ASTM A709/A709M-00
(Specification)Standard Specification for Carbon and High-Strength Low-Alloy Structural Steel Shapes, Plates, and Bars and Quenched-and-Tempered Alloy Structural Steel Plates for Bridges
Standard Specification for Carbon and High-Strength Low-Alloy Structural Steel Shapes, Plates, and Bars and Quenched-and-Tempered Alloy Structural Steel Plates for Bridges
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers carbon and high-strength low-alloy steel structural shapes, plates, and bars and quenched and tempered alloy steel for structural plates intended for use in bridges. Seven grades are available in four yield strength levels as follows: Grade U.S. [SI] Yield Strength, ksi: [MPa] 36 [250] 36 [250] 50 [345] 50 [345] 50S[345W] 50 [345] HPS 50W [HPS 345W]50 [345] HPS 70W [HPS 485W]70 [485] 100 [690] 100 [690] 100W [690W] 100 [690]
1.1.1 Grades 36 [250], 50 [345], 50S [345W], 100 [690], and 100W [690W] are also included in Specifications A 36/A 36M, A 572/A 572M, A 992/A 992M, A 588/A 588M, and A 514/A 514M, respectively. When the supplementary requirements of this specification are specified, they exceed the requirements of Specifications A 36/A 36M, A 572/A 572M, A 992/A 992M, A 588/A 588M, and A 514/A 514M.
1.1.2 Grades 50W [345W], HPS 50W [HPS 345], HPS 70W [HPS 485W], and 100W [690W] have enhanced atmospheric corrosion resistance (see 11.1.2). Product availability is shown in .
1.2 Grade HPS 70W [HPS 485W], 100 [690], or 100W [690W] shall not be substituted for Grades 36 [250], 50 [345], 50S [345S], 50W [345W], or HPS 50W [HPS 345W]. Grade 50W [345W], or HPS 50W [HPS 345W] shall not be substituted for Grades 36 [250], 50 [345] or 50S [345S] without agreement between the purchaser and the supplier.
1.3 When the steel is to be welded, it is presupposed that a welding procedure suitable for the grade of steel and intended use or service will be utilized. See Appendix X3 of Specification A 6/A 6M for information on weldability.
1.4 Supplementary requirements are available but shall apply only when specified by the purchaser at the time of ordering.
1.5 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with this specification.
1.6 For structural products cut from coiled product, the additional requirements, including additional testing requirements and the reporting of additional test results, of Specification A 6/A 6M apply.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: A 709/A 709M – 00
Standard Specification for
Carbon and High-Strength Low-Alloy Structural Steel
Shapes, Plates, and Bars and Quenched-and-Tempered
Alloy Structural Steel Plates for Bridges
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 709/A 709M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.4 Supplementary requirements are available but shall
apply only when specified by the purchaser at the time of
1.1 This specification covers carbon and high-strength low-
ordering.
alloy steel structural shapes, plates, and bars and quenched and
1.5 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
tempered alloy steel for structural plates intended for use in
are to be regarded as standard. Within the text, the SI units are
bridges. Six grades are available in four yield strength levels as
shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not
follows:
exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used inde-
Grade U.S. [SI] Yield Strength, ksi: [MPa]
pendently of the other. Combining values from the two systems
36 [250] 36 [250]
may result in nonconformance with this specification.
50 [345] 50 [345]
50W [345W] 50 [345]
HPS 70W [HPS 485W] 70 [485] 2. Referenced Documents
100 [690] 100 [690]
2.1 ASTM Standards:
100W [690W] 100 [690]
A 6/A 6M Specification for General Requirements for
1.1.1 Grades 36 [250], 50 [345], 50W [345W], 100 [690],
Rolled Structural Steel Bars, Plates, Shapes, and Sheet
and 100W [690W] are also included in Specifications A 36/
Piling
A 36M, A 572/A 572M, A 588/A 588M, A 852/A 852M, and A 2
A 36/A 36M Specification for Carbon Structural Steel
514/A 514M, respectively. When the supplementary require-
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
ments of this specification are specified, they exceed the 3
of Steel Products
requirements of Specifications A 36/A 36M, A 572/A 572M, A
A 435/A 435M Specification for Straight-Beam Ultrasonic
588/A 588M, A 852/A 852M, and A 514/A 514M. 2
Examination of Steel Plates
1.1.2 Grades 50W [345W] and 100W [690W] have en-
A 514/A 514M Specification for High-Yield-Strength,
hanced atmospheric corrosion resistance (see 11.1.2). Product
Quenched and Tempered Alloy Steel Plate, Suitable for
availability is shown in Table 1.
