ASTM D6258-09(2014)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Solvent Red 164 Dye Concentration in Diesel Fuels
Standard Test Method for Determination of Solvent Red 164 Dye Concentration in Diesel Fuels
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method was developed to provide for the enforcement of 26 CFR 48.4082-1(b), which mandates that all tax-exempt diesel fuels be dyed with an amount of Solvent Red 164 at a concentration that is spectrally equivalent to 3.9 lb/103 bbl (11.1 mg/L) of Solvent Red 26. It is employed to verify that the correct amount of Solvent Red 164 is being added to tax-exempt product at terminals or refineries prior to sale, and to detect the presence of Solvent Red 164 in taxed product intended for on-road use.
5.1.1 Solvent Red 26 is the azo dye shown in Fig. 1. It is the standard against which the concentration of Solvent Red 164 is measured because it is available in a certified pure form. Solvent Red 164 is identical in structure to Solvent Red 26 except that it has hydrocarbon (alkyl) chains incorporated to increase its solubility in diesel and burner fuels. The exact composition of Solvent Red 164 will vary from manufacturer to manufacturer and lot to lot depending upon the extent of alkylation that occurs during production; however, its visible spectrum is virtually identical to the spectrum of Solvent Red 26. Solvent Red 164 is employed in the field (instead of Solvent Red 26) to dye tax-exempt diesel and burner fuels because of its higher solubility and relatively low cost.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the procedure for determining the concentration of dye Solvent Red 164 in commercially available diesel and burner fuels using visible spectroscopy.
Note 1: This test method is suitable for all No. 1 and No. 2 grades in Specifications D396 and D975 and for grades DMA and DMB in Specification D2069.
1.2 The concentration ranges specified for the calibration standards are established in response to the Internal Revenue Service dyeing requirements which state that tax-exempt diesel fuel satisfies the dyeing requirement only if it contains the dye Solvent Red 164 (and no other dye) at a concentration spectrally equivalent to 3.9 lb of the solid dye standard Solvent Red 26 per thousand bbl (11.1 mg/L) of diesel fuel.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6258 − 09 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Solvent Red 164 Dye Concentration in
Diesel Fuels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6258; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E131 Terminology Relating to Molecular Spectroscopy
E169 PracticesforGeneralTechniquesofUltraviolet-Visible
1.1 This test method covers the procedure for determining
Quantitative Analysis
the concentration of dye Solvent Red 164 in commercially
E275 Practice for Describing and Measuring Performance of
available diesel and burner fuels using visible spectroscopy.
Ultraviolet and Visible Spectrophotometers
NOTE 1—This test method is suitable for all No. 1 and No. 2 grades in
E288 Specification for Laboratory Glass Volumetric Flasks
Specifications D396 and D975 and for grades DMA and DMB in
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Specification D2069.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.2 The concentration ranges specified for the calibration
E969 Specification for Glass Volumetric (Transfer) Pipets
standards are established in response to the Internal Revenue
2.2 Federal Regulation:
Servicedyeingrequirementswhichstatethattax-exemptdiesel
26 CFR 48.4082-1(b) Federal Excise Tax Regulation
fuel satisfies the dyeing requirement only if it contains the dye
Solvent Red 164 (and no other dye) at a concentration
3. Terminology
spectrally equivalent to 3.9 lb of the solid dye standard Solvent
3.1 Definitions:
Red 26 per thousand bbl (11.1 mg/L) of diesel fuel.
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
to Terminology E131.
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
4. Summary of Test Method
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 The absorbance of each sample is recorded over a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
specified wavelength range, and the scan is analyzed using
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
derivative analysis software to determine the dye concentra-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
tion.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.2 Derivative analysis methodology is employed to mini-
2. Referenced Documents
mize interferences caused by variations in the color and
composition of the fuel samples regularly tested using this test
2.1 ASTM Standards:
method.
