ASTM D1191-84(1994)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Concrete Joint Sealers (Withdrawn 1996)
Standard Test Method for Concrete Joint Sealers (Withdrawn 1996)
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover tests for evaluating concrete joint sealers of the hot poured elastic type.
1.2 Test procedures can be the following: Test Paragraph Bond 7.1 Flow 7.2 Penetration 7.3
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
[[Tb Designation: D 1191 - 84 (Reapproved 1994)''
1916 Race St Philadelphia, Pa 191 03
Reprinted from the Annual Book oi ASTM Standards. CoDvriaht ASTM
If &t listed in the current combined rndeq will appear in thé nk edltion
Standard Test Methods for
Concrete Joint Sealers'
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D I 191; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
onginal adoption or, in the case. of revision. the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (6) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
fi NOTE-Kevwords were added editonallv in June 1994.
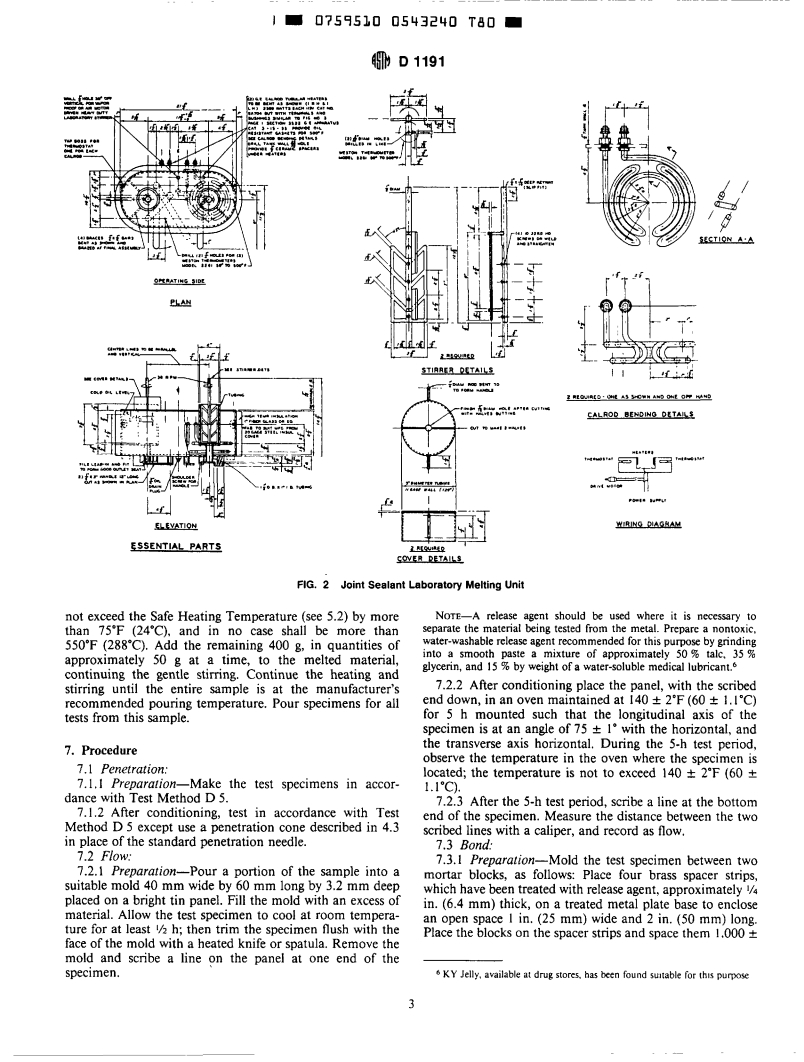
the oil bath and material in the melting vat. The heat source
1. Scope
for the oil bath shall be thermostatically controlled and
1.1 These test methods cover tests for evaluating concrete
capable of maintaining temperatures up to 550°F (288'C).
joint sealers of the hot poured elastic type.
Mechanical agitator speed of approximately 30 & 5 rpm is
1.2 Test procedures can be the following:
recommended. See Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 for typical laboratory
Test Paragraph
melters.
7. I
Bond
4.2 Penetrometer-As described in Test Method D 5.
Flow 1.2
4.3 Cone Penetrometer-As described in Test Method
Penetration 7.3
D 2 17 except that the interior construction may be modified
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
as desired. The total moving weight of the cone and
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
attachments shall be 150.0 -C 0.1 g.
to establish appro-
responsibility ofthe user of this standard
4.4 Forced-dra$ Oven-This oven shall be capable of
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
i 2°F (60 -C
uniformly maintaining a temperature of 140
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1"C).
