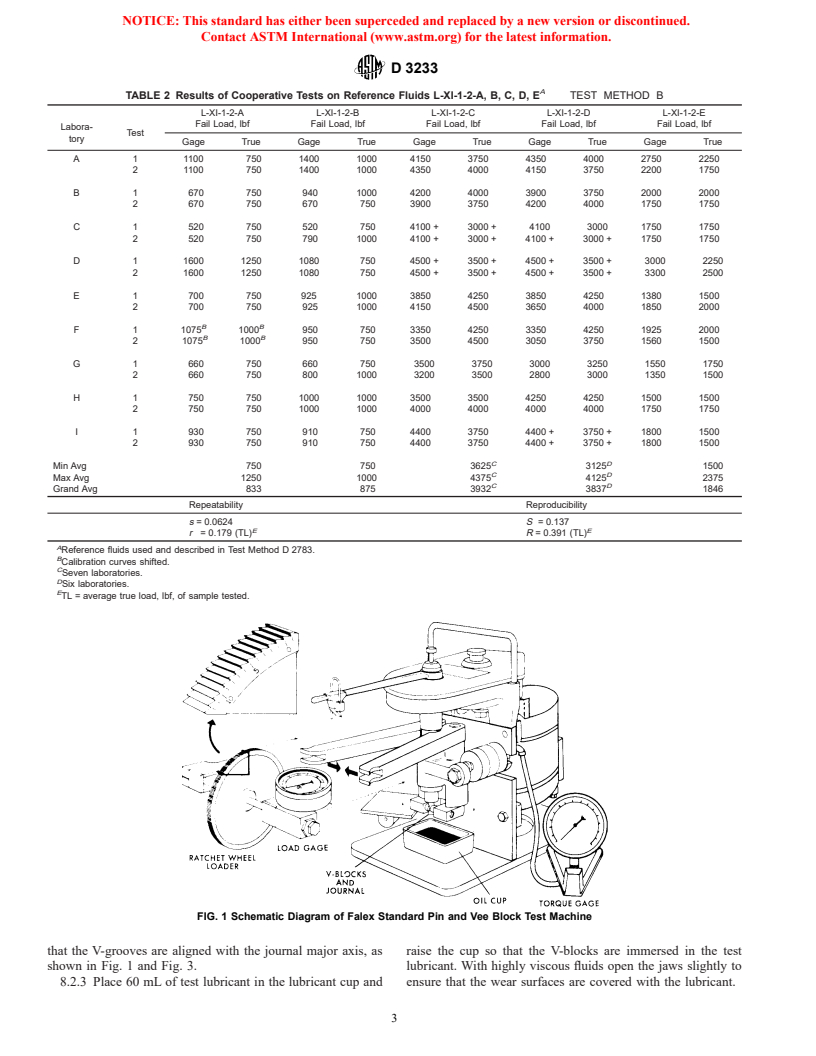
FIG. 1 Schematic Diagram of Falex Standard Pin and Vee Block Test Machine
that the V-grooves are aligned with the journal major axis, as raise the cup so that the V-blocks are immersed in the test
shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 3. lubricant. With highly viscous fluids open the jaws slightly to
8.2.3 Place 60 mL of test lubricant in the lubricant cup and ensure that the wear surfaces are covered with the lubricant.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 3233
FIG. 2 Falex Digital Pin and Vee Block Test Machine
from the left jaw socket (Fig. 5).
10.2 Insert the special Allen screw with the attached 10-mm
Brinnell ball into the working face of the left jaw. Adjust so
that the ball projects about ⁄32 in. (approximately 4 mm) from
the face of the jaw.
10.3 Insert the back-up plug in the counterbore of the
right-hand jaw. Adjust so that the plug projects about ⁄32 in.
(approximately 0.8 mm) from the face.
10.4 Support the standard test coupon so that the upper edge
of the coupon is about ⁄32in. (approximately 2.5 mm) below
the upper surface of the jaws. Place a steel rule across the face
of the jaws. Adjust the Allen screw with the attached 10-mm
ball until the face of the jaws are parallel to the steel rule with
the test coupon in position for indentation.
FIG. 3 Exploded View of V-Blocks and Journal Arrangement,
10.5 With the test coupon in position for the first impres-
Falex Pin and Vee Block Test Machines
sion, place the load gage assembly on the level arms. Remove
the slack from the assembly by moving the ratchet wheel by
8.2.4 Place the automatic loading device, with attached
hand.
gage, on the jaw arms.
10.6 Place the loading lever on the ratchet wheel and actuate
9. Preparation of True Load Calibration Curve the motor. Allow the motor to run until the load gage indicates
a load of 500 lbf (2224 N). A slight take-up on the ratchet
9.1 On log-log paper (K & E 467080 or equivalent) draw a
wheel is required to hold the load due to the ball sinking into
straight-line plot of load, pounds-force (newtons) (ordinate),
the test coupon. After a 500-lbf (2224-N) load is obtained, hold
versus indentation diameter, millimetres (abscissa), using the
for 1 min for the indentation to form.
data points shown below. Label this curve “True Load” (Note
10.7 Turn off the machine and back off the load until the test
5).
coupon is free of the jaws. Advance the test coupon approxi-
Load, lbf (N) Diameter, mm
(Ordinate) (Abscissa) mately ⁄8 in. (approximately 9.5 mm). Additional indentations
should be separated by a minimum distance of 2.5 times the
500 (2224) 2.62
diameter of the initial indentation. Check the alignment of the
1000 (4450) 3.42
1500 (6672) 4.00 jaws, and repeat the procedure described in 10.6 at gage loads
2000 (8896) 4.47
of 1000, 1500, and 2000 lbf (4448, 6672, and 8896 N).
NOTE 5—Fig. 3 shows the true-load calibration curve for the prescribed
10.8 Remove the load gage assembly and test coupon and
4500-lbf (20 000-N) gage, prepared as covered in 9.1. Copies of Fig. 4, 8
measure the diameter of each indentation to 0.01 mm with a
by 11 in., are available at a nominal cost from ASTM. Although not
microscope. Make three measurements of the indentation
originally used in development of these test methods, the 3000-lb direct
diameter, rotating the test coupon to ensure that no two
reading load gage should be satisfactory providing results are corrected
measurements represent the same points. Average the three
and reported with respect to the true load (4500-lbf) reference line. Refer
measurements of each impression and record.
to Test Method D 2670 for calibration of 3000-lb load gage.
10.9 Plot the four impression readings on the same log-log
10. Calibration of Load Gage 4500 lbf (20 000 N)
plot of true load prepared as prescribed in 9.1 and shown as
10.1 Remove the Allen set screw and ⁄2-in. (12.70-mm) ball Fig. 4. Draw a straight line thr
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.