ASTM F2321-03
(Specification)Standard Specification for Flexible Insulated Temporary By-Pass Jumpers
Standard Specification for Flexible Insulated Temporary By-Pass Jumpers
SCOPE
1.1 These specifications cover the equipment making up the flexible insulated temporary bypass jumpers (bypass jumpers) used on energized power lines and equipment.
1.2 It is common practice for the user of this protective equipment to prepare complete instructions and safety regulations to govern in detail the correct and safe use of such equipment.
1.3 The use and maintenance of this equipment are beyond the scope of these specifications.
1.4 These specifications for a system of bypass jumpers is covered in four parts as follows:TitleSectionsClamps for Bypass JumpersFerrules for Bypass JumpersCable for Bypass JumpersBypass Jumpers (complete assemblywith clamps, ferrules, and cable)
1.5 Each of the four parts is an entity of itself, but is listed as a part of the system for completeness and clarification.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. See ASTM SI 10.
1.7 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portions, Sections 13, 26, and of these specifications.This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory requirements prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F 2321 – 03
Standard Specification for
Flexible Insulated Temporary By-Pass Jumpers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 2321; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope B 173 Specification for Rope-Lay-Stranded Copper Con-
ductors Having Concentric-Stranded Members, for Elec-
1.1 These specifications cover the equipment making up the
trical Conductors
flexible insulated temporary bypass jumpers (bypass jumpers)
D 2768 Specification for General-Purpose Ethylene-
used on energized power lines and equipment.
Propylene Rubber Jacket for Wire and Cable
1.2 It is common practice for the user of this protective
D 2770 Specification for Ozone-Resisting Ethylene-
equipment to prepare complete instructions and safety regula-
Propylene Rubber Integral Insulation and Jacket for Wire
tions to govern in detail the correct and safe use of such
and Cable
equipment.
E 8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
1.3 The use and maintenance of this equipment are beyond
F 819 Terminology Relating to Electrical Protective Equip-
the scope of these specifications.
ment for Workers
1.4 These specifications for a system of bypass jumpers is
SI 10 Practice for Use of the International System of Units
covered in four parts as follows:
(SI) (the Modernized Metric System)
Title Sections
2.2 ANSI Standard:
Clamps for Bypass Jumpers 5-17
Ferrules for Bypass Jumpers 18-31
ANSI C119.4 American National Standard for Electrical
Cable for Bypass Jumpers 32-40
Connectors
Bypass Jumpers (complete assembly 41-53
with clamps, ferrules, and cable) 2.3 NEMA Standard:
WC 8 Ethylene-Propylene-Rubber Insulated Wire and
1.5 Each of the four parts is an entity of itself, but is listed
Cable for the Transmission and Distribution of Electrical
as a part of the system for completeness and clarification.
Energy (formerly ICEA S-68-516)
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. See ASTM SI 10.
3. Terminology
1.7 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the
3.1 Definitions:
test method portions, Sections 13, 26, and 48 of these specifi-
3.1.1 flexible insulated temporary bypass jumpers—devices
cations. This standard does not purport to address all of the
designed and used to keep electric supply circuits effectively
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
continuous (electrically bridged) for short periods of time at
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
work locations when conductors or equipment may otherwise
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
be opened or made electrically discontinuous during work
bility of regulatory requirements prior to use.
operations.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—The devices are normally installed,
2. Referenced Documents
used, and removed as part of a protective insulating system
2.1 ASTM Standards:
composed of insulating covers and/or observances of required
B 172 Specification for Rope-Lay-Stranded Copper Con-
minimum safe approach distances for workers.
ductors Having Bunch-Stranded Members, for Electric
3.2 For definitions of other terms, refer to Terminology
Conductors
F 819.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F18 on
Electrical Protective Equipment for Workers and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee F18.45 on Mechanical Equipment.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2003. Published January 2004.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnual Book ofASTM 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), 1300
the ASTM website. N. 17th St., Suite 1847, Rosslyn, VA 22209.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F2321–03
4. Significance and Use
4.1 These specifications cover the minimum electrical and
physical properties designated by the manufacturer and the
detailed procedures by which such properties are to be deter-
mined. The purchaser may at his option perform or have
performed any of these tests in order to verify the manufactur-
er’sdesignation.Claimsforfailuretomeetthespecificationare
subject to verification by the manufacturer.
