ASTM A387/A387M-17a(2023)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, Chromium-Molybdenum
Standard Specification for Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, Chromium-Molybdenum
ABSTRACT
This specification covers chromium-molybdenum alloy steel plates for welded broilers and pressure vessels designed for elevated temperature service. Materials considered under this specification are available in grades 2, 12, 11, 22, 22L, 21, 21L, 5, 9 and 91. The steel materials shall be killed and shall be thermally treated. The steel specimens shall undergo heat analysis and product analysis and shall conform to the chemical requirements for carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon, chromium, molybdenum, nickel, vanadium, columbium, boron, nitrogen, aluminum, titanium, and zirconium. The steel specimens shall also undergo tension tests and shall conform to the required values of tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification2 covers chromium-molybdenum alloy steel plates intended primarily for welded boilers and pressure vessels designed for elevated temperature service.
1.2 Plates are available under this specification in several grades having different alloy contents as follows:
Nominal
Nominal
Chromium
Molybdenum
Grade
Content, %
Content, %
2
0.50
0.50
12
1.00
0.50
11
1.25
0.50
22
2.25
1.00
21
3.00
1.00
5
5.00
0.50
9
9.00
1.00
91
9.00
1.00
1.3 Each grade except Grade 91 is available in two classes of tensile strength levels as defined in the Tensile Requirements tables. Grade 91 is available only as Class 2. Grade 91 consists of two types, with Type 2 differentiated from Type 1 by requiring restricted composition for the enhancement of creep resistance.
Note 1: Grade 911, previously covered by this specification, is now covered by Specification A1017/A1017M.
1.4 The maximum thickness of plates is limited only by the capacity of the composition to meet the specified mechanical property requirements.
1.5 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents. Therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with this specification.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: A387/A387M − 17a (Reapproved 2023) Used in USDOE-NE Standards
Standard Specification for
Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, Chromium-
Molybdenum
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A387/A387M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
2 two systems may result in nonconformance with this specifi-
1.1 This specification covers chromium-molybdenum alloy
cation.
steel plates intended primarily for welded boilers and pressure
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
vessels designed for elevated temperature service.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.2 Plates are available under this specification in several
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
grades having different alloy contents as follows:
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
Nominal Nominal
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Chromium Molybdenum
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Grade Content, % Content, %
2 0.50 0.50
12 1.00 0.50
2. Referenced Documents
11 1.25 0.50
22 2.25 1.00 2.1 ASTM Standards:
21 3.00 1.00
A20/A20M Specification for General Requirements for Steel
5 5.00 0.50
Plates for Pressure Vessels
9 9.00 1.00
91 9.00 1.00 A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
of Steel Products
1.3 Each grade except Grade 91 is available in two classes
A435/A435M Specification for Straight-Beam Ultrasonic
of tensile strength levels as defined in the Tensile Requirements
Examination of Steel Plates
tables. Grade 91 is available only as Class 2. Grade 91 consists
A577/A577M Specification for Ultrasonic Angle-Beam Ex-
of two types, with Type 2 differentiated from Type 1 by
amination of Steel Plates
requiring restricted composition for the enhancement of creep
A578/A578M Specification for Straight-Beam Ultrasonic
resistance.
Examination of Rolled Steel Plates for Special Applica-
NOTE 1—Grade 911, previously covered by this specification, is now
covered by Specification A1017/A1017M.
tions
A1017/A1017M Specification for Pressure Vessel Plates,
1.4 The maximum thickness of plates is limited only by the
Alloy Steel, Chromium-Molybdenum-Tungsten
capacity of the composition to meet the specified mechanical
2.2 AWS Specifications:
property requirements.
A5.5/A5.5M Low-Alloy Steel Electrodes for Shielded Metal
1.5 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
Arc Welding
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
A5.23/A5.23M Low-Alloy Steel Electrodes and Fluxes for
SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each
Submerged Arc Welding
system are not exact equivalents. Therefore, each system must
A5.28/A5.28M Low-Alloy Steel Electrodes and Rods for
Gas Shielded Arc Welding
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.11 on Steel Plates for Boilers and Pressure Vessels. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2023. Published September 2023. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1955. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as A387/A387M – 17a. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/A0387_A0387M-17AR23. the ASTM website.
