ASTM E331-00(2023)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Water Penetration of Exterior Windows, Skylights, Doors, and Curtain Walls by Uniform Static Air Pressure Difference
Standard Test Method for Water Penetration of Exterior Windows, Skylights, Doors, and Curtain Walls by Uniform Static Air Pressure Difference
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is a standard procedure for determining the resistance to water penetration under uniform static air pressure differences. The air-pressure differences acting across a building envelope vary greatly. These factors should be fully considered prior to specifying the test pressure difference to be used.
Note 1: In applying the results of tests by this test method, note that the performance of a wall or its components, or both, may be a function of proper installation and adjustment. In service, the performance will also depend on the rigidity of supporting construction and on the resistance of components to deterioration by various causes, vibration, thermal expansion and contraction, etc. It is difficult to simulate the identical complex wetting conditions that can be encountered in service, with large wind-blown water drops, increasing water drop impact pressures with increasing wind velocity, and lateral or upward moving air and water. Some designs are more sensitive than others to this upward moving water.
Note 2: This test method does not identify unobservable liquid water which may penetrate into the test specimen.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the resistance of exterior windows, curtain walls, skylights, and doors to water penetration when water is applied to the outdoor face and exposed edges simultaneously with a uniform static air pressure at the outdoor face higher than the pressure at the indoor face.
1.2 This test method is applicable to any curtain-wall area or to windows, skylights, or doors alone.
1.3 This test method addresses water penetration through a manufactured assembly. Water that penetrates the assembly, but does not result in a failure as defined herein, may have adverse effects on the performance of contained materials such as sealants and insulating or laminated glass. This test method does not address these issues.
1.4 The proper use of this test method requires a knowledge of the principles of pressure measurement.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses after SI units are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see 7.1.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E331 − 00 (Reapproved 2023)
Standard Test Method for
Water Penetration of Exterior Windows, Skylights, Doors,
and Curtain Walls by Uniform Static Air Pressure
Difference
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E331; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the resis- 2.1 ASTM Standard:
tance of exterior windows, curtain walls, skylights, and doors E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
to water penetration when water is applied to the outdoor face
3. Terminology
and exposed edges simultaneously with a uniform static air
pressure at the outdoor face higher than the pressure at the
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of general terms relating to
indoor face.
building construction used in this test method, see Terminology
E631.
1.2 This test method is applicable to any curtain-wall area or
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
to windows, skylights, or doors alone.
3.2.1 specimen, n—the entire assembled unit submitted for
1.3 This test method addresses water penetration through a
test as described in Section 8.
manufactured assembly. Water that penetrates the assembly,
3.2.2 test pressure difference, n—the specified difference in
but does not result in a failure as defined herein, may have
static air pressure across the closed and locked or fixed
adverse effects on the performance of contained materials such
specimen expressed as Pascals (lbf/ft ).
as sealants and insulating or laminated glass. This test method
does not address these issues. 3.2.3 water penetration, n—penetration of water beyond a
plane parallel to the glazing (the vertical plane) intersecting the
1.4 The proper use of this test method requires a knowledge
innermost projection of the test specimen, not including
of the principles of pressure measurement.
interior trim and hardware, under the specified conditions of air
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
pressure difference across the specimen. For products with
standard. The values given in parentheses after SI units are
non-planer glazing surfaces (domes, vaults, pyramids, etc.), the
provided for information only and are not considered standard.
plane defining water penetration is the plane defined by the
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the innermost edges of the unit frame.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4. Summary of Test Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
4.1 This test method consists of sealing the test specimen
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
into or against one face of a test chamber, supplying air to or
For specific hazard statements, see 7.1.
exhausting air from the chamber at the rate required to
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
maintain the test pressure difference across the specimen, while
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
spraying water onto the outdoor face of the specimen at the
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
required rate and observing any water penetration.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
5. Significance and Use
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5.1 This test method is a standard procedure for determining
the resistance to water penetration under uniform static air
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.51
on Performance of Windows, Doors, Skylights and Curtain Walls. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2023. Published February 2023. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1967. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as E331 – 00 (2016). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/E0331-00R23. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
E331 − 00 (2023)
pressure differences. The air-pressure differences acting across 6.2 Major Components (Fig. 1):
a building envelope vary greatly. These factors should be fully
6.2.1 Test Chamber—A test chamber or box with an
considered prior to specifying the test pressure difference to be
opening, a removable mounting panel, or one open side in
used.
which or against which the specimen is installed and sealed. At
least one static pressure tap shall be provided to measure the
NOTE 1—In applying the results of tests by this test method, note that
chamber pressure, and shall be so located that the reading is
the performance of a wall or its components, or both, may be a function
of proper installation and adjustment. In service, the performance will also unaffected by the velocity of the air supply to or from the
depend on the rigidity of supporting construction and on the resistance of
chamber. The air supply opening into the chamber shall be
components to deterioration by various causes, vibration, thermal expan-
arranged so that the air does not impinge directly on the test
sion and contraction, etc. It is difficult to simulate the identical complex
specimen with any significant velocity. A means of access into
wetting conditions that can be encountered in service, with large wind-
the chamber may be provided to facilitate adjustments and
blown water drops, increasing water drop impact pressures with increas-
ing wind velocity, and lateral or upward moving air and water. Some
observations after the specimen has been installed.
designs are more sensitive than others to this upward moving water.