4.5 Bond Extension Equipment-The extension machine
2. Referenced Documents
used in the bond test shall be so designed that the specimen
2.1 ASTM Standards: can be extended 0.50 in. (12.7 mm) at a uniform rate of
C 33 Specification for Concrete Aggregates' approximately '/8 in. (3.2 mm)/h. It shall consist essentially
C 109 Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic of one or more screws rotated by an electric motor through
Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or 50-mm Cube Speci-
suitable gear reductions. Self-aligning plates or grips, one
fixed and the other carried by the rotating screw or screws,
men~)~
C 150 Specification for Portland Cement3 shall be provided for holding the test specimen in position
C 192 Practice for Making and Curing Concrete Test during the test. A machine suitable for testing three speci-
Specimens in the Laboratory' mens simultaneously is shown in Fig 3.
D 5 Test Method for Penetration of Bituminous Materials4 4.5.1 The extension machine may be an integral part of a
D 2 17 Test Method for Cone Penetration of Lubricating low temperature environmental chest or capable of being
Grease5 placed in a low temperature chest capable of maintaining O f
2°F (-17.8 * 1.1'C).
3. Significance and Use 4.6 Vernier Caliper, with accuracy of I0.25 mm.
3.1 These test methods establish test procedures for labo-
5. Standard Conditions for Test
ratory evaluation of materials that will form a resilient and
5.1 The laboratory atmospheric conditions, hereinafter
adhesive compound capable of effectively sealing joints
referred to as standard conditions, shall be a temperature of
against the infiltration of moisture and foreign material
75 * 7°F (24 f 4°C) and a relative humidity of 50 le 10 %.
throughout repeated cycles of expansion and contraction
5.2 The Safe Heating Temperature and Pouring Temper-
with temperature changes.
ature for the sealer shall be SUDDhd bv the manufacturer.
The Safe Heating Temperature shall no; be exceeded during
4. Apparatus
the melting of the sealer or at the time of preparation of test
4.1 Laboratory Melter-The equipment for melting of the
specimens.
joint sealer must be a double-boiler, oil-jacketed melter
5.3 After test specimens have been prepared, the speci-
equipped with a mechanical agitator and thermometers for
mens shall be stored at laboratory standard conditions for 24
f 2 h before the beginning of any test.
I These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-4 on
6. Preparation for Testing
Road and Paving Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
6.1 Mortar Blocks-Prepare cement mortar blocks, each
DO4.33 on Formed-In-Place Sealants for Joints and Cracks in Pavement.
Current edition approved June 29, 1984. Published August 1984.
1 by 2 by 3 in. (25 by 50 by 75 mm) in size, using one part of
* Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.02.
high early strength portland cement conforming to Type III
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.01.
of Specification C 150 to two parts by weight of clean,
4 Annual Bwk of ASTM Standardr, Vol 04.03.
Annual Bwk o/ASTM Standards, Vol 05.0 I. uniformly graded, concrete fine aggregate conforming to
~~
1- 0759510 O543239 2bî
OPLRATIYG fio€
PLAN
-
END VIEW
ELEVATION
DRIVE AND FRAME
FIG. 1 Joint Sealant Laboratory Melting Unit
of the blocks of film or powder by vigorous
Specification C 33. Use sufficient water to produce a flow of the surface
100 f 5 when tested in accordance with the procedure for brushing with a stiff-bristled fiber brush. Store the prepared
the determination of consistency of cement mortar described blocks in the desiccator until ready for the pouring opera-
in Method C 109. Afier curing 1 day in moist air and 6 days tion.
in water at 73.4 f 3'F (23 f 1.6'C), surface one 2 by 3 in. (50 6.2 Melting of the Hot Pour Sealer-Select a sample of the
by 75 mm) face of each block by wet grinding with a silicon fresh material, weighing approximately 600 g, in such a
carbide stone, designated as C-30-Q + - VHD, until the manner as to avoid inclusion of the surface layer. Cut sample
aggregate is uniformly exposed. Return the blocks to lime into approximately 50 g segments by the use of a knife or
water storage until needed. Prior to use, oven-dry the blocks spatula. Heat 200 g of the sample, with gentle stirring, to a
to constant weight at a temperature of 220 to 230'F (104 to pouring consistency in a clean container placed in an oil bath
I 10'C), cool to room temperature in a desiccator, and clean
or similar heating unit. The temperature of the batch shall
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.