ASTM E1154-14
(Specification)Standard Specification for Piston or Plunger Operated Volumetric Apparatus
Standard Specification for Piston or Plunger Operated Volumetric Apparatus
ABSTRACT
This specification covers piston or plunger operated volumetric apparatus (POVA), in particular, the requirements, operating conditions, and test methods. POVA covered by this specification are pipettes, dispensers (with and without valve), dilutors, and displacement burets (with and without valve). Single measurement, replicate delivery, durability, functional (such as tests for leakage, broken parts, existence of air bubbles, and contamination), volumetric, and gravimetric tests shall be performed and shall conform to the requirements specified.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers requirements, operating conditions, and test methods for piston or plunger operated volumetric apparatus (POVA).
1.2 This specification includes specifications applicable for all types of POVA or those given by the manufacturer. The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 13, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E1154 − 14
Standard Specification for
1
Piston or Plunger Operated Volumetric Apparatus
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1154; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
4
1. Scope 3.1.1 accuracy —the accuracy of an instrument is the
closeness of agreement between the nominal volume and the
1.1 This specification covers requirements, operating
mean volume, obtained by applying the test procedure speci-
conditions, and test methods for piston or plunger operated
fied in Section 13 of this specification. It is quantified by the
volumetric apparatus (POVA).
inaccuracy of the mean.
1.2 This specification includes specifications applicable for
all types of POVA or those given by the manufacturer. The 3.1.2 dead volume—the dead volume is that part of the total
following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method
liquid volume, held in the operational part of the device, which
portion, Section 13, of this specification: This standard does
is not delivered.
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
3.1.2.1 Discussion—The dead volume should not be con-
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
fused with the dead space of an air displacement instrument.
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices
3.1.3 disposable—those parts of an instrument that are
and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
intended to be used once only and then discarded. Disposable
to use.
parts are generally intended for use in applications where
2. Referenced Documents
sample carryover is intolerable.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.4 maximum error—the maximum difference between
E617 Specification for Laboratory Weights and Precision
the nominal volume and any single individual volume obtained
Mass Standards
by applying the test procedure specified in Section 13 of this
E898 Test Method of Testing Top-Loading, Direct-Reading
Specification.
Laboratory Scales and Balances
2
3.1.5 maximum expectable error—with more than 95 %
2.2 ISO Documents:
probability, the maximum expectable error is calculated as
ISO 3534 Statistics—Vocabulary and Symbols
follows:
ISO 653 Long Solid-Stem Thermometers for Precision Use
ISO 655 Long Enclosed-Scale Thermometers for Precision
6 1E 112s (1)
~ !
T
Use
where:
ISO 4787 Laboratory Glassware—Volumetric Glassware—
E = inaccuracy of the mean, and
Methods for Testing and Use
T
3
s = standard deviation from the repeatability test in Section
2.3 Other Documents
13.
OIML R 111-1 Weights of classes E , E , F , F , M , M ,
1 2 1 2 1 1–2
M , M and M : Part 1: Metrological and technical
2 2–3 3
3.1.6 nominal volume(s)—the stated volume(s) for which
requirements
performance is specified.
3. Terminology
3.1.7 piston or plunger operated volumetric apparatus
(POVA)—the volume of liquid to be measured with POVA is
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
defined by one or more strokes of one or more pistons or
plungers. POVA may be operated manually or mechanically
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E41 on
(for example, electrically, pneumatically or by hydrostatic
Laboratory Apparatus and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E41.06 on
pressure).
Laboratory Instruments and Equipment.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2014. Published January 2015. Originally
3.1.7.1 Discussion—In the following text the word ‘piston’
approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as E1154 – 89 (2008).
means ‘piston or plunger.’
DOI: 10.1520/E1154-14.
