ASTM D5227-01(2008)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measurement of Hexane Extractable Content of Polyolefins
Standard Test Method for Measurement of Hexane Extractable Content of Polyolefins
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
FDA requirements for maximum extractables are specified for resin and uses. This test method provides a means to determine the amount of hexane-soluble low molecular weight material present in polyolefins. It is applicable to resins containing greater than 0.20 % extractables.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes an extraction/gravimetric procedure for determination of the amount of hexane soluble low molecular weight material present in polyethylene, polypropylene, ethylene-propylene copolymers, and ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers. This test method is a modification of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) procedure for determining hexane extractables of polyolefins. This test method is based upon the presumption that the weight of the residue extract present in the solvent is equal to the amount extracted from the film sample and could therefore be quantified by measuring the weight loss of the extracted film, eliminating the complex and time-consuming evaporation process described in 21 CFR 177.1520.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. Units used in 21 CFR 177.1520 are also used in this test method. Units are in conformance with Federal Code 21 CFR 177.1520, from which this test method is derived.
Note 1—There is no known ISO equivalent ISO to this test method.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation:D5227 −01(Reapproved 2008)
Standard Test Method for
Measurement of Hexane Extractable Content of Polyolefins
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5227; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
´ NOTE—Reapproved with editorial changes in November 2008.
1. Scope E131 Terminology Relating to Molecular Spectroscopy
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
1.1 This test method describes an extraction/gravimetric
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
procedure for determination of the amount of hexane soluble
2.2 Federal Document:
low molecular weight material present in polyethylene,
21 CFR 177.1520
polypropylene, ethylene-propylene copolymers, and ethylene-
vinyl acetate copolymers. This test method is a modification of
3. Terminology
the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) procedure for
3.1 The definitions given inTerminology D883, D1600, and
determining hexane extractables of polyolefins. This test
E131 are applicable to this test method.
method is based upon the presumption that the weight of the
residue extract present in the solvent is equal to the amount
3.2 Abbreviations:
extracted from the film sample and could therefore be quanti-
3.2.1 EVA—ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer.
fied by measuring the weight loss of the extracted film,
3.2.2 LDPE—low-density polyethylene.
eliminating the complex and time-consuming evaporation
3.2.3 HDPE—high-density polyethylene.
process described in 21 CFR 177.1520.
3.2.4 LLDPE—linear low-density polyethylene.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 3.2.5 FDA—Food and Drug Administration.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2.6 PP—polypropylene.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4. Summary of Test Method
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
4.1 Film samples are extracted with hexane for 2 h at 49.5
standard. Units used in 21 CFR 177.1520 are also used in this
6 0.5°C, dried, and weighed.
test method. Units are in conformance with Federal Code 21
4.2 The loss in weight of the film is presumed to be equal to
CFR 177.1520, from which this test method is derived.
the extractable content determined by solvent evaporation in
NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent ISO to this test method.
the FDA protocol.
2. Referenced Documents
5. Significance and Use
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1 FDArequirements for maximum extractables are speci-
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
fied for resin and uses. This test method provides a means to
D1239 Test Method for Resistance of Plastic Films to
determine the amount of hexane-soluble low molecular weight
Extraction by Chemicals
material present in polyolefins. It is applicable to resins
D1600 Terminology forAbbreviatedTerms Relating to Plas-
containing greater than 0.20 % extractables.
tics
6. Apparatus
6.1 Water Bath, maintained at 49.5 6 0.5°C.
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
6.2 Resin Kettle, 1500-mL.
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical Methods.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2008. Published March 2009. Originally
approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D5227 - 01. DOI:
10.1520/D5227-01R08E01. Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM www.dodssp.daps.mil.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Ace Glass, Inc., Cat. No. 6476–15, or its equivalent, has been found
the ASTM website. satisfactory.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
´1
D5227−01 (2008)
6.3 Kettle Head, 3-neck, with one 45/50 and two 24/40
female joints, and appropriate stoppers.
6.4 Clamp.
6.5 Allihn Condenser, Size C, with 45/50 male joint.
6.6 Plastic Sleeves, tetrafluoroethylene (TFE), to fit Allihn
condenser 45/50 male joint.
6.7 Vacuum Oven, capable of maintaining 80 6 5°C and a
minimum of 25-in. Hg pressure.
6.8 Magnetic Stirring Bar, egg-shaped, TFE-coated, 1 ⁄2 by
⁄8 in.
6.9 Submersible Magnetic Stirring Motor, with power sup-
ply.