4.2 Bypass jumpers are devices designed and used to keep
electrical circuits effectively continuous (electrically bridged)
for short periods of time at work locations when conductors or
equipment may otherwise be opened or made discontinuous
during work operations. Bypass jumpers are insulated to
temporarily protect personnel from brush or accidental contact
only; therefore, when authorizing their use, a margin of safety
should be provided between the maximum voltage used on,
and the proof-test voltage at which they are tested. The
relationship between proof-test voltage and the maximum
FIG.1StyleIClamp
voltage at which bypass jumpers are used is shown in Table 1.
Warning—Portions of these devices (clamps and ferrules) are
not insulated and offer no protection from accidental contact.
CLAMPS FOR BYPASS JUMPERS
5. Scope
5.1 Thisspecificationcoversclampsusedintheassemblyof
bypass jumpers.
6. Classification
6.1 Clamps are furnished in, but not limited to, two styles
according to their function and method of installation.
6.1.1 Style I—Clamps equipped with insulated handles for
installation on energized conductors with rubber gloves. See
Fig. 1.
6.1.1.1 Insulated handles may be either clear or opaque.
6.1.1.2 Insulating materials used in this specification in-
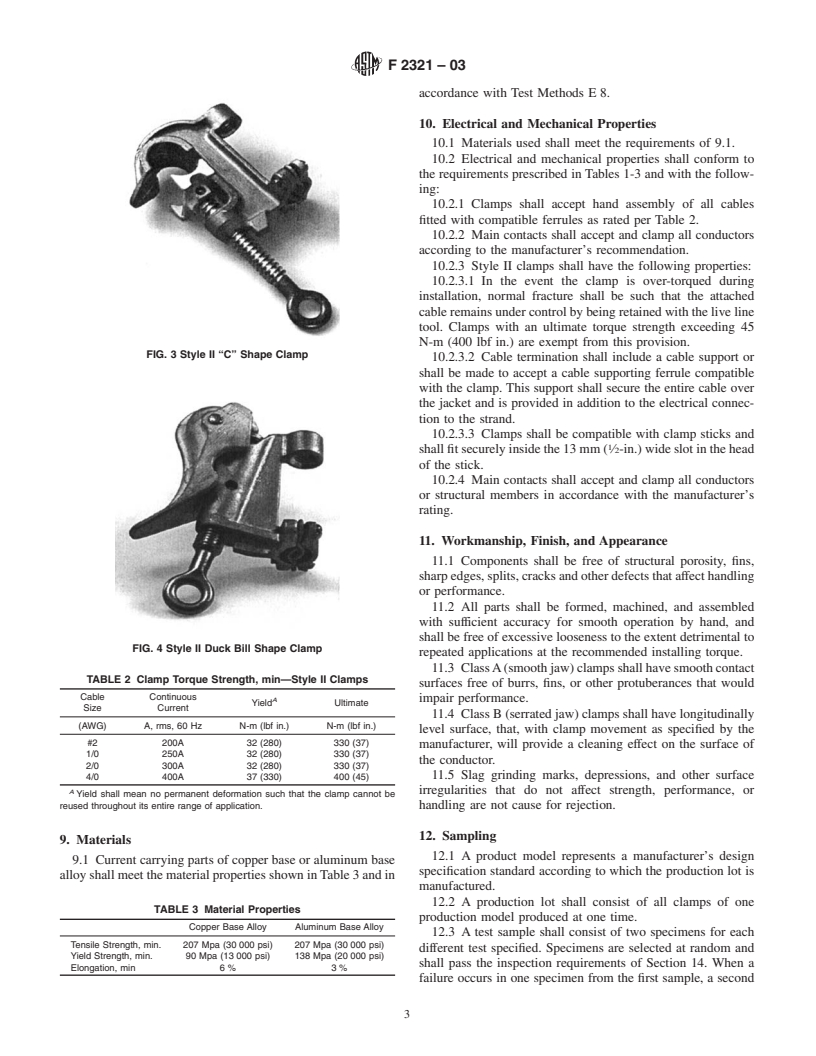
FIG. 2 Style II “C” Shape Clamp
clude thermo-set plastic, elastomers, elastomer compounds,
thermoplastic polymers or any combination, regardless of
origin.