D396 Specification for Fuel Oils
4.2.1 Naturally occurring diesel test fuels range in color
D975 Specification for Diesel Fuel Oils
3 from water white to nearly black, and many of the samples
D2069 Specification for Marine Fuels (Withdrawn 2003)
tested using this test method have also had used oils and other
D3699 Specification for Kerosine
products blended with them. These variations in color and
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
composition have a significant effect upon absorbance charac-
Petroleum Products
teristics of the samples in the region of the visible spectrum
where azo dyes absorb. Standard operating procedures to
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
correct for these background variations would involve running
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
SubcommitteeD02.05onPropertiesofFuels,PetroleumCokeandCarbonMaterial.
a neat (undyed) sample and subtracting out the background
CurrenteditionapprovedMay1,2014.PublishedJuly2014.Originallyapproved
absorbance. In most situations involved with the application of
in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as D6258 – 09. DOI: 10.1520/
this test method, however, neat material is not available, so no
D6258-09R14.
background corrections can be made.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4.2.2 The second derivative of the absorbance of these dyes
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
in the visible region is a function of the fine structure of the
the ASTM website.
3 dye’s absorbance peak (versus its height or area) and is
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org. relatively unaffected by changes in background absorbance.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D6258 − 09 (2014)
NOTE 2—Instruments having different specifications, for example,
minimum slit width 2 to 4 nm, no data storage, diode array
spectrophotometers, and so forth, may be used if they provide demonstra-
bly equivalent results. Equivalence can be demonstrated by successful
(within reproducibility limits) participation in inter- or intra-laboratory
studies using this test method.
6.1.1 For applicable general techniques and methods of
testing spectrophotometers to be used in this test method, refer
to Practices E169 and E275.
6.2 Sample Cells (Cuvettes), one or more fused silica or
glass cells having sample path length of 1.0 cm.
FIG. 1 Structure of Solvent Red 26
6.3 Analytical Balance, 0.1 mg sensitivity, 60.05 mg pre-
cision.
Further, the specific sections (maxima and minima) of the
6.4 Volumetric Pipettes, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 mL, Class A,
second derivative spectra employed for this analysis are a
according to Specification E969.
function of the fine structure of the top of the absorbance curve
which has been found to be unique to the azo dyes. 6.5 Volumetric Flasks, 100 mL and 250 mL, Class A,
borosilicate glass, according to Specification E288.
5. Significance and Use
7. Reagents
5.1 This test method was developed to provide for the
7.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
enforcement of 26 CFR 48.4082-1(b), which mandates that all
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
tax-exemptdieselfuelsbedyedwithanamountofSolventRed
all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Commit-
164 at a concentration that is spectrally equivalent to 3.9 lb/10
tee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society
bbl(11.1mg/L)ofSolventRed26.Itisemployedtoverifythat
where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
the correct amount of Solvent Red 164 is being added to
used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
tax-exempt product at terminals or refineries prior to sale, and
sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the
to detect the presence of Solvent Red 164 in taxed product
accuracy of the determination.
intended for on-road use.
5.1.1 Solvent Red 26 is the azo dye shown in Fig. 1.Itisthe
7.2 Solvent Red 26 (Dye Standard)—Dye, Color Index
standard against which the concentration of Solvent Red 164 is
Solvent Red 26, 1-[[2,5-dimethyl-4-[(2-methylphenyl)
measured because it is available in a certified pure form.
azo]phenyl]azo]-2-naphthol, Chemical Abstract Services Reg-
Solvent Red 164 is identical in structure to Solvent Red 26
istry No. 4477-79-6, dry powder with certified purity, and
except that it has hydrocarbon (alkyl) chains incorporated to
maximum absorbance at 512 6 20 nm.
increase its solubility in diesel and burner fuels. The exact
7.3 Kerosine—1-K, water-white, conforming to Specifica-
composition of Solvent Red 164 will vary from manufacturer
tion D3699, and having a maximum absorbance against air of
to manufacturer and lot to lot depending upon the extent of
0.08 absorbance units over the wavelength range 450 to
alkylation that occurs during production; however, its visible
750 nm (1.0 cm cell, 120 nm/min scan rate, slit width 1.0 nm).
spectrum is virtually identical to the spectrum of Solvent Red
(Warning—Flammable; harmful if swallowed, inhaled, or
26. Solvent Red 164 is employed in the field (instead of
brought into contact with skin or eyes.)
