ASTM D5581-96(2001)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Resistance to Plastic Flow of Bituminous Mixtures Using Marshall Apparatus (6 inch-Diameter Specimen)
Standard Test Method for Resistance to Plastic Flow of Bituminous Mixtures Using Marshall Apparatus (6 inch-Diameter Specimen)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the resistance to plastic flow of cylindrical specimens of bituminous paving mixture loaded on the lateral surface by means of the Marshall apparatus. This test method is for use with mixtures containing asphalt cement and aggregate up to 1 1/2 in. (37.5 mm) nominal maximum size.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard except for reference to sieve sizes and size of aggregate as measured by testing sieves in which SI units are standard according to Specification E11. The SI equivalent shown in parentheses may be approximate.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D5581–96 (Reapproved 2001)
Standard Test Method for
Resistance to Plastic Flow of Bituminous Mixtures Using
Marshall Apparatus (6 inch-Diameter Specimen)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5581; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope load and flow for bituminous paving specimens cored from
pavements or prepared by other methods. These results may
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the resis-
differ from values obtained on specimens prepared by this test
tance to plastic flow of cylindrical specimens of bituminous
method.
paving mixture loaded on the lateral surface by means of the
3.2 It has been determined that 75 and 112 compaction
Marshall apparatus. This test method is for use with mixtures
blows applied to a 6-in. (152.4 mm) diameter specimen using
containing asphalt cement and aggregate up to 1 ⁄2 in. (37.5
the apparatus and procedure in this standard give densities
mm) nominal maximum size.
equivalent to 50 and 75 compaction blows, respectively,
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
applied to a 4-in. (101.6 mm) diameter specimen using Test
as standard except for reference to sieve sizes and size of
Method D 1559.
aggregate as measured by testing sieves in which SI units are
standard according to Specification E 11. The SI equivalent
4. Apparatus
shown in parentheses may be approximate.
4.1 Specimen Mold Assembly—Mold cylinders nominal 6.5
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
in. (165.1 mm) outside diameter steel tubing with
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
6.000 6 0.008 in. (152.4 6 0.2 mm) inside diameter by 4.5 in.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
(114.3 mm) in height, base plates, and extension collars shall
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
conform to the details shown in Fig. 1. Nine mold cylinders are
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
recommended.
2. Referenced Documents 4.2 Specimen Extractor—steel, in the form of a disk with a
diameter from 5.950 to 5.990 in. (151.1 to 152.1 mm) and 0.5
2.1 ASTM Standards:
in. (13 mm) thick for extracting the compacted specimen from
C 670 Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements
2 the specimen mold with the use of the mold collar. A suitable
for Test Methods for Construction Materials
bar is required to transfer the load from the ring dynamometer
D 1559 Test Method for Resistance to Plastic Flow of
3 adapter to the extension collar while extracting the specimen.
Bituminous Mixtures Using Marshall Apparatus
4.3 Mechanical Compactor and Compaction Hammer—
E 11 Specification for Wire Cloth and Sieves for Testing
4 Compactor with ⁄3 hp (250W) minimum motor, chain lift,
Purposes
frame, and automatic sliding weight release. The compaction
3. Significance and Use hammer (Fig. 2) shall have a flat, circular tamping face 5.88 in.
(149.4 mm) in diameter and a 22.50 6 0.02 lb (10.21 6 0.01
3.1 This test method is used in the laboratory mix design of
kg) sliding weight with a free fall of 18.0 6 0.1 in.
bituminous mixtures. Specimens are prepared in accordance
(457.2 6 2.5 mm). Two compaction hammers are recom-
with the method and tested for maximum load and flow.
mended.
Density and voids properties may also be determined on
4.4 Compaction Pedestal—The compaction pedestal shall
specimenspreparedinaccordancewiththemethod.Thetesting
consist of an 8 by 8 by 18-in. (203.2 by 203.2 by 457.2-mm)
section of this method can also be used to obtain maximum
wooden post capped with a 12 by 12 by 1-in. (304.8 by 304.8
by25.4-mm)steelplate.Thewoodenpostshallbeoak,pine,or
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D04 on Road
other wood having an average dry weight of 42 to 48
3 3
and Paving Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.20 on
lb/ft (0.67 to 0.77 g/cm ).The wooden post shall be secured by
Mechanical Tests of Bituminous Mixes.
four angle brackets to a solid concrete slab. The steel cap shall
Current edition approved Jan. 10, 1996. Published March 1996. Originally
be firmly fastened to the post. The pedestal assembly shall be
published as D 5581 – 94. Last previous edition D 5581 – 94.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.02.