7. Sizes
6.1.2 Style II—Clamps equipped with eyes for installation
7.1 Clamp size is the combination of the main contact and
on energized conductors with live line tools. See Figs. 2-4.
cable size ranges as listed by the manufacturers.
6.1.2.1 Clamps are furnished according to mechanical
strength and current rating. See Table 2.
6.2 Clamps are furnished in two classes according to the 8. Ordering Information
characteristics of the main contact jaws.
8.1 Orders for clamps under this specification shall include
6.2.1 Class A—Clamp jaws with smooth contact surfaces.
this ASTM designation and the following information:
6.2.2 Class B—Clamp jaws with serrations, crosshatching
8.1.1 Quantity,
or other means intended to abrade or bite through corrosion
8.1.2 Name (Bypass Jumper Clamp),
products on the surface of the conductor being clamped.
8.1.3 Main contact size ranges, conductor descriptions, and
type of materials which are to be clamped,
TABLE 1 Proof Test/Use Voltage Relationship
8.1.4 Cable size, material, and description by which clamps
Maximum Nominal AC Proof DC Proof
are to be assembled,
Voltage
Use Voltage Test Voltage Test Voltage
Rating
(rms) V (rms) V (avg) V 8.1.5 Style (see 6.1),
15 kV 15 000 20 000 50 000 8.1.6 Class (see 6.2), and
25 kV 25 000 30 000 60 000
8.1.7 Clamps for bypass jumpers, at the customer’s request,
35 kV 35 000 40 000 70 000
shall meet ANSI C119.4.
F2321–03
accordance with Test Methods E 8.
10. Electrical and Mechanical Properties
10.1 Materials used shall meet the requirements of 9.1.
10.2 Electrical and mechanical properties shall conform to
the requirements prescribed in Tables 1-3 and with the follow-
ing:
10.2.1 Clamps shall accept hand assembly of all cables
fitted with compatible ferrules as rated per Table 2.
10.2.2 Main contacts shall accept and clamp all conductors
according to the manufacturer’s recommendation.
10.2.3 Style II clamps shall have the following properties:
10.2.3.1 In the event the clamp is over-torqued during
installation, normal fracture shall be such that the attached
cableremainsundercontrolbybeingretainedwiththeliveline
tool. Clamps with an ultimate torque strength exceeding 45
N-m (400 lbf in.) are exempt from this provision.
FIG. 3 Style II “C” Shape Clamp
10.2.3.2 Cable termination shall include a cable support or
shall be made to accept a cable supporting ferrule compatible
with the clamp. This support shall secure the entire cable over
the jacket and is provided in addition to the electrical connec-
tion to the strand.
10.2.3.3 Clamps shall be compatible with clamp sticks and
shallfitsecurelyinsidethe13mm( ⁄2-in.)wideslotinthehead
of the stick.
10.2.4 Main contacts shall accept and clamp all conductors
or structural members in accordance with the manufacturer’s
rating.
11. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
11.1 Components shall be free of structural porosity, fins,
sharpedges,splits,cracksandotherdefectsthataffecthandling
or performance.
11.2 All parts shall be formed, machined, and assembled
with sufficient accuracy for smooth operation by hand, and
shall be free of excessive looseness to the extent detrimental to
FIG. 4 Style II Duck Bill Shape Clamp
repeated applications at the recommended installing torque.
11.3 ClassA(smoothjaw)clampsshallhavesmoothcontact
TABLE 2 Clamp Torque Strength, min—Style II Clamps
surfaces free of burrs, fins, or other protuberances that would
Cable Continuous
A impair performance.
Yield Ultimate
Size Current
11.4 Class B (serrated jaw) clamps shall have longitudinally
(AWG) A, rms, 60 Hz N-m (lbf in.) N-m (lbf in.)
level surface, that, with clamp movement as specified by the
#2 200A 32 (280) 330 (37)
manufacturer, will provide a cleaning effect on the surface of
1/0 250A 32 (280) 330 (37)
the conductor.
2/0 300A 32 (280) 330 (37)
11.5 Slag grinding marks, depressions, and other surface
4/0 400A 37 (330) 400 (45)
A irregularities that do not affect strength, performance, or
Yield shall mean no permanent deformation such that the clamp cannot be
reused throughout its entire range of application.
handling are not cause for rejection.