6.2.2 Air System—A controllable blower, compressed air
NOTE 2—This test method does not identify unobservable liquid water
supply, exhaust system, or reversible blower designed to
which may penetrate into the test specimen.
provide the required maximum air-pressure difference across
6. Apparatus
the specimen. The system must provide essentially constant
airflow at a fixed pressure for the required test period.
6.1 The description of apparatus in this section is general in
nature and any arrangement of equipment capable of perform- 6.2.3 Pressure-Measuring Apparatus—A device to measure
ing the test procedure within the allowable tolerances is the test pressure difference within a tolerance of 62 % or
permitted. 62.5 Pa (60.01 in. of water column), whichever is greater.
NOTE 1—For a negative pressure system, the water-spray grid would be located outside the chamber and the air supply would be replaced by an
air-exhaust system.
FIG. 1 General Arrangement of the Water Leakage Apparatus Positive Chamber System
E331 − 00 (2023)
6.2.4 Water-Spray System—The water-spray system shall 8.2 Window, skylight, door, or other component test speci-
deliver water uniformly against the exterior surface of the test
mens shall consist of the entire assembled unit, including frame
specimen at a minimum rate of 3.4 L ⁄m · min
and anchorage as supplied by the manufacturer for installation
(5.0 U.S. gal ⁄ft · h).
in the building.
6.2.4.1 The water-spray system shall have nozzles spaced
8.2.1 If only one specimen is to be tested, the selection shall
on a uniform grid, located at a uniform distance from the test
be determined by the specifying authority.
specimen, and shall be adjustable to provide the specified
quantity of water in such a manner as to wet all of the test
NOTE 3—It should be recognized, especially with windows, that
performance is likely to be a function of size and geometry. Therefore,
specimen uniformly and to wet those areas vulnerable to water
select specimens covering the range of sizes to be used in a building. In
penetration. If additional nozzles are required to provide
general, the largest size of a particular design, type, construction, and
uniformity of water spray at the edge of the test specimen, they
configuration to be used should be tested.
shall be equally spaced around the entire spray grid.
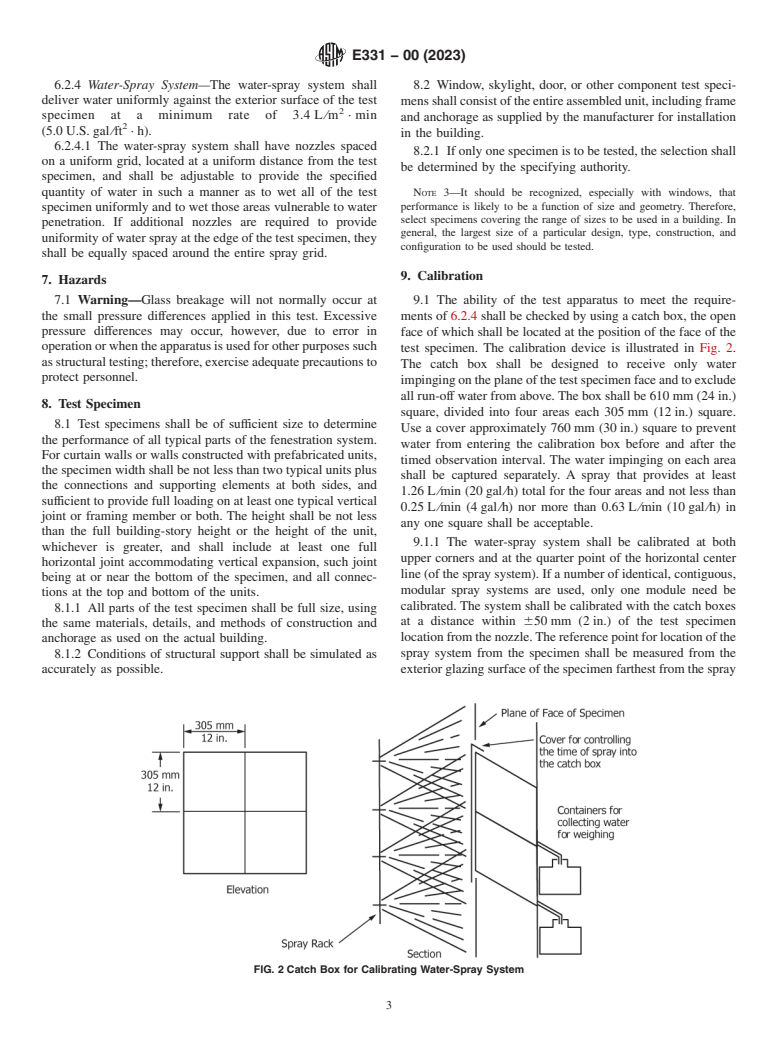
9. Calibration
7. Hazards
9.1 The ability of the test apparatus to meet the require-
7.1 Warning—Glass breakage
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.