6.10 Analytical Balance, capable of weighing to 0.1 mg.
7. Reagents and Materials
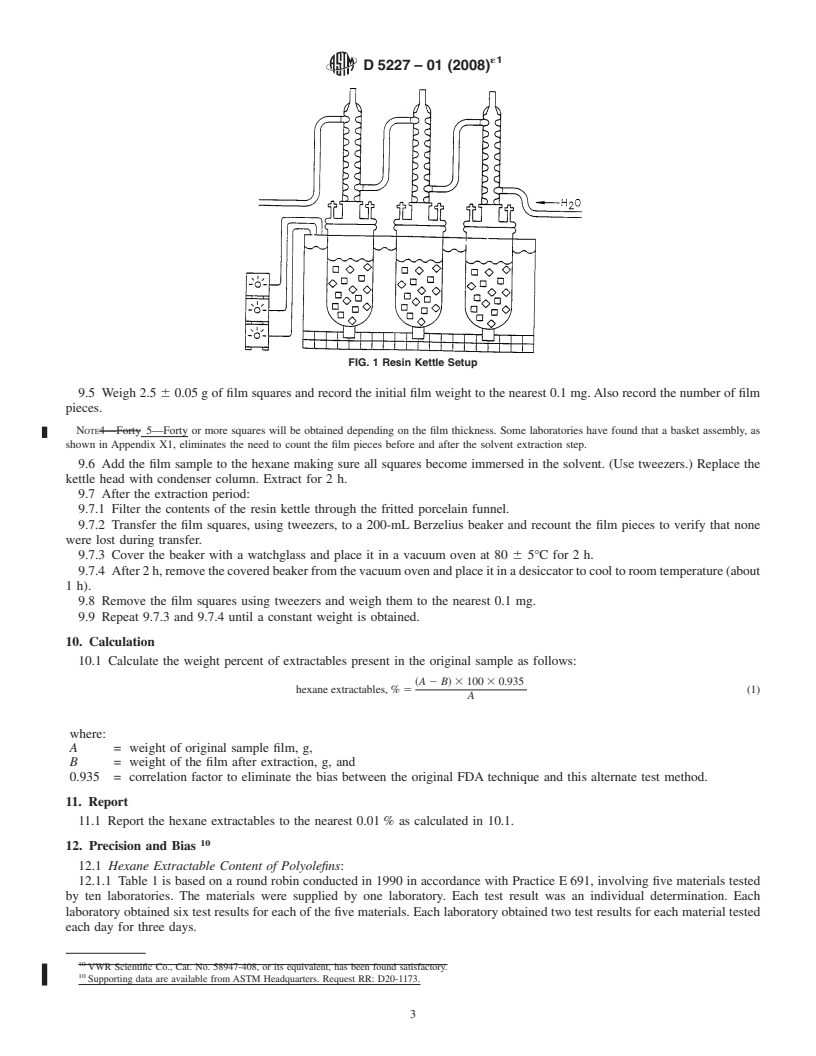
FIG. 1 Resin Kettle Setup
7.1 n-Hexane, aromatic free (<1 mg/L), minimum 85 %
n-Hexane-reagent grade or equivalent. The solvent must be
free of aromatic compounds that would significantly increase
the solubility of the resin. The solvent grade specified repre-
NOTE 4—Care must be exercised when cutting the samples to avoid
sents the minimum required purity.
ragged edges on the specimen. Small shards of film or contamination
present at initial weighing can easily be lost during the test, adversely
8. Materials
affecting the test results.
8.1 Blown Film,compressionmoldedfilms,orcastfilmsare
9.5 Weigh2.5 60.05goffilmsquaresandrecordtheinitial
suitable for testing.
film weight to the nearest 0.1 mg. Also record the number of
film pieces.
8.2 Film, approximately 2.5 g, with a thickness not exceed-
ing 4 mil is required for a single determination.
NOTE 5—Forty or more squares will be obtained depending on the film
thickness. Some laboratories have found that a basket assembly, as shown
9. Procedure in Appendix X1, eliminates the need to count the film pieces before and
after the solvent extraction step.
9.1 Assemble the resin kettle setup with glass stopper,
9.6 Add the film sample to the hexane making sure all
clamp, and magnetic stirring bar. (See Fig. 1.)
squares become immersed in the solvent. (Use tweezers.)
9.2 Add 1000 mL of n-Hexane to the kettle assembly.
Replacethekettleheadwithcondensercolumn.Extractfor2h.
9.3 Stopperthekettleandclamptheassemblyintothewater
9.7 After the extraction period:
bath set at 49.5 6 0.5°C.
9.7.1 Filterthecontentsoftheresinkettlethroughthefritted
porcelain funnel.
NOTE 2—Temperature is a critical factor in this analysis and must not
vary more than 1°C. If the temperature exceeds these limits, the test must 9.7.2 Transfer the film squares,
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
An American National Standard Designation: D 5227 – 01 (Reapproved 2008)
Designation:D5227–95
Standard Test Method for
Measurement of Hexane Extractable Content of Polyolefins
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5227; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
´ NOTE—Reapproved with editorial changes in November 2008.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method describes an extraction/gravimetric procedure for determination of the amount of hexane soluble low
molecular weight material present in polyethylene, polypropylene, ethylene-propylene copolymers, and ethylene-vinyl acetate
copolymers. This test method is a modification of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) procedure for determining hexane
extractables of polyolefins. This test method is based upon the presumption that the weight of the residue extract present in the
solvent is equal to the amount extracted from the film sample and could therefore be quantified by measuring the weight loss of
the extracted film, eliminating the complex and time-consuming evaporation process described in 21 CFR 177.1520.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. Units used in 21 CFR 177.1520 are also used in this test
method. Units are in conformance with Federal Code 21 CFR 177.1520, from which this test method is derived.
NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent ISO to this test method.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D 1239 Test Method for Resistance of Plastics FibersPlastic Films to Extraction by Chemicals
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
E 131 Terminology Relating to Molecular Spectroscopy
E380Practice for Use of the International System of Units (SI) (the Modernized Metric System) Terminology Relating to
Molecular Spectroscopy
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
2.2 Federal Document:
21 CFR 177.1520
3. Terminology
3.1Units, symbols, and abbreviations used in this test method are in accordance with the definitions given in Terminology 883,
and Terminology E131 or Practice E380.
3.1 The definitions given in Terminology D 883, D 1600, and E 131 are applicable to this test method.
3.2 Abbreviations:Abbreviations:
3.2.1 EVA—ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer.
3.2.2 LDPE—low-density polyethylene.
3.2.3 HDPE—high-density polyethylene.
3.2.4 LLDPE—linear low-density polyethylene.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical Methods .
Current edition approved June 15, 1995. Published August 1995. Originally published as D5227–92. Last previous edition D5227–92.
This edition includes revisions to Section 10, Calculation.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical Methods .
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2008. Published March 2009. Originally approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D 5227 - 01.
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 08.01.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.01.
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4, Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://www.dodssp.daps.mil.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
´1
D 5227 – 01 (2008)
3.2.5 FDA—Food and Drug Administration.
3.2.6 PP—polypropylene.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Film samples are extracted with hexane for2hat 49.5 6 0.5°C, dried, and weighed.
4.2 The loss in weight of the film is presumed to be equal to the extractable content determined by solvent evaporation in the
FDA protocol.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 FDA requirements for maximum extractables are specified for resin and uses. This test method provides a means to
determine the amount of hexane-soluble low molecular weight material present in polyolefins. It is applicable to resins containing
greater than 0.20 % extractables.
6. Apparatus
6.1 Water Bath, maintained at 49.5 6 0.5°C.
6.2 Resin Kettle, 1500-mL.
6.3 Kettle Head, 3-neck, with one 45/50 and two 24/40 female joints, and appropriate stoppers.
6.4 Clamp.
6.5 Allihn Condenser, Size C, with 45/50 male joint.
6.6 Plastic Sleeves, tetrafluoroethylene (TFE), to fit Allihn condenser 45/50 male joint.
6.7 Vacuum Oven, capable of maintaining 80 6 5°C and a minimum of 25-in. Hg pressure.
1 5
6.8 Magnetic Stirring Bar, egg-shaped, TFE-coated, 1 ⁄2 by ⁄8 in.
6.9 Submersible Magnetic Stirring Motor, with power supply.
6.10 Analytical Balance, capable of weighing to 0.1 mg.
7. Reagents and Materials
7.1 n-Hexane, aromatic free (<1 mg/L), minimum 85 % n-Hexane-reagent grade or equivalent. The solvent must be free of
aromatic compounds that would significantly increase the solubility of the resin. The solvent grade specified represents the
minimum required purity.
8. Materials
8.1 Blown Film, compression molded films, or cast films can be tested. , compression molded films, or cast films are suitable
for testing.
8.2 Film, approximately 2.5 g, with a thickness not exceeding 4 mil is required for a single determination.
9. Procedure
9.1 Assemble the resin kettle setup with glass stopper, clamp, and magnetic stirring bar. (See Fig. 1.)
9.2 Add 1000 mL of n-Hexane to the kettle assembly.
9.3 Stopper the kettle and clamp the assembly into the water bath set at 49.5 6 0.5°C.
NOTE 12—Temperature is a critical factor in this analysis and must not vary more than 1°C. If the temperature exceeds these limits, the test must be
discontinued and restarted. The FDA protocol also states the temperature of the contents must be brought to 49.5 6 0.5°C within 20 to 25 min.
NOTE2—The 3—The level of water in the bath must be kept at least 2 cm above the level of the solvent in the kettle to ensure the temperature
equilibrium. Position the kettle so that the center bottle of the kettle is sitting on a submersible stirrer. Start stirring and allow the hexane to heat for 1
h.
9.4 Using gloves and metal tweezers to avoid sample contamination, cut about 2.7 g of the prepared film sample (4 mil or less
in thickness) into about 1-in. squares using clean sharp scissors.
NOTE3—Care 4—Care must be exercised when cutting the samples to avoid ragged edges on the spec
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.