12. Sampling
9. Materials
12.1 A product model represents a manufacturer’s design
9.1 Current carrying parts of copper base or aluminum base
specification standard according to which the production lot is
alloyshallmeetthematerialpropertiesshowninTable3andin
manufactured.
12.2 A production lot shall consist of all clamps of one
TABLE 3 Material Properties
production model produced at one time.
Copper Base Alloy Aluminum Base Alloy
12.3 A test sample shall consist of two specimens for each
Tensile Strength, min. 207 Mpa (30 000 psi) 207 Mpa (30 000 psi)
different test specified. Specimens are selected at random and
Yield Strength, min. 90 Mpa (13 000 psi) 138 Mpa (20 000 psi)
shall pass the inspection requirements of Section 14. When a
Elongation, min 6 % 3 %
failure occurs in one specimen from the first sample, a second
F2321–03
sample from the same lot shall be selected and tested. If the tested, and inspected in accordance with this specification and
second sample (two specimens) passes, the lot shall be ac- have been found to meet the requirements. When specified in
cepted. If one specimen from the second sample fails, the lot the purchase order or contract, a report of design test shall be
shall be rejected. furnished.
13. Design Tests
17. Packaging and Package Marking
13.1 The design tests that follow shall be made on test 17.1 Clamps shall be marked with the name or logo of the
samples of each product model to verify that the requirements
manufacturer, identity number, and date code to indicate year
of this specification are met. of manufacture.
13.2 Mechanical Torque Strength:
17.2 Apacking list indicating manufacturer’s product num-
13.2.1 Install the clamp on the main conductor of the bers and quantities of each different clamp shall be provided
minimum and maximum size for which the clamp is rated and with each shipment.
apply torsion force to the main screw. Force may be applied to 17.3 Each shipment shall be packaged to provide protection
other devices designed to secure the clamp on the conductor. of the contents appropriate for the mode of transportation.
13.2.2 Measure torque by a torque wrench that indicates
CABLE FERRULES FOR BYPASS JUMPERS
torque directly or by other manner easily convertible.
13.2.3 The main conductor is defined as the material(s) on
18. Scope
which the clamp is rated to be used.
18.1 This specification covers ferrules used with bypass
13.2.4 Yield and ultimate strength shall equal or exceed the
jumpers.
values shown in Table 2.
18.2 Two styles of ferrules are available and are designated
13.3 Continuous Current Rating:
as shrouded or unshrouded.
13.3.1 Test the clamp at the continuous current level for
which it is rated. The temperature shall be measured at the
19. Classification
warmest spot on clamp and on the metal strand at the midpoint
19.1 Ferrules are furnished in four types as follows:
of an attached cable, which is a minimum of 1.5 m (5 ft.) in
19.1.1 Type I—Compression ferrule is cylindrical and made
length. The maximum temperature of the clamp shall be lower
for installation on cable stranding by compression.
than the midpoint temperature of the maximum size copper
19.1.2 Type III—Plain stud-shrouded compression ferrule
main or tap cable for which the clamp is rated.
has a stepped bore that accepts entire cable and jacket. (See
14. Inspection and Product Testing
Fig. 5.)
19.1.3 Type IV—Threaded stud shrouded compression fer-
14.1 The clamps shall be inspected and tested as follows:
rulehasasteppedborethatacceptsentirecableoverjacketand
14.1.1 Verification of the main contact and cable capacities
has male threads at forward end. (See Fig. 6.)
are in accordance with 10.2.2 and 10.2.3.
19.1.4 Type VI—Threaded stud compression ferrule has
14.1.2 Visualinspectionandhandoperationshallbedoneto
male threads at forward end. (See Fig. 7.)
verify workmanship, finish, and appearance, which shall be in
accordance with Section 11.
20. Size
14.1.3 Torque test on a test sample shall be in accordance
20.1 Ferrule size is the combination of cable capacity, stud
with 13.2.
description, and size after installation of cable.
15. Acceptance, Rejection and Rehearing
21. Ordering Information
15.1 At the option of the purchaser, a production lot may be
21.1 Orders for ferrules under this specification should
subjected to the following:
include thisASTM designation and the following information:
15.1.1 Inspection in accordance with 14.1 for
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.