ASTM E971-11
(Practice)Standard Practice for Calculation of Photometric Transmittance and Reflectance of Materials to Solar Radiation
Standard Practice for Calculation of Photometric Transmittance and Reflectance of Materials to Solar Radiation
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Glazed apertures in buildings are commonly utilized for the controlled admission of both light and solar radiant heat energy into the structure. Other devices may also be used to reflect light and solar radiant heat into a building.
Most of the solar radiant energy entering a building in this manner possesses wavelengths that lie between 300 and 2500 nm (3000 to 25 000 Å). Only the portion between 380 and 760 nm is visible radiation, however. In daylighting applications, it is therefore important to distinguish the solar radiant energy transmittance and reflectance of these materials from their luminous (visual or photometric) transmittance and reflectance.
For comparisons of the energy and illumination performances of building fenestration systems it is important that the calculation or measurement, or both, of solar radiant and luminous transmittance and reflectance of materials used in fenestration systems use the same incident solar spectral irradiance distribution.
Solar luminous transmittance and reflectance are important properties in describing the performance of components of solar illumination systems (for example, windows, clerestories, skylights, shading and reflecting devices) and other fenestrations that permit the passage of daylight as well as solar energy into buildings.
This practice is useful for determining the luminous transmittance and reflectance of glazing materials and diffusely or quasi-diffusely reflecting materials used in daylighting systems. For the results of this practice to be meaningful, inhomogeneities or corrugations in the sample must not be large. Test Method E1175 (or Test Method E972) is available for sheet materials that do not satisfy this criterion.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice describes the calculation of luminous (photometric) transmittance and reflectance of materials from spectral radiant transmittance and reflectance data obtained from Test Method E903.
1.2 Determination of luminous transmittance by this practice is preferred over measurement of photometric transmittance by methods using the sun as a source and a photometer as detector except for transmitting sheet materials that are inhomogeneous, patterned, or corrugated.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E971 −11
Standard Practice for
Calculation of Photometric Transmittance and Reflectance
1
of Materials to Solar Radiation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E971; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Reflectance, Transmittance, andAbsorptance of Materials
Using a Large Diameter Integrating Sphere
1.1 This practice describes the calculation of luminous
4
2.2 CIE Standard:
(photometric) transmittance and reflectance of materials from
spectral radiant transmittance and reflectance data obtained Standard Illuminator D65
from Test Method E903.
3. Terminology
1.2 Determination of luminous transmittance by this prac-
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of other terms used in this
tice is preferred over measurement of photometric transmit-
practice, refer to Terminology E772.
tance by methods using the sun as a source and a photometer
3.1.1 illuminance, n—luminous irradiance.
as detector except for transmitting sheet materials that are
inhomogeneous, patterned, or corrugated.
3.1.2 luminous (photometric), adj—referring to a radiomet-
ric quantity, indicates the weighted average of the spectral
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
radiometric quantity, with the photopic spectral luminous
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
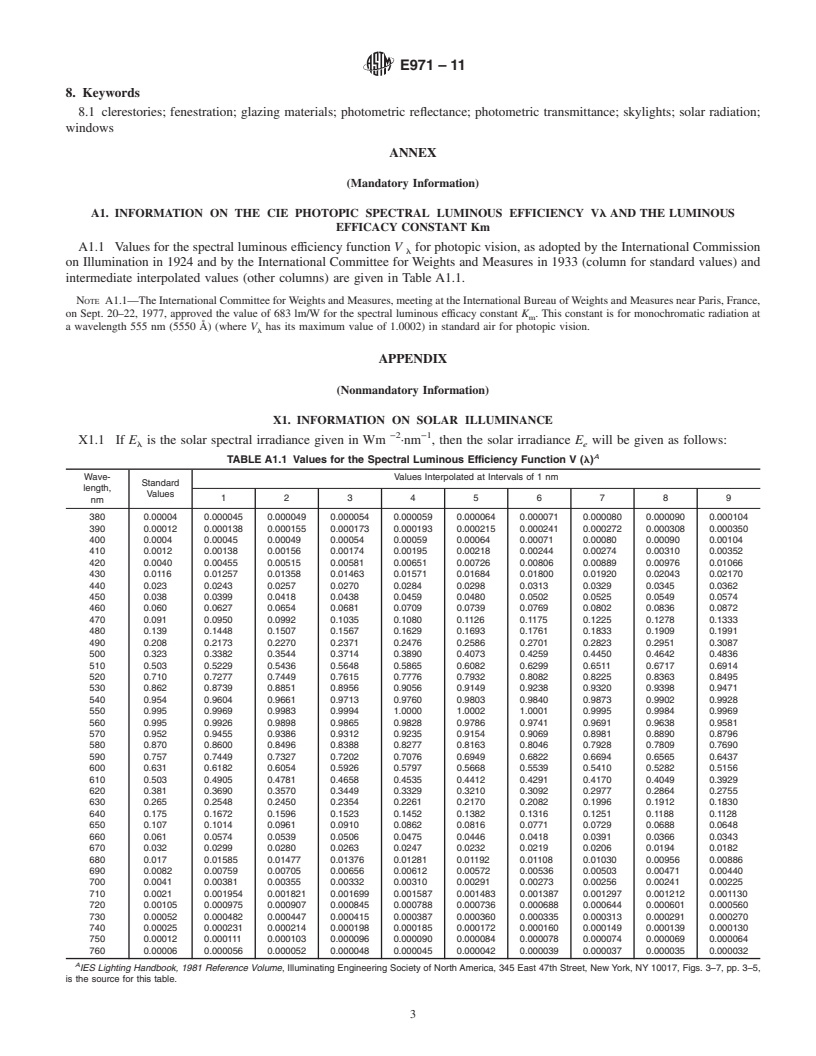
efficiency function given in Annex A1 being the weighting
standard.
function (see Appendix X1).
