ASTM F683-14
(Practice)Standard Practice for Selection and Application of Thermal Insulation for Piping and Machinery
Standard Practice for Selection and Application of Thermal Insulation for Piping and Machinery
ABSTRACT
This practice provides the design and dimensional details required for the proper selection of the type of, and correct installation procedures for, thermal insulation materials suitable for use on piping, machinery, and equipment employed in nonnuclear shipboard applications. The insulation and lagging requirements for the removable covers of valves, fittings, flanges, and machinery or equipment, as well as the requirements for thermal insulating tape, are also detailed completely.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice provides guidance in the selection of types and thicknesses of thermal insulation materials for piping, machinery, and equipment for nonnuclear shipboard applications. Methods and materials for installation, including lagging, are also detailed.
1.2 Supplemental requirements and exceptions to the requirements discussed herein for ships of the U.S. Navy are included in Supplementary Requirements S1.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F683 − 14 An American National Standard
Standard Practice for
Selection and Application of Thermal Insulation for Piping
1
and Machinery
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF683;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope Chromium-Nickel Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip (With-
4
drawn 2014)
1.1 This practice provides guidance in the selection of types
A653/A653M Specification for Steel Sheet, Zinc-Coated
and thicknesses of thermal insulation materials for piping,
(Galvanized) or Zinc-Iron Alloy-Coated (Galvannealed)
machinery, and equipment for nonnuclear shipboard applica-
by the Hot-Dip Process
tions. Methods and materials for installation, including
B209 Specification for Aluminum and Aluminum-Alloy
lagging, are also detailed.
Sheet and Plate
1.2 Supplemental requirements and exceptions to the re-
B209M Specification for Aluminum and Aluminum-Alloy
quirements discussed herein for ships of the U.S. Navy are
Sheet and Plate (Metric)
included in Supplementary Requirements S1.
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded C195 Specification for Mineral Fiber Thermal Insulating
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
Cement
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
C449/C449M Specification for Mineral Fiber Hydraulic-
and are not considered standard.
Setting Thermal Insulating and Finishing Cement
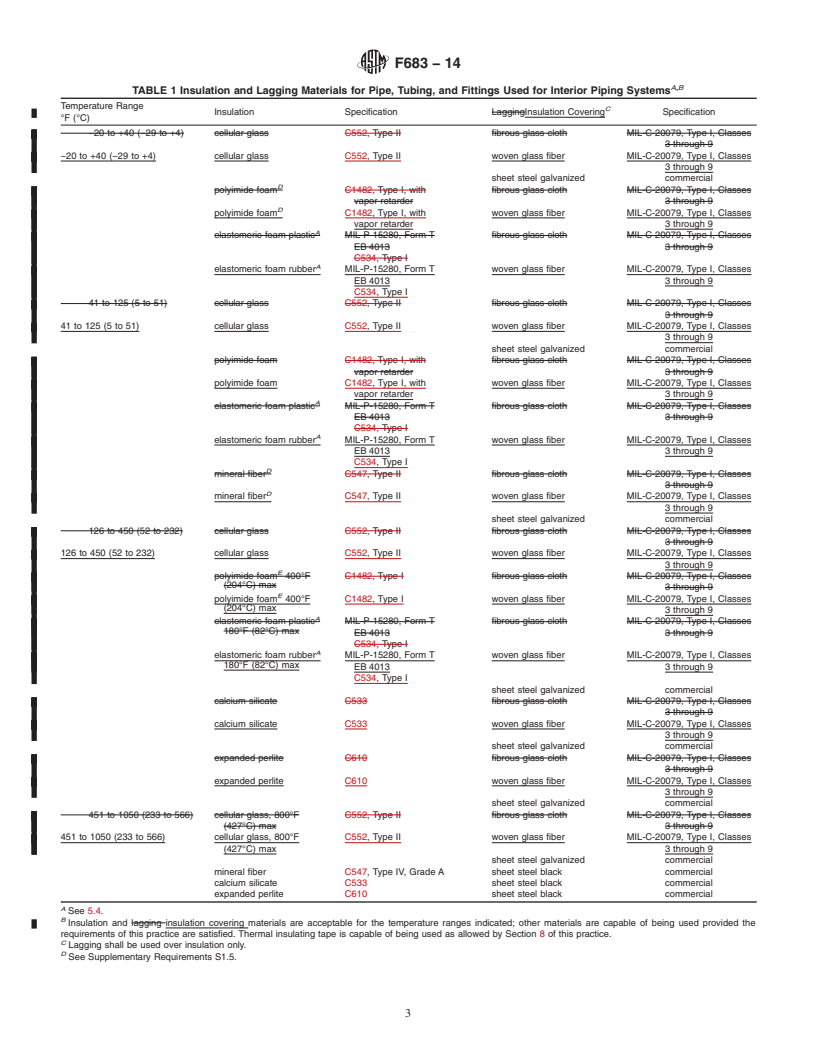
C533 Specification for Calcium Silicate Block and Pipe
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Thermal Insulation
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
C534 Specification for Preformed Flexible Elastomeric Cel-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
lular Thermal Insulation in Sheet and Tubular Form
priate safety, health and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. C547 Specification for Mineral Fiber Pipe Insulation
C552 Specification for Cellular Glass Thermal Insulation
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
C553 Specification for Mineral Fiber Blanket Thermal Insu-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the lation for Commercial and Industrial Applications
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- C610 Specification for Molded Expanded Perlite Block and
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Pipe Thermal Insulation
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
C612 Specification for Mineral Fiber Block and Board
Thermal Insulation
2
2. Referenced Documents
C680 Practice for Estimate of the Heat Gain or Loss and the
3
Surface Temperatures of Insulated Flat, Cylindrical, and
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Spherical Systems by Use of Computer Programs
A167 Specification for Stainless and Heat-Resisting
C892 Specification for High-Temperature Fiber Blanket
Thermal Insulation
C1482 Specification for Polyimide Flexible Cellular Ther-
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships and
mal and Sound Absorbing Insulation
Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.02 on
Insulation/Processes. D962 Specification for Aluminum Powder and Paste Pig-
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2014. Published December 2014. Originally
ments for Paints
approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as F683 – 10. DOI:
F1138 Specification for Spray Shields for Mechanical Joints
10.1520/F0683-14.
