ASTM A572/A572M-15
(Specification)Standard Specification for High-Strength Low-Alloy Columbium-Vanadium Structural Steel
Standard Specification for High-Strength Low-Alloy Columbium-Vanadium Structural Steel
ABSTRACT
This specifiation covers the standard requirements for Grades 42 [290], 50 [345], 55 [380], 60 [415], and 65 [450] of high-strength low-alloy columbium-vanadium structural steel shapes, plates, sheet piling, and bars for applications in bolted, welded, and riveted structures in bridges and buildings. The alloy shall conform to the required contents of columbium, vanadium, titanium, and nitrogen. Permissible values for the product thickness and size is given. Tensile requirements (including yield point, tensile strength, and minimum elongation) and alloy content are also specified. General delivery and test report requirements are also cited.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers five grades of high-strength low-alloy structural steel shapes, plates, sheet piling, and bars. Grades 42 [290], 50 [345], and 55 [380] are intended for riveted, bolted, or welded structures. Grades 60 [415] and 65 [450] are intended for riveted or bolted construction of bridges, or for riveted, bolted, or welded construction in other applications.
1.2 For applications, such as welded bridge construction, where notch toughness is important, notch toughness requirements are to be negotiated between the purchaser and the producer.
1.3 Specification A588/A588M shall not be substituted for Specification A572/A572M without agreement between the purchaser and the supplier.
1.4 The use of columbium, vanadium, titanium, nitrogen, or combinations thereof, within the limitations noted in Section 5, is required; the selection of type (1, 2, 3, or 5) is at the option of the producer, unless otherwise specified by the purchaser. (See Supplementary Requirement S90.)
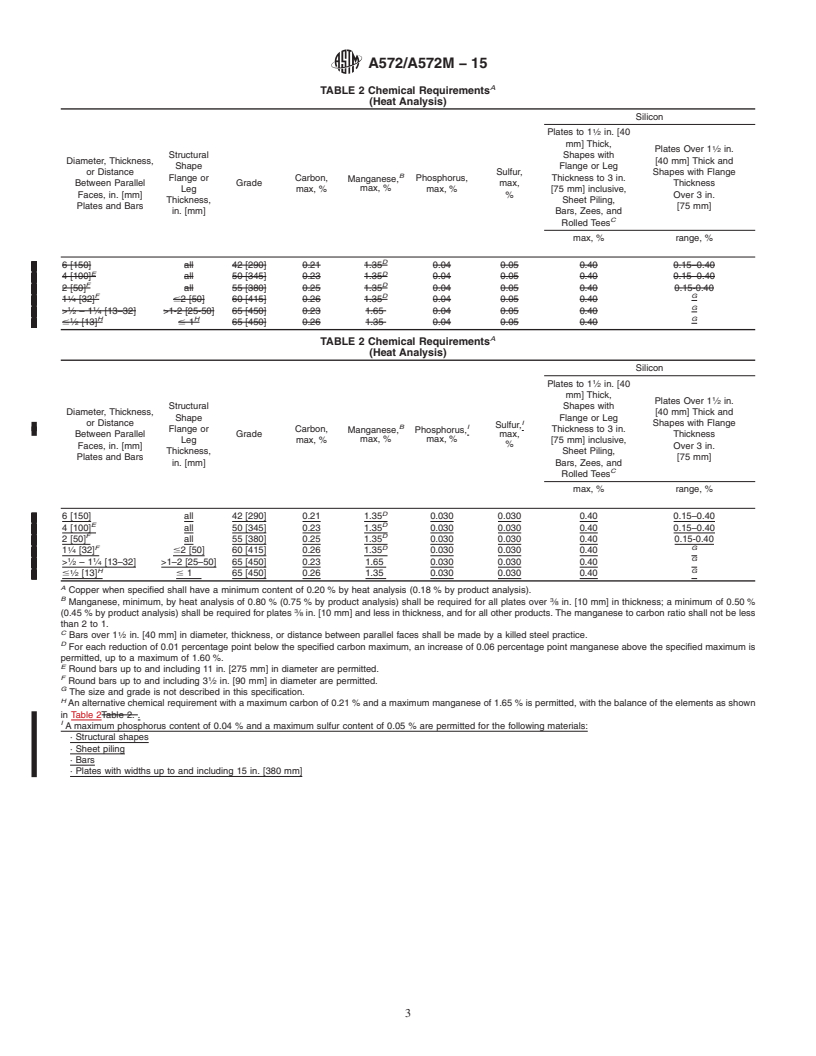
1.5 The maximum thicknesses available in the grades and products covered by this specification are shown in Table 1. (A) In the above tabulation, Grades 42, 50, and 60 [290, 345, and 415], are the yield point levels most closely approximating a geometric progression pattern between 36 ksi [250 MPa], min, yield point steels covered by Specification A36/A36M and 100 ksi [690 MPa], min, yield strength steels covered by Specification A514/A514M.(B) Round bars up to and including 11 in. [275 mm] in diameter are permitted.(C) Round bars up to and including 31/2 in. [90 mm] in diameter are permitted.