Solvent Red 26) to dye tax-exempt diesel and burner fuels
7.4 Xylene—(Warning—Extremely flammable; harmful if
because of its higher solubility and relatively low cost.
swallowed, inhaled, or brought into contact with skin or eyes.)
6. Apparatus
8. Sampling
6.1 Spectrophotometer, equipped with automated scanning,
8.1 Use the principles of Practice D4057 in acquisition of
backgroundcorrection,andelectronicdatastoragecapabilities,
test sample(s).
and the ability to automatically record absorbance or transmit-
tance of solutions in the spectral region from 400 to 800
8.2 Precautions must be taken to shield the samples from
nanometers (nm) with a spectral slit width of 1.0 nm or less
sunlight prior to analysis.
(Note 2). Wavelength measurements shall be repeatable and
NOTE 3—Studies have shown that exposure to direct sunlight will show
known to be accurate to within 60.2 nm or less at deuterium
a decrease in dye concentration over time.
peak 656.1 nm. In the absorbance range from 0.01 to 1.0,
9. Calibration and Standardization
absorbancemeasurementsshallhaveaphotometricaccuracyof
60.005 or less and a photometric repeatability of 60.002 or
9.1 Preparation of Stock Standard:
less.
Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For Suggestions on the testing of reagents not
listed by the American Chemical Society, see Annual Standards for Laboratory
Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville,
MD.
D6258 − 09 (2014)
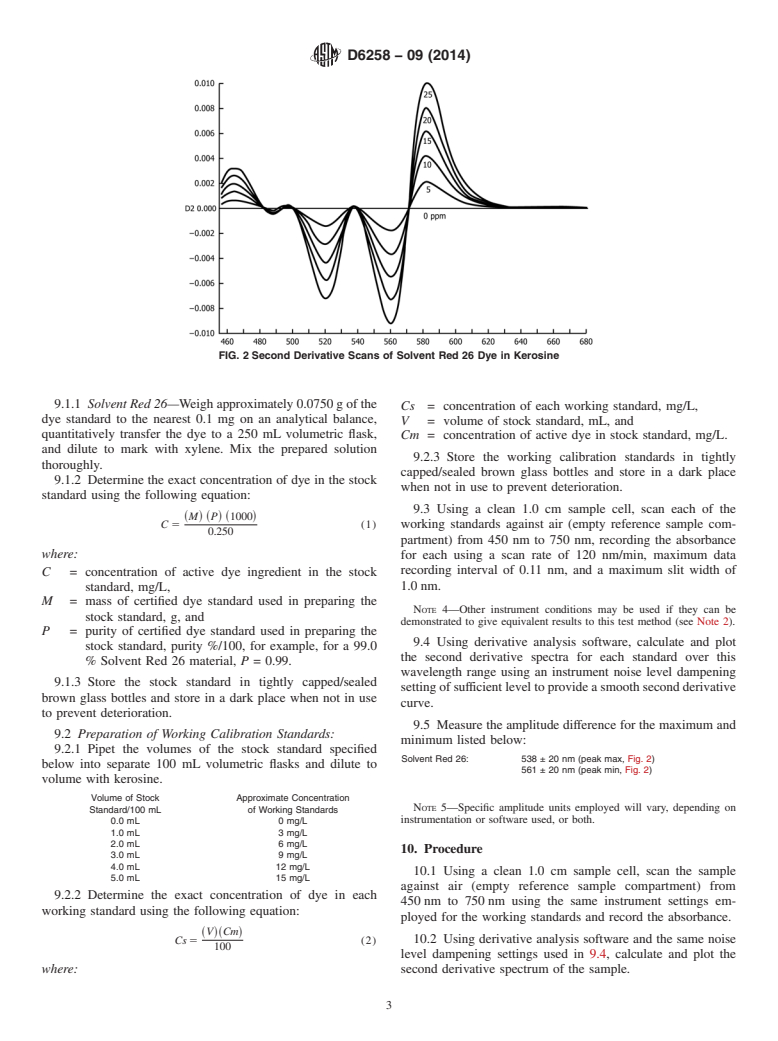
FIG. 2 Second Derivative Scans of Solvent Red 26 Dye in Kerosine
9.1.1 Solvent Red 26—Weigh approximately 0.0750 g of the
Cs
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6258 − 09 D6258 − 09 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Solvent Red 164 Dye Concentration in
Diesel Fuels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6258; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*Scope
1.1 This test method covers the procedure for determining the concentration of dye Solvent Red 164 in commercially available
diesel and burner fuels using visible spectroscopy.
