ASTM A268/A268M-10
(Specification)Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless Steel Tubing for General Service
Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless Steel Tubing for General Service
ABSTRACT
This guide covers standard specification for a number of grades of nominal-wall-thickness, welded ferritic and martensitic stainless steel tubing for general corrosion-resisting and high-temperature service. The steel shall conform to the required chemical composition for carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, aluminum, copper, nitrogen, titanium, and columbium. The number of tubes in a lot heat treated by the continuous process shall be determined from the size of the tubes. The steel shall conform to the following tensile properties: tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation. The tubes shall have a hardness number that will not exceed the prescribed Brinell and Rockwell hardness values. Several mechanical tests shall be conducted, namely: tension test; flaring test (for seamless tubes); flange test (for welded tubes); hardness test; reverse flattening test; intergranular corrosion test; and hydrostatic or nondestructive electric test.
SCOPE
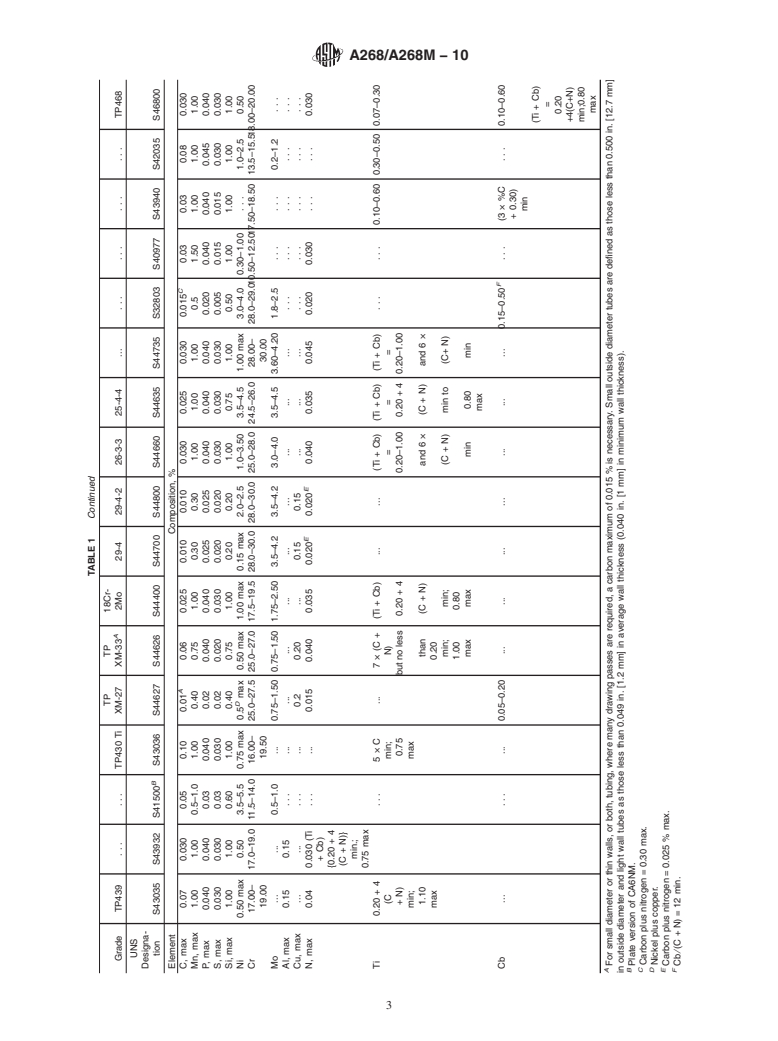
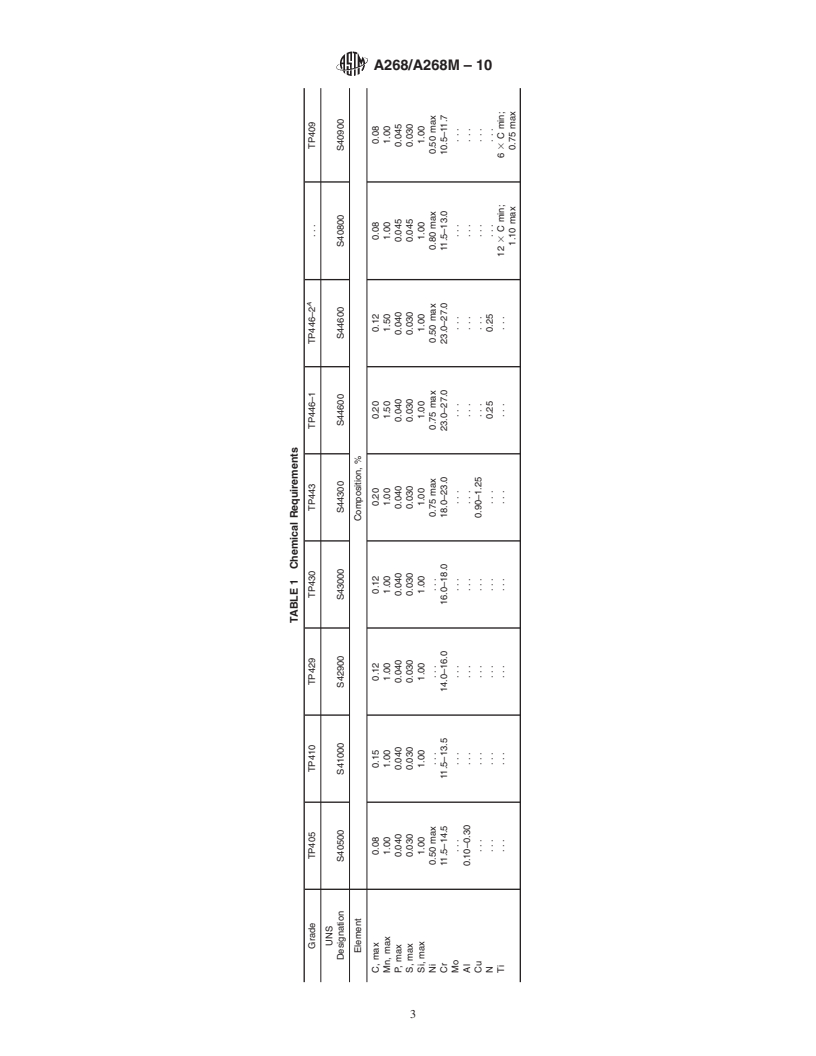
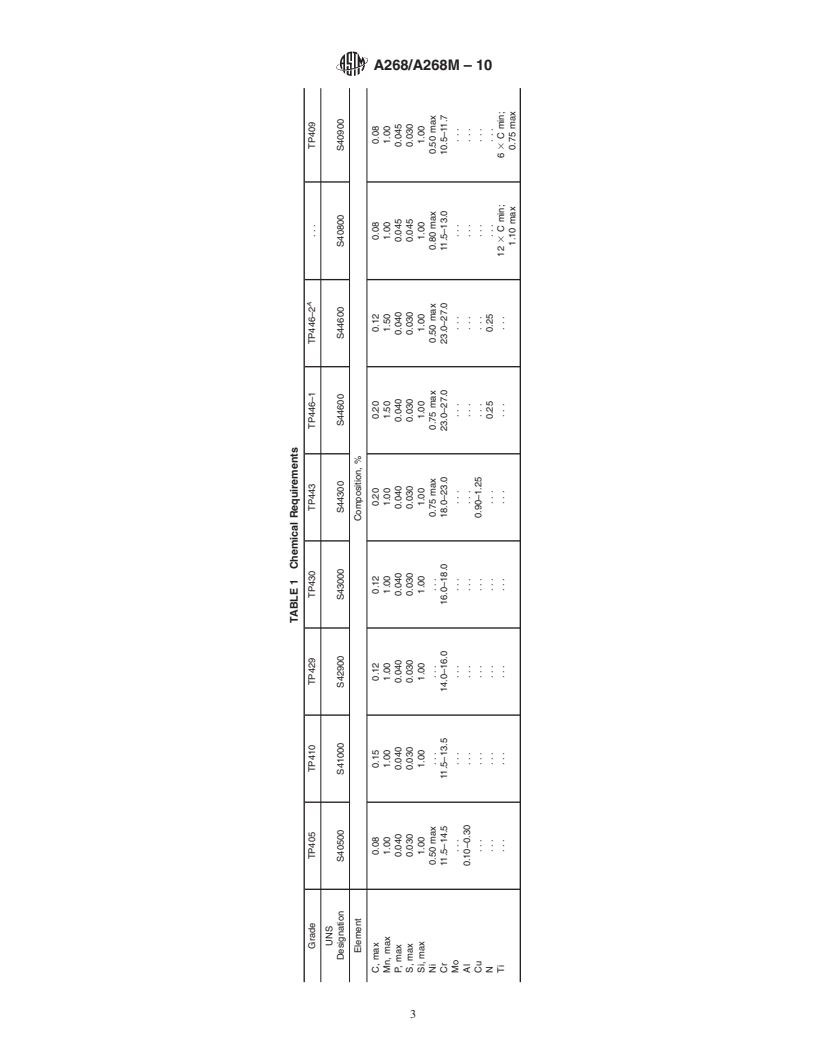