2
The latest revision of all referenced documents shall apply.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F683 − 14
5
2.2 Federal Specifications: 2.6 NAVSEA:
HH-P-31 Packing and Lagging Material, Fibrous Glass Me- Naval Ships Technical Manual, Chapter 635—Thermal,
8
tallic and Plain Cloth and Tape Fire, and Acoustic Insulation
TT-P-28 Paint, Aluminum, Heat Resisting (1200°F)
5
3. Terminology
2.3 Military Specifications:
MIL–PRF–24596 Coating Compounds, Nonflaming, Fire-
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms r
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F683 − 10 F683 − 14 An American National Standard
Standard Practice for
Selection and Application of Thermal Insulation for Piping
1
and Machinery
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F683; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice provides guidance in the selection of types and thicknesses of thermal insulation materials for piping,
machinery, and equipment for nonnuclear shipboard applications. Methods and materials for installation, including lagging, are
also detailed.
1.2 Supplemental requirements and exceptions to the requirements discussed herein for ships of the U.S. Navy are included in
Supplementary Requirements S1.
1.3 Asbestos or asbestos-containing materials shall not be used.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only.mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4
A167 Specification for Stainless and Heat-Resisting Chromium-Nickel Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip (Withdrawn 2014)
A653/A653M Specification for Steel Sheet, Zinc-Coated (Galvanized) or Zinc-Iron Alloy-Coated (Galvannealed) by the
Hot-Dip Process
B209 Specification for Aluminum and Aluminum-Alloy Sheet and Plate
B209M Specification for Aluminum and Aluminum-Alloy Sheet and Plate (Metric)
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
C195 Specification for Mineral Fiber Thermal Insulating Cement
C449/C449M Specification for Mineral Fiber Hydraulic-Setting Thermal Insulating and Finishing Cement
C533 Specification for Calcium Silicate Block and Pipe Thermal Insulation
C534 Specification for Preformed Flexible Elastomeric Cellular Thermal Insulation in Sheet and Tubular Form
C547 Specification for Mineral Fiber Pipe Insulation
C552 Specification for Cellular Glass Thermal Insulation
C553 Specification for Mineral Fiber Blanket Thermal Insulation for Commercial and Industrial Applications
C610 Specification for Molded Expanded Perlite Block and Pipe Thermal Insulation
C612 Specification for Mineral Fiber Block and Board Thermal Insulation
C680 Practice for Estimate of the Heat Gain or Loss and the Surface Temperatures of Insulated Flat, Cylindrical, and Spherical
Systems by Use of Computer Programs
C892 Specification for High-Temperature Fiber Blanket Thermal Insulation
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships and Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.02 on
Insulation/Processes.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2010Aug. 1, 2014. Published October 2010December 2014. Originally approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 20082010
as F683 – 08.F683 – 10. DOI: 10.1520/F0683-10.10.1520/F0683-14.
2
The latest revision of all referenced documents shall apply.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
4
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F683 − 14
C1482 Specification for Polyimide Flexible Cellular Thermal and Sound Absorbing Insulation
D962 Specification for Aluminum Powder and Paste Pigments for Paints
F1138 Specification for Spray Shields for Mechanical Joints
5
2.2 Federal Specifications:
HH-P-31 Packing and Lagging Material, Fibrous Glass Metallic and Plain Cloth and Tape
TT-P-28 Paint, Aluminum, Heat Resisting (1200°F)
5
2.3 Military Specifications:
MIL–PRF–24596 Coating Compounds, Nonflaming, Fire-Protective (Metric)
DoD-E-24607 Enamel, Interior, Nonflamin
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.