1.6 When the steel is to be welded, a welding procedure suitable for the grade of steel and intended use or service is to be utilized. See Appendix X3 of Specification A6/A6M for information on weldability. (A) Copper when specified shall have a minimum content of 0.20 % by heat analysis (0.18 % by product analysis).(B) Manganese, minimum, by heat analysis of 0.80 % (0.75 % by product analysis) shall be required for all plates over 3/8 in. [10 mm] in thickness; a minimum of 0.50 % (0.45 % by product analysis) shall be required for plates 3/8 in. [10 mm] and less in thickness, and for all other products. The manganese to carbon ratio shall not be less than 2 to 1.(C) Bars over 11/2 in. [40 mm] in diameter, thickness, or distance between parallel faces shall be made by a killed steel practice.(D) For each reduction of 0.01 percentage point below the specified carbon maximum, an increase of 0.06 percentage point manganese above the specified maximum is permitted, up to a maximum of 1.60 %.
(E) Round bars up to and including 11 in. [275 mm] in diameter are permitted.(F) Round bars up to and including 31/2 in. [90 mm] in diameter are permitted.(G) The size and grade is not described in this specification.
(H) An alternative chemical requirement with a maximum carbon of 0.21 % and a maximum manganese of 1.65 % is permitted, with the balance of the elements as shown in Table 2.(I) A maximum phosphorus content of 0.04 % and a maximum sulfur content of 0.05 % are permitted for the following materials:
· Structural shapes
· Sheet piling
· Bars
· Plates with widths up to and including 15 in. [380 mm]
1.7 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are ...
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A572/A572M −15 American Association State
Highway and Transportation
Officals Standard
AASHTO No.: M223
Standard Specification for
High-Strength Low-Alloy Columbium-Vanadium Structural
1
Steel
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA572/A572M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system is to
be used independently of the other, without combining values
1.1 This specification covers five grades of high-strength
in any way.
low-alloy structural steel shapes, plates, sheet piling, and bars.
1.8 Thetextofthisspecificationcontainsnotesorfootnotes,
Grades 42 [290], 50 [345], and 55 [380] are intended for
or both, that provide explanatory material. Such notes and
riveted, bolted, or welded structures. Grades 60 [415] and 65
footnotes, excluding those in tables and figures, do not contain
[450] are intended for riveted or bolted construction of bridges,
any mandatory requirements.
or for riveted, bolted, or welded construction in other applica-
tions.
1.9 For structural products produced from coil and fur-
nished without heat treatment or with stress relieving only, the
1.2 For applications, such as welded bridge construction,
additional requirements, including additional testing require-
where notch toughness is important, notch toughness require-
ments and the reporting of additional tests, of Specification
ments are to be negotiated between the purchaser and the
A6/A6M apply.
producer.
1.3 Specification A588/A588M shall not be substituted for
2. Referenced Documents
Specification A572/A572M without agreement between the
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
purchaser and the supplier.
A6/A6M Specification for General Requirements for Rolled
1.4 The use of columbium, vanadium, titanium, nitrogen, or Structural Steel Bars, Plates, Shapes, and Sheet Piling
combinations thereof, within the limitations noted in Section 5, A36/A36M Specification for Carbon Structural Steel
is required; the selection of type (1, 2, 3, or 5) is at the option A514/A514M Specification for High-Yield-Strength,
of the producer, unless otherwise specified by the purchaser. Quenched and Tempered Alloy Steel Plate, Suitable for
(See Supplementary Requirement S90.) Welding
A588/A588M Specification for High-Strength Low-Alloy
1.5 The maximum thicknesses available in the grades and
Structural Steel, up to 50 ksi [345 MPa] Minimum Yield
products covered by this specification are shown in Table 1.