1.1 This specification covers a number of grades of nominal-wall-thickness, stainless steel tubing for general corrosion-resisting and high-temperature service. Most of these grades are commonly known as the “straight-chromium” types and are characterized by being ferromagnetic. Two of these grades, TP410 and UNS S 41500 (Table 1), are amenable to hardening by heat treatment, and the high-chromium, ferritic alloys are sensitive to notch-brittleness on slow cooling to ordinary temperatures. These features should be recognized in the use of these materials. Grade TP439 is used primarily for hot-water tank service and does not require post-weld heat treatment to prevent attack of the heat affected zone.
1.2 An optional supplementary requirement is provided, and when desired, shall be so stated in the order.
1.3 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard. The inch-pound units shall apply unless the “M” designation of this specification is specified in the order.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A268/A268M −10
StandardSpecification for
Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless
1
Steel Tubing for General Service
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA268/A268M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* A763 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular
2 Attack in Ferritic Stainless Steels
1.1 This specification covers a number of grades of
A1016/A1016M Specification for General Requirements for
nominal-wall-thickness, stainless steel tubing for general
Ferritic Alloy Steel, Austenitic Alloy Steel, and Stainless
corrosion-resistingandhigh-temperatureservice.Mostofthese
Steel Tubes
grades are commonly known as the “straight-chromium” types
E213 Practice for Ultrasonic Testing of Metal Pipe and
and are characterized by being ferromagnetic. Two of these
Tubing
grades, TP410 and UNS S 41500 (Table 1), are amenable to
E273 Practice for Ultrasonic Testing of the Weld Zone of
hardening by heat treatment, and the high-chromium, ferritic
Welded Pipe and Tubing
alloys are sensitive to notch-brittleness on slow cooling to
ordinary temperatures. These features should be recognized in
3. Terminology
the use of these materials. Grade TP439 is used primarily for
hot-water tank service and does not require post-weld heat 3.1 Lot Definitions:
3.1.1 For flange and flaring requirements, the term lot
treatment to prevent attack of the heat affected zone.
applies to all tubes, prior to cutting, of the same nominal size
1.2 Anoptionalsupplementaryrequirementisprovided,and
and wall thickness that are produced from the same heat of
when desired, shall be so stated in the order.
steel. If final heat treatment is in a batch-type furnace, a lot
1.3 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
shall include only those tubes of the same size and from the
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
same heat that are heat treated in the same furnace charge. If
SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each
the final heat treatment is in a continuous furnace, the number
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system
of tubes of the same size and from the same heat in a lot shall
shall be used independently of the other. Combining values
be determined from the size of the tubes as given in Table 2.