2
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
3
Available from International Organization of Legal Metrology, 11 rue Turgot,
4
75009 Paris, France. www.oilm.org/en/ These definitions apply only in the cases where the distributions are Gaussian.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1154 − 14
4
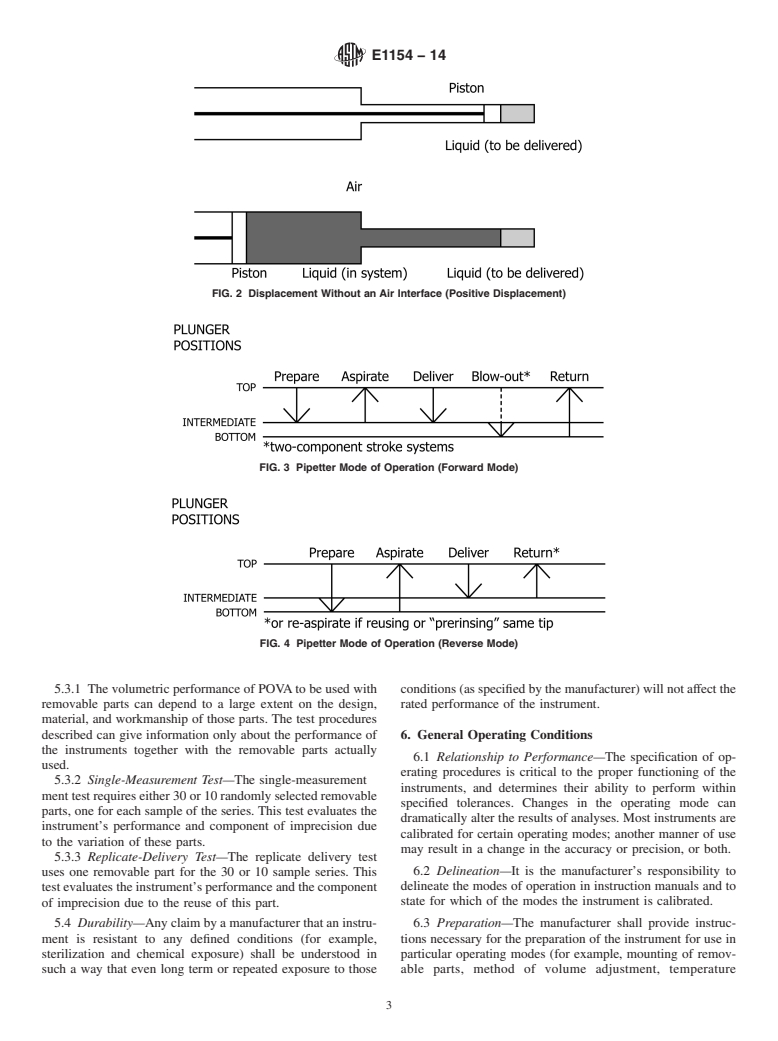
3.1.8 precision —the closeness of agreement between the 4.1.2 Dispenser—A measuring instrument for delivering
individual volumes obtained by applying the test procedure predetermined volumes of liquid from a reservoir. The reser-
specified in this specification. It is quantified by the impreci- voir may be integrated with the instrument or connected
sion. externally.
3.1.8.1 Discussion—The test procedure specified gives only 4.1.3 Dilutor—A measuring instrument for taking up differ-
a measure of the repeata
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E1154 − 89 (Reapproved 2008) E1154 − 14
Standard Specification for
1
Piston or Plunger Operated Volumetric Apparatus
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1154; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers requirements, operating conditions, and test methods for piston or plunger operated volumetric
apparatus (POVA).
1.2 This specification includes specifications applicable for all types of POVA or those given by the manufacturer. The following
precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 13, of this specification: This standard does not purport to
address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish
appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E617 Specification for Laboratory Weights and Precision Mass Standards
E898 Test Method of Testing Top-Loading, Direct-Reading Laboratory Scales and Balances
2
2.2 ISO Documents:
ISO 3534 Statistics—Vocabulary and Symbols
ISO 653 Long Solid-Stem Thermometers for Precision Use
ISO 655 Long Enclosed-Scale Thermometers for Precision Use
ISO 4787 Laboratory Glassware—Volumetric Glassware—Methods for Testing and Use
3
2.3 Other Documents
OIML R 111-1 Weights of classes E , E , F , F , M , M , M , M and M : Part 1: Metrological and technical requirements
1 2 1 2 1 1–2 2 2–3 3
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
4
3.1.1 accuracy —the accuracy of an instrument is the closeness of agreement between the nominal volume and the mean
volume, obtained by applying the test procedure specified in Section 13 of this specification. It is quantified by the inaccuracy of
the mean.
3.1.2 dead volume—the dead volume is that part of the total liquid volume, held in the operational part of the device, which
is not delivered.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E41 on Laboratory Apparatus and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E41.06 on Weighing
Devices.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2008Dec. 1, 2014. Published January 2009January 2015. Originally approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 20032008 as
E1154- 89 (2003).-89 (2008). DOI: 10.1520/E1154-89R08.10.1520/E1154-14.
2
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
3
Available from International Organization of Legal Metrology, 11 rue Turgot, 75009 Paris, France. www.oilm.org/en/
4
These definitions apply only in the cases where the distributions are Gaussian.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—
The dead volume should not be confused with the dead space of an air displacement instrument.
3.1.3 disposable—those parts of an instrument that are intended to be used once only and then discarded. Disposable parts are
generally intended for use in applications where sample carryover is intolerable.
3.1.4 maximum error—the maximum difference between the nominal volume and any single individual volume obtained by
applying the test procedure specified in Section 13 of this ISO Standard. Specification.
3.1.5 maximum expectable error—with more than 95 % probability, the maximum expectable error is calculated as follows:
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1154 − 14
6 1E 112s (1)
~ !
T
where:
E = inaccuracy of the mean, and
T
s = standard deviation from the repeatability test in Section 13.
3.1.6 nominal volume(s)—the stated volume(s) for which performance is specified.
3.1.7 unit of volume—the millilitre or the microlitre, that are accepted substitutes for the cubic centimetre or cubic millimetre.
3.1.7.1 Discussion—
It is recommended that volumes should be specified in microlitres up to 999 μL, and in millilitres from 1 mL.
3.1.7 piston or plunger operated volumetric apparatus (POVA)—the volume of liquid to be measured with POVA is defined by
one or more strokes of one or more pistons or plungers. POVA may be operated manually or mechanically (for example,
electrically, pneumatically or by hydrostatic pressure).
3.
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.