Welding
1.1.3 Grade HPS 70W [HPS 485 W] has enhanced tough-
A 572/A 572M Specification for High-Strength Low-Alloy
ness when Supplementary Requirements S 83 or S 84 are
Columbium-Vanadium Structural Steel
specified.
A 588/A 588M Specification for High-Strength Low-Alloy
1.2 Grades HPS 70W [HPS 485W], 100 [690], or 100W
Structural Steel with 50 ksi (345 MPa) Minimum Yield
[690W] shall not be substituted for Grades 36 [250], 50 [345], 2
Point to 4 in. (100 mm) Thick
or 50W [345W]. Grade 50W [345W] shall not be substituted
A 673/A 673M Specification for Sampling Procedure for
for Grades 36 [250] or 50 [345] without agreement between the 2
Impact Testing of Structural Steel
purchaser and supplier.
A 852/A 852M Specification for Quenched and Tempered
1.3 When the steel is to be welded, it is presupposed that a
Low-Alloy Structural Steel Plate with 70 ksi (485 MPa)
welding procedure suitable for the grade of steel and intended
Minimum Yield Strength to 4 in. (100 mm) Thick
use or service will be utilized. See Appendix X3 of Specifica-
E 112 Test Methods for Determining the Average Grain
tion A 6/A 6M for information on weldability.
Size
G 101 Guide for Estimating the Atmospheric Corrosion
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A-1 on Steel,
Stainless Steel, and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.02 on Structural Steel for Bridges, Buildings, Rolling Stock, and Ships. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.04.
Current edition approved March 10, 1999. Published May 2000. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03.
published as A 709 – 74. Last previous edition A 709 – 99. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A 709/A 709M
A
TABLE 1 Tensile and Hardness Requirements
NOTE 1— Where “. . .” appears in this table, there is no requirement.
Minimum Elongation, %
Yield Point
Reduc- Brinell
EC E
or Yield Tensile Plates and Bars Shapes
Plate Thickness, Structural Shapes tion of Hard-
B
Grade Strength, Strength,
C,D
in. [mm] Groups 8 in. 2 in. 8 in. 2 in. Area ness
min, ksi ksi [MPa]
min, % Number
or 200 or 50 or 200 or 50
[MPa]
mm mm mm mm
F G
36 [250] to 4 [100], incl to 426 lb/ft (634 kg/m) 36 [250] 58–80 [400–550] 20 23 20 21 .
G
over 426 lb/ft (634 kg/m) 36 [250] 58 min [400] . . 20 19 .
F G
50 [345] to 4 [100], incl all 50 [345] 65 min [450] 18 21 18 21 .
H G
50W [345W] to 4 [100], incl all 50 [345] 70 min [485] 18 21 18 21 .
I B G
HPS 70W [HPS to 4 [100], incl 70 [485] 85–110 [585–760] . . . 19 . . . . . . . . .
485 W]
I B J K L G
100 [690] and to21 2 [65], 100 [690] 110–130 [760–895] . 18 . . 40 –50 235–293
/
100W [690W] incl
I B J K LG
100 [690] and over 2 1 2to4 90 [620] 100–130 [690–895] . 16 . . 40 –50
/
100W [690 W] [65
to 100]
A
See specimen orientation and preparation subsection in the Tension Tests section of Specification A 6/A 6 M.
B
Measured at 0.2 % offset or 0.5 % extension under load as described in Section 13 of Test Methods A 370.
C
Elongation and reduction of area not required to be determined for floor plates.
D
For plates wider than 24 in. [600 mm], the reduction of area requirement, where applicable, is reduced by five percentage points.