2 4
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Specifi- Available from American Welding Society (AWS), 550 NW LeJeune Rd.,
cation SA-387/SA-387M in Section II of that Code. Miami, FL 33126, http://www.aws.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A387/A387M − 17a (2023)
A5.29/A5.29M Low-Alloy Steel Electrodes for Flux Cored 6. Chemical Requirements
Arc Welding
6.1 The steel shall conform to the requirements as to
chemical composition shown in Table 1 unless otherwise
3. General Requirements and Ordering Information
modified in accordance with Supplementary Requirement S17,
3.1 Material supplied to this material specification shall
Vacuum Carbon-Deoxidized Steel, in Specification A20/A20M
conform to Specification A20/A20M. These requirements out-
for grades other than Grade 11.
line the testing and retesting methods and procedures, permis-
sible variations in dimensions and weight, quality and repair of 7. Metallurgical Structure
defects, marking, loading, and ordering information.
7.1 Austenitic Grain Size—Grade 2 material shall have a
3.2 In addition to the basic requirements of this coarse austenitic grain size.
specification, certain supplementary requirements are available
8. Mechanical Requirements
when additional control, testing, or examination is required to
meet end use requirements. The purchaser is referred to the
8.1 Tension Test Requirements:
listed supplementary requirements in this specification and to
8.1.1 The material as represented by the tension test speci-
the detailed requirements in Specification A20/A20M.
mens shall conform to the applicable requirements of Table 2
or Table 3, as specified on the order.
3.3 If the requirements of this specification are in conflict
8.1.2 Adjustment of the percentage elongation requirements
with the requirements of Specification A20/A20M, the require-
is permitted in accordance with Specification A20/A20M for
ments of this specification shall prevail.
plates up to ⁄4 in. [20 mm] inclusive, in thickness when an 8 in.
4. Manufacture
[200 mm] gauge length is used.
4.1 Steelmaking Practice—The steel shall be killed.
9. Repair Welding
5. Heat Treatment
9.1 Repair welding shall be permitted only with the ap-
proval of the purchaser. Repair welds shall meet the require-
5.1 Except for Grade 91, all plates shall be thermally treated
ments of the construction code specified by the purchaser.
either by annealing, normalizing and tempering, or, when
permitted by the purchaser, accelerated cooling from the
9.2 All repair welds in Grade 91 shall be made with one of
austenitizing temperature by air blasting or liquid quenching,
the following welding processes and consumables: SMAW,
followed by tempering. Minimum tempering temperatures
A5.5/A5.5M E90XX-B9; SAW, A5.23/A5.23M EB9 + neutral
shall be as follows:
flux; GTAW, A5.28/A5.28M ER90S-B9; and FCAW A5.29/
Grade Temperature, °F [°C] A5.29M E91T1-B9. In addition, the sum of the Ni+Mn content
2, 12, and 11 1150 [620]
of all welding consumables used to weld repair Grade 91 plate
22, 21, and 9 1250 [675]
shall not exceed 1.0 %.
5 1300 [705]
5.1.1 Grade 91 plates shall be thermally treated, either by
10. Marking
normalizing and tempering or by accelerated cooling from the
10.1 In addition to the marking required in Specification
austenitizing temperature by air blasting or liquid quenching,
A20/A20M, each plate shall be legibly stamped or stenciled,
followed by tempering. Grade 91 plates shall be austenitized at
depending upon the ordered thickness, with the letter A for
1900 °F to 1975 °F [1040 °C to 1080 °C] and shall be tem-
annealed, N for normalized and tempered, and Q for acceler-
pered at 1350 °F to 1470 °F [730 °C to 800 °C].
ated cooled and tempered, as applicable. Grade 91 plates shall
5.2 Grade 5, 9, 21, 22, and 91 plates ordered without the
be marked with the appropriate type. Plates ordered to, and
heat treatment required by 5.1 shall be furnished in either the
conforming to, Type 2 may be marked Type 1 as well.
stress relieved or the annealed condition.