NOTE 1—This test method is suitable for all No. 1 and No. 2 grades in Specifications D396 and D975 and for grades DMA and DMB in Specification
D2069.
1.2 The concentration ranges specified for the calibration standards are established in response to the Internal Revenue Service
dyeing requirements which state that tax-exempt diesel fuel satisfies the dyeing requirement only if it contains the dye Solvent Red
164 (and no other dye) at a concentration spectrally equivalent to 3.9 lb of the solid dye standard Solvent Red 26 per thousand
bbl (11.1 mg/L) of diesel fuel.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D396 Specification for Fuel Oils
D975 Specification for Diesel Fuel Oils
D2069 Specification for Marine Fuels (Withdrawn 2003)
D3699 Specification for Kerosine
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
E131 Terminology Relating to Molecular Spectroscopy
E169 Practices for General Techniques of Ultraviolet-Visible Quantitative Analysis
E275 Practice for Describing and Measuring Performance of Ultraviolet and Visible Spectrophotometers
E288 Specification for Laboratory Glass Volumetric Flasks
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
E969 Specification for Glass Volumetric (Transfer) Pipets
2.2 Federal Regulation:
26 CFR 48.4082-1(b) Federal Excise Tax Regulation
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology E131.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D02.05 on Properties of Fuels, Petroleum Coke and Carbon Material.
Current edition approved March 1, 2009May 1, 2014. Published March 2009July 2014. Originally approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 20042009 as
D6258D6258 – 09.–04. DOI: 10.1520/D6258-09.10.1520/D6258-09R14.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D6258 − 09 (2014)
FIG. 1 Structure of Solvent Red 26
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The absorbance of each sample is recorded over a specified wavelength range, and the scan is analyzed using derivative
analysis software to determine the dye concentration.
4.2 Derivative analysis methodology is employed to minimize interferences caused by variations in the color and composition
of the fuel samples regularly tested using this test method.
4.2.1 Naturally occurring diesel test fuels range in color from water white to nearly black, and many of the samples tested using
this test method have also had used oils and other products blended with them. These variations in color and composition have
a significant effect upon absorbance characteristics of the samples in the region of the visible spectrum where azo dyes absorb.
Standard operating procedures to correct for these background variations would involve running a neat (undyed) sample and
subtracting out the background absorbance. In most situations involved with the application of this test method, however, neat
material is not available, so no background corrections can be made.
4.2.2 The second derivative of the absorbance of these dyes in the visible region is a function of the fine structure of the dye’s
absorbance peak (versus its height or area) and is relatively unaffected by changes in background absorbance. Further, the specific
sections (maxima and minima) of the second derivative spectra employed for this analysis are a function of the fine structure of
the top of the absorbance curve which has been found to be unique to the azo dyes.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method was developed to provide for the enforcement of 26 CFR 48.4082-1(b), which mandates that all tax-exempt
diesel fuels be dyed with an amount of Solvent Red 164 at a concentration that is spectrally equivalent to 3.9 lb/10 bbl (11.1 mg/L)
of Solvent Red 26. It is employed to verify that the correct amount of Solvent Red 164 is being added to tax-exempt product at
terminals or refineries prior to sale, and to detect the presence of Solvent Red 164 in taxed product intended for on-road use.