E
For plates wider than 24 in. [600 mm], the elongation requirement is reduced two percentage points. See elongation requirement adjustments in the Tension Tests
section of Specification A 6/A 6M.
F
Elongation in 2 in. or 50 mm: 19 % for shapes over 426 lb/ft [634 kg/m].
G
Brinell requirements apply only to material ⁄8 in. [10 mm] and thinner for Grades 100 and 100W.
H
For wide flange shapes over 426 lb/ft [634 kg/m], elongation in 2 in. of 18 % minimum applies.
I
The grade is not described for this product.
J
When measured on the Fig. 3 (Test Methods A 370) 1 ⁄2–in. [40–mm] wide specimen the elongation is determined in a 2–in. or 50–mm gage length which includes the
fracture and shows the greatest elongation.
K
When measured on the Fig. 3 (Test Methods A 370) 1 ⁄2-in. [40-mm] wide specimen.
L
When measured on the Fig. 4 (Test Methods A 370) ⁄2–in. [12.5–mm] round specimen.
Resistance of Low-Alloy Steels conform to the tensile and hardness requirements of Table 1 by
heating to not less than 1650°F [900°C], quenching in water or
3. General Requirements for Delivery
oil, and tempering at not less than 1100°F [593°C] for Grades
3.1 Material furnished under this specification shall con-
70W [485W] and HPS 70W [HPS 485 W] and not less than
form to the requirements of the current edition of Specification 1150°F [620°C] for Grades 100 [690] and 100W [690W]. The
A 6/A 6M, for the ordered material, unless a conflict exists in
heat-treating temperatures shall be reported on the test certifi-
which case this specification shall prevail. cates.
4. Manufacture 6. Chemical Requirements
6.1 The heat analysis shall conform to the requirements of
4.1 The steel shall be made by one of the following
processes: open-hearth, basic-oxygen, or electric-furnace. Ad- the specified grade in Tables 2-7.
6.2 The steel shall conform on product analysis to the
ditional refining in the ladle, by electroslag remelting (ESR) or
requirements prescribed in Tables 2-7, subject to the product
vacuum-arc remelting (VAR) is permitted.
analysis tolerances in Specification A 6/A 6M, except as speci-
4.2 Grades 36 [250] and 50 [345] steel shall be made of
fied in 6.3.
other than rimmed or capped steel.
6.3 Product analysis is not applicable for bar size shapes and
4.3 Grades 50W [345W] and HPS 70W [HPS 485 W] shall
for flat bars ⁄2 in. [12.5 mm] and under in thickness.
be made to a killed fine grain practice.
4.4 Grade HPS 70W [HPS 485 W] shall be made using a
7. Tensile Requirements
low-hydrogen practice, such as vacuum degassing or con-
7.1 The material as represented by test specimens, except as
trolled soaking and/or cooling of ingots, slabs, or plates, or
specified in 7.2, shall conform to the requirements for tensile
combination thereof.
properties prescribed in Table 1.
4.5 Grades 100 [690] and 100W [690W] steel shall be killed
2 2
7.2 For Grade 36 [250] shapes less than 1 in. [645 mm ]in
and shall conform to the fine austenitic grain size requirement
cross section and bars, other than flats, less than ⁄2 in. [12.5
of Specification A 6/A 6M.
mm] in thickness or diameter need not be subjected to tension
5. Heat Treatment
tests by the manufacturer.