from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the
3.1.2 Fortensileandhardnesstestrequirements,thetermlot
standard. The inch-pound units shall apply unless the “M”
applies to all tubes, prior to cutting, of the same nominal
designation of this specification is specified in the order.
diameter and wall thickness that are produced from the same
heat of steel. If final heat treatment is in a batch-type furnace,
2. Referenced Documents
a lot shall include only those tubes of the same size and the
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
same heat that are heat treated in the same furnace charge. If
A480/A480M Specification for General Requirements for
the final heat treatment is in a continuous furnace, a lot shall
Flat-Rolled Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Plate,
include all tubes of the same size and heat, heat treated in the
Sheet, and Strip
samefurnaceatthesametemperature,timeatheat,andfurnace
speed.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
4. Ordering Information
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.10 on Stainless and Alloy Steel Tubular Products.
4.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published May 2010. Originally
requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this
approved in 1944. Last previous edition approved in 2005a as A268/A268M–05a.
specification. Such requirements may include, but are not
DOI: 10.1520/A0268_A0268M-10.
2
limited to, the following:
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specifi-
cation SA-268 in Section II of that Code.
4.1.1 Quantity (feet, metres, or number of lengths),
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
4.1.2 Name of material (seamless or welded tubes),
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4.1.3 Grade (Table 1),
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. 4.1.4 Size (outside diameter and nominal wall thickness),
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM Internat
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:A268/A268M–05a Designation: A268/A268M – 10
Standard Specification for
Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless
1
Steel Tubing for General Service
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA268/A268M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
2
1.1 This specification covers a number of grades of nominal-wall-thickness, stainless steel tubing for general corrosion-
resisting and high-temperature service. Most of these grades are commonly known as the “straight-chromium” types and are
characterized by being ferromagnetic.Two of these grades,TP410 and UNS S 41500 (Table 1), are amenable to hardening by heat
treatment, and the high-chromium, ferritic alloys are sensitive to notch-brittleness on slow cooling to ordinary temperatures.These
features should be recognized in the use of these materials. Grade TP439 is used primarily for hot-water tank service and does not
require post-weld heat treatment to prevent attack of the heat affected zone.
1.2 An optional supplementary requirement is provided, and when desired, shall be so stated in the order.
1.3 Thevaluesstatedineitherinch-poundunitsorSIunitsaretoberegardedseparatelyasstandard.Withinthetext,theSIunits
are shown in brackets.The values stated in each system aremay not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system mustshall be used
independentlyoftheother.Combiningvaluesfromthetwosystemsmayresultinnon-conformancewiththespecification.standard.
The inch-pound units shall apply unless the “M” designation of this specification is specified in the order.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A480/A480M Specification for General Requirements for Flat-Rolled Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip
A763 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular Attack in Ferritic Stainless Steels
A1016/A1016M Specification for General Requirements for Ferritic Alloy Steel, Austenitic Alloy Steel, and Stainless Steel
Tubes
E213 Practice for Ultrasonic Testing of Metal Pipe and Tubing
E273 Practice for Ultrasonic Testing of the Weld Zone of Welded Pipe and Tubing
3. Terminology
3.1 Lot Definitions:
3.1.1 For flange and flaring requirements, the term lot applies to all tubes, prior to cutting, of the same nominal size and wall
thickness that are produced from the same heat of steel. If final heat treatment is in a batch-type furnace, a lot shall include only
those tubes of the same size and from the same heat that are heat treated in the same furnace charge. If the final heat treatment
is in a continuous furnace, the number of tubes of the same size and from the same heat in a lot shall be determined from the size
of the tubes as given in Table 2.