11. Keywords
5.3 For plates ordered without the heat treatment required
11.1 alloy steel; alloy steel plate; creep resistance; elevated
by 5.1, heat treatment of the plates to conform to 5.1 and to
Table 2 or Table 3, as applicable, shall be the responsibility of temperature; pressure containing parts; pressure vessel steels;
the purchaser. steel plates; steel plates for pressure vessels
A387/A387M − 17a (2023)
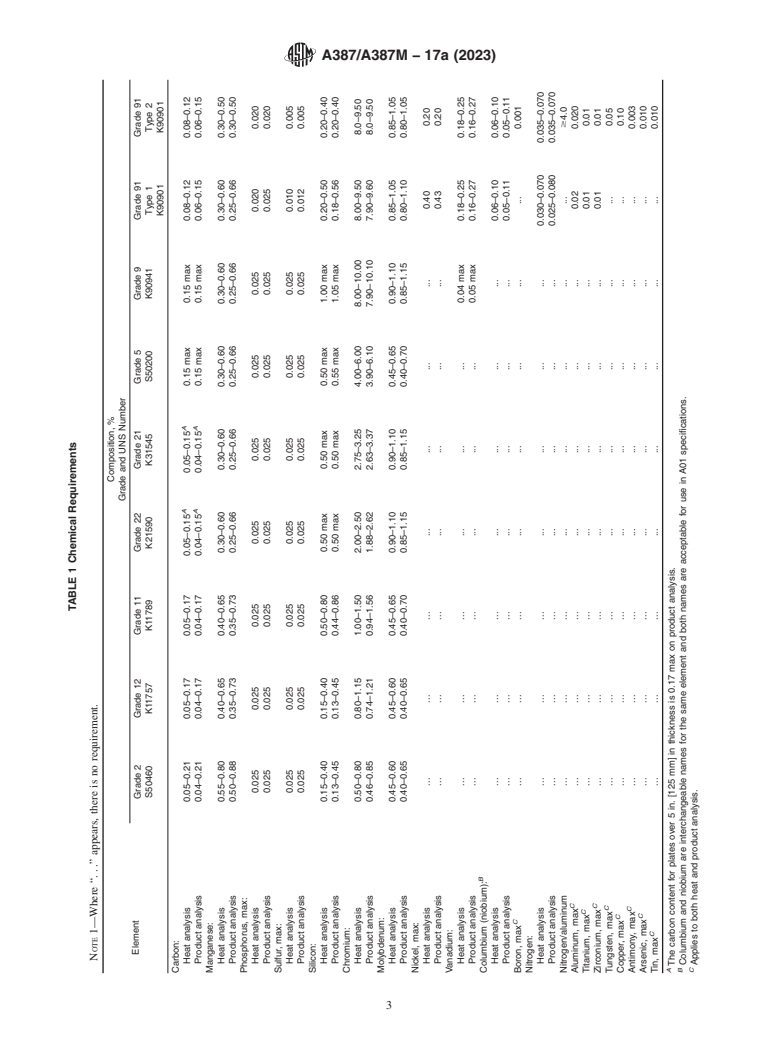
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
NOTE 1—Where “. . .” appears, there is no requirement.
Composition, %
Grade and UNS Number
Element
Grade 2 Grade 12 Grade 11 Grade 22 Grade 21 Grade 5 Grade 9 Grade 91 Grade 91
S50460 K11757 K11789 K21590 K31545 S50200 K90941 Type 1 Type 2
K90901 K90901
Carbon:
A A
Heat analysis 0.05–0.21 0.05–0.17 0.05–0.17 0.05–0.15 0.05–0.15 0.15 max 0.15 max 0.08–0.12 0.08–0.12
A A
Product analysis 0.04–0.21 0.04–0.17 0.04–0.17 0.04–0.15 0.04–0.15 0.15 max 0.15 max 0.06–0.15 0.06–0.15
Manganese:
Heat analysis 0.55–0.80 0.40–0.65 0.40–0.65 0.30–0.60 0.30–0.60 0.30–0.60 0.30–0.60 0.30–0.60 0.30–0.50
Product analysis 0.50–0.88 0.35–0.73 0.35–0.73 0.25–0.66 0.25–0.66 0.25–0.66 0.25–0.66 0.25–0.66 0.30–0.50
Phosphorus, max:
Heat analysis 0.025 0.025 0.025 0.025 0.025 0.025 0.025 0.020 0.020
Product analysis 0
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.