5.1 Grades HPS 70W [HPS 485 W], 100 [690], and 100W
8. Brinell Hardness Requirements for Grades 100 [690]
[690W] steel shall be heat treated by the manufacturer to
and 100W [690W]
8.1 For plates ⁄8in. [10 mm] and under in thickness, a
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.02. Brinell hardness test may be used instead of tension testing
A 709/A 709M
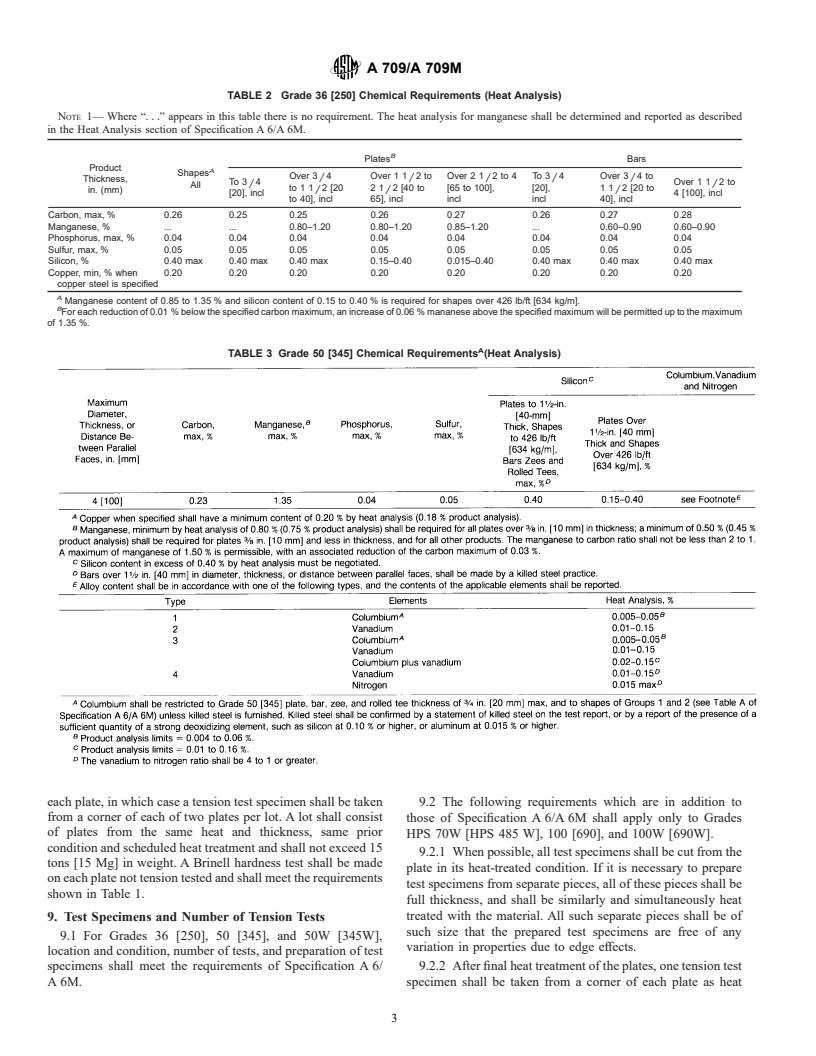
TABLE 2 Grade 36 [250] Chemical Requirements (Heat Analysis)
NOTE 1— Where “. . .” appears in this table there is no requirement. The heat analysis for manganese shall be determined and reported as described
in the Heat Analysis section of Specification A 6/A 6M.
B
Plates Bars
Product
A
Shapes
Over 3 4 Over 1 1 2to Over 2 1 2to4 To 3 4 Over 3 4to
Thickness, / / / / /
To 3 4 Over 1 1 2to
All / /
to11 2 [20 21 2 [40 to [65 to 100], [20], 11 2 [20 to
in. (mm)
/ / /
[20], incl 4 [100], incl
to 40], incl 65], incl incl incl 40], incl
Carbon, max, % 0.26 0.25 0.25 0.26 0.27 0.26 0.27 0.28
Manganese, % . . 0.80–1.20 0.80–1.20 0.85–1.20 . 0.60–0.90 0.60–0.90
Phosphorus, max, % 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04
Sulfur, max, % 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05
Silicon, % 0.40 max 0.40 max 0.40 max 0.15–0.40 0.015–0.40 0.40 max 0.40 max 0.40 max
Copper, min, % when 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
copper steel is specified
A
Manganese content of 0.85 to 1.35 % and silicon content of 0.15 to 0.40 % is required for shapes over 426 lb/ft [634 kg/m].
B
For each reduction of 0.01 % below the specified carbon maximum, an increase of 0.06 % mananese above the specified maximum will be permitted up to the maximum
of 1.35 %.