Point, with Atmospheric Corrosion Resistance
1.6 When the steel is to be welded, a welding procedure
3. General Requirements for Delivery
suitable for the grade of steel and intended use or service is to
be utilized. See Appendix X3 of Specification A6/A6M for
3.1 Structural products furnished under this specification
information on weldability.
shall conform to the requirements of the current edition of
Specification A6/A6M, for the specific structural product
1.7 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
ordered, unless a conflict exists in which case this specification
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
shall prevail.
SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each
3.2 Coils are excluded from qualification to this specifica-
tion until they are processed into a finished structural product.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
2
A01.02 on Structural Steel for Bridges, Buildings, Rolling Stock and Ships. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved March 1, 2015. Published March 2015. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as A572/A572M – 13a. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/A0572_A0572M-15. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A572/A572M−15
TABLE 1 Maximum Product Thickness or Size
Yield Point, min Maximum Thickness or Size
Structural Shape
Zees and Rolled
Grade Plates and Bars Flange or Leg
Tees
ksi [MPa] Sheet Piling
Thickness
in. [mm] in. [mm]
A
42 [290] 42 [290] 6 [150] all all all all
A B B
50
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A572/A572M − 13a A572/A572M − 15 American Association State
Highway and Transportation
Officals Standard
AASHTO No.: M223
Standard Specification for
High-Strength Low-Alloy Columbium-Vanadium Structural
1
Steel
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A572/A572M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers five grades of high-strength low-alloy structural steel shapes, plates, sheet piling, and bars. Grades
42 [290], 50 [345], and 55 [380] are intended for riveted, bolted, or welded structures. Grades 60 [415] and 65 [450] are intended
for riveted or bolted construction of bridges, or for riveted, bolted, or welded construction in other applications.
1.2 For applications, such as welded bridge construction, where notch toughness is important, notch toughness requirements are
to be negotiated between the purchaser and the producer.
1.3 Specification A588/A588M shall not be substituted for Specification A572/A572M without agreement between the
purchaser and the supplier.
1.4 The use of columbium, vanadium, titanium, nitrogen, or combinations thereof, within the limitations noted in Section 5, is
required; the selection of type (1, 2, 3, or 5) is at the option of the producer, unless otherwise specified by the purchaser. (See
Supplementary Requirement S90.)
1.5 The maximum thicknesses available in the grades and products covered by this specification are shown in Table 1.
1.6 When the steel is to be welded, a welding procedure suitable for the grade of steel and intended use or service is to be
utilized. See Appendix X3 of Specification A6/A6M for information on weldability.
1.7 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units
are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system is to be used
independently of the other, without combining values in any way.
1.8 The text of this specification contains notes or footnotes, or both, that provide explanatory material. Such notes and
footnotes, excluding those in tables and figures, do not contain any mandatory requirements.
1.9 For structural products produced from coil and furnished without heat treatment or with stress relieving only, the additional
requirements, including additional testing requirements and the reporting of additional tests, of A6/A6M apply.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A6/A6M Specification for General Requirements for Rolled Structural Steel Bars, Plates, Shapes, and Sheet Piling
A36/A36M Specification for Carbon Structural Steel
A514/A514M Specification for High-Yield-Strength, Quenched and Tempered Alloy Steel Plate, Suitable for Welding
A588/A588M Specification for High-Strength Low-Alloy Structural Steel, up to 50 ksi [345 MPa] Minimum Yield Point, with
Atmospheric Corrosion Resistance
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A01.02
on Structural Steel for Bridges, Buildings, Rolling Stock and Ships.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2013March 1, 2015. Published November 2013March 2015. Originally approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as
A572/A572M – 13.A572/A572M – 13a. DOI: 10.1520/A0572_A0572M-13A. 10.1520/A0572_A0572M-15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A572/A572M − 15
TABLE 1 Maximum Product Thickness or Size
Yield Point, min Maximum Thickness or Size
Structural Shape
Zees and Rolled
Grade Plates and Bars Flange or Leg
Tees
ksi [MPa] Sheet Piling
Thickness
in. [mm] in. [mm]
A
42 [290] 42 [290] 6 [150] all all all all
A B B
50 [345] 50 [345] 4 [100] all all all all
55 [380] 55 [380] 2
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.