5.1.1 Solvent Red 26 is the azo dye shown in Fig. 1. It is the standard against which the concentration of Solvent Red 164 is
measured because it is available in a certified pure form. Solvent Red 164 is identical in structure to Solvent Red 26 except that
it has hydrocarbon (alkyl) chains incorporated to increase its solubility in diesel and burner fuels. The exact composition of Solvent
Red 164 will vary from manufacturer to manufacturer and lot to lot depending upon the extent of alkylation that occurs during
production; however, its visible spectrum is virtually identical to the spectrum of Solvent Red 26. Solvent Red 164 is employed
in the field (instead of Solvent Red 26) to dye tax-exempt diesel and burner fuels because of its higher solubility and relatively
low cost.
6. Apparatus
6.1 Spectrophotometer, equipped with automated scanning, background correction, and electronic data storage capabilities, and
the ability to automatically record absorbance or transmittance of solutions in the spectral region from 400 to 800 nanometers (nm)
with a spectral slit width of 1.0 nm or less (Note 2). Wavelength measurements shall be repeatable and known to be accurate to
within 60.2 nm or less at deuterium peak 656.1 nm. In the absorbance range from 0.01 to 1.0, absorbance measurements shall
have a photometric accuracy of 60.005 or less and a photometric repeatability of 60.002 or less.
D6258 − 09 (2014)
NOTE 2—Instruments having different specifications, for example, minimum slit width 2 to 4 nm, no data storage, diode array spectrophotometers, and
so forth, may be used if they provide demonstrably equivalent results. Equivalence can be demonstrated by successful (within reproducibility limits)
participation in inter- or intra-laboratory studies using this test method.
6.1.1 For applicable general techniques and methods of testing spectrophotometers to be used in this test method, refer to
Practices E169 and E275.
6.2 Sample Cells (Cuvettes), one or more fused silica or glass cells having sample path length of 1.0 cm.
6.3 Analytical Balance, 0.1 mg sensitivity, 60.05 mg precision.
6.4 Volumetric Pipettes, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 mL, Class A, according to Specification E969.
6.5 Volumetric Flasks, 100 mL and 250 mL, Class A, borosilicate glass, according to Specification E288.
7. Reagents
7.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that all
reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Committee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society where
such specifications are available. Other grades may be used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of sufficiently high
purity to permit its use without lessening the accuracy of the determination.
7.2 Solvent Red 26 (Dye Standard) —Standard)—Dye, Color Index Solvent Red 26, 1-[[2,5-dimethyl-4-[(2-methylphenyl)
azo]phenyl]azo]-2-naphthol, Chemical Abstract Services Registry No. 4477-79-6, dry powder with certified purity, and maximum
absorbance at 512 6 20 nm.
7.3 Kerosine—1-K, water-white, conforming to Specification D3699, and having a maximum absorbance against air of 0.08
absorbance units over the wavelength range 450 to 750 nm 750 nm (1.0 cm cell, 120 nm/min scan rate, slit width 1.0 nm).
(Warning—Flammable; harmful if swallowed, inhaled, or brought into contact with skin or eyes.)
7.4 Xylene—(Warning—Extremely flammable; harmful if swallowed, inhaled, or brought into contact with skin or eyes.)
8. Sampling
8.1 Use the principles of Practice D4057 in acquisition of test sample(s).
8.2 Precautions must be taken to shield the samples from sunlight prior to analysis.
NOTE 3—Studies have shown that exposure to direct sunlight will show a decrease in dye concentration over time.
9. Calibration and Standardization
9.1 Preparation of Stock Standard : Standard:
9.1.1 Solvent Red 26— Weigh approximately 0.0750 g of the dye standard to the nearest 0.1 mg on an analytical balance,
quantitatively transfer the dye to a 250 mL volumetric flask, and dilute to mark with xylene. Mix the prepared solution thoroughly.
9.1.2 Determine the exact concentration of dye in the stock standard using the following equation:
M P 1000
~ ! ~ ! ~ !
C 5 (1)
0.250
where:
C = concentration of active dye ingredient in t
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.