A
TABLE 3 Grade 50 [345] Chemical Requirements (Heat Analysis)
each plate, in which case a tension test specimen shall be taken 9.2 The following requirements which are in addition to
from a corner of each of two plates per lot. A lot shall consist
those of Specification A 6/A 6M shall apply only to Grades
of plates from the same heat and thickness, same prior
HPS 70W [HPS 485 W], 100 [690], and 100W [690W].
condition and scheduled heat treatment and shall not exceed 15
9.2.1 When possible, all test specimens shall be cut from the
tons [15 Mg] in weight. A Brinell hardness test shall be made
plate in its heat-treated condition. If it is necessary to prepare
on each plate not tension tested and shall meet the requirements
test specimens from separate pieces, all of these pieces shall be
shown in Table 1.
full thickness, and shall be similarly and simultaneously heat
treated with the material. All such separate pieces shall be of
9. Test Specimens and Number of Tension Tests
such size that the prepared test specimens are free of any
9.1 For Grades 36 [250], 50 [345], and 50W [345W],
variation in properties due to edge effects.
location and condition, number of tests, and preparation of test
specimens shall meet the requirements of Specification A 6/ 9.2.2 After final heat treatment of the plates, one tension test
A 6M. specimen shall be taken from a corner of each plate as heat
A 709/A 709M
TABLE 4 Grade 50W [345 W] Chemical Requirements (Heat
requirements, at the manufacturer’s option, may be subjected
Analysis)
to tension testing and shall be accepted if the results conform
to the requirements of Table 1.
NOTE 1—Types A, B, and C are equivalent to Specification A 588/
A 588M Grades A, B, and C, respectively. 10.3 The manufacturer may reheat treat Grades HPS 70W
[HPS 485 W], 100 [690], and 100W [690W] plates that fail to
A
Composition, %
meet the mechanical property requirements of this specifica-
Element
Type A Type B Type C
tion. All mechanical property tests shall be repeated when the
material is resubmitted for inspection.
Carbon 0.19 max 0.20 max 0.15 max
Manganese 0.80–1.25 0.75–1.35 0.80–1.35
11. Atmospheric Corrosion Resistance
Phosphorus 0.04 max 0.04 max 0.04 max
Sulfur 0.05 max 0.05 max 0.05 max
11.1 Steels meeting this specification provide two levels of
Silicon 0.30–0.65 0.15–0.50 0.15–0.40
atmospheric corrosion resistance:
Nickel 0.40 max 0.50 max 0.25–0.50
Chromium 0.40–0.65 0.40–0.70 0.30–0.50
11.1.1 Steel grades without suffix provide a level of atmo-
Copper 0.25–0.40 0.20–0.40 0.20–0.50
spheric corrosion resistance typical of carbon or alloy steel
Vanadium 0.02–0.10 0.01–0.10 0.01–0.10
without copper.
A
Weldability data for these types have been qualified by FHWA for use in bridge
11.1.2 To comply with Specification A 709, steel grade 50W
construction.
[345W], and HPS 70W [HPS 485W] shall have an atmospheric
corrosion resistance index of 6.0 or higher, calculated from the
TABLE 5 Grade 70W [485 W] Chemical Requirements (Heat
heat analysis in accordance with Guide G 101 (see Note 2).
Analysis)
When properly exposed to the atmosphere, these steels can be
Element Composition, % used bare (unpainted) for many applications. Steel grade 100W
provides an improved level of atmospheric corrosion resistance
Carbon 0.19 max
Manganese 0.80–1.35
over alloy steel without copper.
Phosphorus 0.035 max
Sulfur 0.04 max
NOTE 2—For methods of estimating the atmospheric corrosion resis-
Silicon 0.20–0.65
tance of low-alloy steels, see Guide G 101.
Copper 0.20–0.40
The user is cautioned that the Guide G 101 predictive equation for
Nickel 0.50 max
calculation of an atmospheric corrosion resistance index has only been
Chromium 0.40–0.70
verified for the composition limits stated in that guide.
Vanadium 0.02–0.10
12. Marking
12.1 In addition to the marking requirements of Specifica-
treated (except as specified in 8.1).
tion A 6/A 6M, material identification shall also include the
NOTE 1—The term “plate” identifies the “plate as heat treated.”
composition type for Grades 50W [345W], 100 [690] and
100W [
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.