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.3 radiant flux,Φ = dQ/dt [Watt(W)],n—power emitted,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
transferred, or received in the form of electromagnetic waves
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
or photons. See radiometric properties and quantities.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1.4 solar irradiance at a point of a surface, E =dΦ/dA ,
s
n—the quotient of the solar flux incident on an element of a
2. Referenced Documents
surface containing the point, by the area of that element,
2
measured in watts per square metre.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E772Terminology of Solar Energy Conversion
3.1.5 solar, adj—(1) referring to a radiometric term, indi-
G173TablesforReferenceSolarSpectralIrradiances:Direct
cates that the quantity has the sun as a source or is character-
Normal and Hemispherical on 37° Tilted Surface
istic of the sun. (2) referring to an optical property, indicates
E903Test Method for Solar Absorptance, Reflectance, and
the weighted average of the spectral optical property, with the
Transmittance of Materials Using Integrating Spheres
solar spectral irradiance E used as the weighting function.
sλ
3
(Withdrawn 2005)
3.1.6 spectral, adj—(1) for dimensionless optical
E972Test Method for Solar Photometric Transmittance of
properties, indicates that the property was evaluated at a
Sheet Materials Using Sunlight
specific wavelength, λ, within a small wavelength interval, ∆λ
E1175Test Method for Determining Solar or Photopic
about λ. Symbol wavelength in parentheses, as L (350 nm,
3500Å), or as a function of wavelength, symbol L(λ). (2) for a
radiometric quantity, indicates the concentration of the quan-
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E44 on
tity per unit wavelength or frequency, indicated by the sub-
Solar, Geothermal and Other Alternative Energy Sources and is the direct respon-
sibility of Subcommittee E44.20 on Glass for Solar Applications.
script lambda, as L = dL/dλ, at a specific wavelength. The
λ
Current edition approved Aug. 15, 2011. Published September 2011. Originally
wavelength at which the spectral concentration is evaluated
approvedin1983.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2003asE971–88(2003).DOI:
may be indicated by the wavelength in parentheses following
10.1520/E0971-11.
2
the symbol, L (350 nm).
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
λ
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3 4
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on AvailablefromCommissionInternationaledel’Eclairage,BureauCentraldela
www.astm.org. CIE, 4 Av. du Recteur Poincaré, 75-Paris, France.
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E971−11
4. Summary of Practice large. Test Method E1175 (or Test Method E972) is available
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:E971–88(Reapproved2003) Designation: E971 – 11
Standard Practice for
Calculation of Photometric Transmittance and Reflectance
1
of Materials to Solar Radiation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E971; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice describes the calculation of luminous (photometric) transmittance and reflectance of materials from spectral
radiant transmittance and reflectance data obtained from Test Method E903.
1.2 Determination of luminous transmittance by this practice is preferred over measurement of photometric transmittance by
methods using the sun as a source and a photometer as detector except for transmitting sheet materials that are inhomogeneous,
patterned, or corrugated.
1.3
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E772 Terminology Relating to Solar Energy Conversion
E891Tables for Terrestrial Direct Normal Solar Spectral Irradiance for Air Mass 1.5
G173 Tables for Reference Solar Spectral Irradiances: Direct Normal and Hemispherical on 37 Tilted Surface
E903 Test Method for Solar Absorptance, Reflectance, and Transmittance of Materials Using Integrating Spheres
E972 Test Method for Solar Photometric Transmittance of Sheet Materials Using Sunlight
E1175 TestMethodforDeterminingSolarorPhotopicReflectance,Transmittance,andAbsorptanceofMaterialsUsingaLarge
Diameter Integrating Sphere
3
2.2 CIE Standard:
Standard Illuminator D65
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of other terms used in this practice, refer to Terminology E772.
3.1.1 illuminance, n—luminous irradiance.
3.1.2 luminous (photometric), adj—referring to a radiometric quantity, indicates the weighted average of the spectral
radiometric quantity, with the photopic spectral luminous efficiency function given inAnnexA1 being the weighting function (see
Appendix X1).
3.1.3 radiant flux, F = dQ/dt [Watt(W)], n—power emitted, transferred, or received in the form of electromagnetic waves or
photons. See radiometric properties and quantities.
3.1.4 solar irradiance at a point of a surface, E =dF/dA, n—thequotientofthesolarfluxincidentonanelementofasurface
s
containing the point, by the area of that element, measured in watts per square metre.
3.1.5 solar, adj—(1) referring to a radiometric term, indicates that the quantity has the sun as a source or is characteristic of
the sun. (2) referring to an optical property, indicates the weighted average of the spectral optical property, with the solar spectral
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee E44 on Solar, Geothermal, and OtherAlternative Energy Sources and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee E44.05 on Solar Heating and Cooling Subsystems and Systems.
e1
Current edition approved Aug. 26, 1988. Published December 1988. Originally approved in 1983. Last previous edition approved in 1996 as E971–85(1996) . DOI:
10.1520/E0971-88R03.on Solar Heating and Cooling Systems and Materials.
Current edition approved Aug. 15, 2011. Published September 2011. Originally approved in 1983. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as E971–88(2003). DOI:
10.1520/E0971-11.
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage, Bureau Central de la CIE, 4 Av. du Recteur Poincaré, 75-Paris, France.
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E971 – 11
irradiance E used as the weighting function.
s l
3.1.6 spectral, adj—(1) for dimensionless optical properties,indicatesthatthepropertywasevaluatedataspecificwavelength,
l, within a small wavelength interval, Dl about l. Sy
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.