3.1.2 For tensile and hardness test requirements, the term lot applies to all tubes, prior to cutting, of the same nominal diameter
andwallthicknessthatareproducedfromthesameheatofsteel.Iffinalheattreatmentisinabatch-typefurnace,alotshallinclude
only those tubes of the same size and the same heat that are heat treated in the same furnace charge. If the final heat treatment
is in a continuous furnace, a lot shall include all tubes of the same size and heat, heat treated in the same furnace at the same
temperature, time at heat, and furnace speed.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA01 on Steel, Stainless Steel,Steel and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.10 on Stainless and Alloy Steel Tubular Products .
Current edition approved SeptemberApril 1, 2005.2010. Published September 2005.May 2010. Originally approved in 1944. Last previous edition approved in 2005a as
A268/A268M–05.A268/A268M–05a. DOI: 10.1520/A0268_A0268M-105A.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specification SA-268 in Section II of that Code.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United S
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:A268/A268M–05a Designation: A268/A268M – 10
Standard Specification for
Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless
1
Steel Tubing for General Service
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA268/A268M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
2
1.1 This specification covers a number of grades of nominal-wall-thickness, stainless steel tubing for general corrosion-
resisting and high-temperature service. Most of these grades are commonly known as the “straight-chromium” types and are
characterized by being ferromagnetic.Two of these grades,TP410 and UNS S 41500 (Table 1), are amenable to hardening by heat
treatment, and the high-chromium, ferritic alloys are sensitive to notch-brittleness on slow cooling to ordinary temperatures.These
features should be recognized in the use of these materials. Grade TP439 is used primarily for hot-water tank service and does not
require post-weld heat treatment to prevent attack of the heat affected zone.
1.2 An optional supplementary requirement is provided, and when desired, shall be so stated in the order.
1.3 Thevaluesstatedineitherinch-poundunitsorSIunitsaretoberegardedseparatelyasstandard.Withinthetext,theSIunits
are shown in brackets.The values stated in each system aremay not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system mustshall be used
independentlyoftheother.Combiningvaluesfromthetwosystemsmayresultinnon-conformancewiththespecification.standard.
The inch-pound units shall apply unless the “M” designation of this specification is specified in the order.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A480/A480M Specification for General Requirements for Flat-Rolled Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip
A763 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular Attack in Ferritic Stainless Steels
A1016/A1016M Specification for General Requirements for Ferritic Alloy Steel, Austenitic Alloy Steel, and Stainless Steel
Tubes
E213 Practice for Ultrasonic Testing of Metal Pipe and Tubing
E273 Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of the Weld Zone of Welded Pipe and Tubing
3. Terminology
3.1 Lot Definitions:
3.1.1 For flange and flaring requirements, the term lot applies to all tubes, prior to cutting, of the same nominal size and wall
thickness that are produced from the same heat of steel. If final heat treatment is in a batch-type furnace, a lot shall include only
those tubes of the same size and from the same heat that are heat treated in the same furnace charge. If the final heat treatment
is in a continuous furnace, the number of tubes of the same size and from the same heat in a lot shall be determined from the size
of the tubes as given in Table 2.
3.1.2 For tensile and hardness test requirements, the term lot applies to all tubes, prior to cutting, of the same nominal diameter
andwallthicknessthatareproducedfromthesameheatofsteel.Iffinalheattreatmentisinabatch-typefurnace,alotshallinclude
only those tubes of the same size and the same heat that are heat treated in the same furnace charge. If the final heat treatment
is in a continuous furnace, a lot shall include all tubes of the same size and heat, heat treated in the same furnace at the same
temperature, time at heat, and furnace speed.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA01 on Steel, Stainless Steel,Steel and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.10 on Stainless and Alloy Steel Tubular Products .
Current edition approved SeptemberApril 1, 2005.2010. Published September 2005.May 2010. Originally approved in 1944. Last previous edition approved in 2005a as
A268/A268M–05.A268/A268M–05a. DOI: 10.1520/A0268_A0268M-105A.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specification SA-268 in Section II of that Code.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, Unit
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.