installed so that the post is plumb and the cap is level.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.03.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D5581
FIG. 2 Compaction Hammer (Generic)
FIG. 1 Compaction Mold
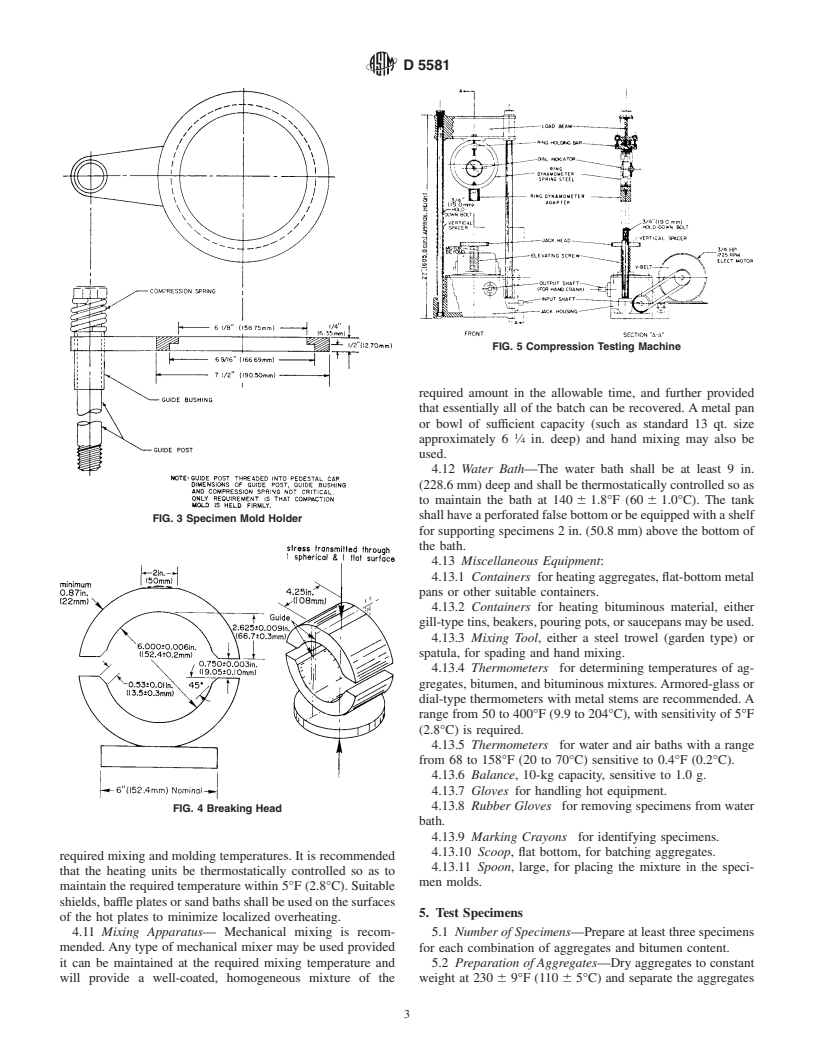
4.8 Ring Dynamometer Assembly—One ring dynamometer
(Fig. 5) of 10 000-lb. (4536-kg) capacity and sensitivity of 10
lb (4.536 kg) up to 1000 lb (453.6 kg) and 25 lb (11.340 kg)
4.5 Specimen Mold Holder—mounted on the compaction
between 1000 and 10 000 lb (453.6 and 4536 kg) shall be
pedestal so as to center the compaction mold over the center of
equipped with a micrometer dial. The micrometer dial shall be
the post as shown in Fig. 3 or equivalent arrangement. It shall
graduated on 0.0001 in. (0.0025 mm). Upper and lower ring
hold the compaction mold, collar, and base plate securely in
dynamometer attachments are required for fastening the ring
position during compaction of the specimen.
dynamometer to the testing frame and transmitting the load to
4.6 Breaking Head— The breaking head (Fig. 4) shall
the breaking head.
consist of upper and lower cylindrical segments or test heads
NOTE 2—Instead of the ring dynamometer assembly, any suitable
having an inside radius of curvature of 3 in. (76.2 mm)
load-measuring device may be used provided the capacity and sensitivity
accurately machined. The lower segment shall be mounted on
meet the above requirements.
a base having two perpendicular guide rods or posts extending
4.9 Flowmeter—The flowmeter shall consist of a guide
upward. Guide sleeves in the upper segments shall be in such
sleeve and a gage. The activating pin of the gage shall slide
a position as to direct the two segments together without
inside the guide sleeve with a slight amount of frictional
appreciable binding or loose motion on the guide rods. When
resistance. The guide sleeve shall slide freely over the guide
a 6.000 in. (152.4 mm) diameter by 4 in. (100 mm) thick metal
rod of the breaking head. The flowmeter gage shall be adjusted
block is placed between the two segments, the inside diameters
to zero when placed in position on the breaking head when
and the gaps between the segments shall conform to Fig. 4.All
each individual test specimen is inserted between the breaking
steel components shall be plated.
head segments. Graduations of the flowmeter gage shall be in
4.7 Loading Jack— The loading jack (Fig. 5) shall consist
0.01-in. (0.25-mm) divisions.
of a screw jack mounted in a test frame and shall produce a
uniform vertical movement of 2 in. (50.8 mm)/min.An electric
NOTE 3—Instead of the flowmeter, a micrometer dial or stress-strain
recorder graduated in 0.001 in. (0.025-mm) may be used to measure flow.
motor may be attached to the jacking mechanism.
4.10 Ovens or Hot Plates—Ovens or hot plates shall be
NOTE 1—Instead of the loading jack, a mechanical or hydraulic testing
provided for heating aggregates, bituminous material, speci-
machine may be used provided the rate of movement can be maintained
at 2 in. (50.8 mm)/min while the load is applied. men molds, compaction hammers, and other equipment to the
D5581
FIG. 5 Compression Testing Machine
required amount in the allowable time, and further provided
that essentially all of the batch can be recovered. A metal pan
or bowl of sufficient capacity (such as standard 13 qt. size
approximately 6 ⁄4 in. deep) and hand mixing may also be
used.
4.12 Water Bath—The water bath shall be at least 9 in.
(228.6 mm) deep and shall be thermostatically controlled so as
to maintain the bath at 140 6 1.8°F (60 6 1.0°C). The tank
shallhaveaperforatedfalsebottomorbeequippedwithashelf
FIG. 3 Specimen Mold Holder
for supporting specimens 2 in. (50.8 mm) above the bottom of
the bath.
4.13 Miscellaneous Equipment:
4.13.1 Containers for heating aggregates, flat-bottom metal
pans or other suitable containers.
4.13.2 Containers for heating bituminous material, either
gill-type tins, beakers, pouring pots, or saucepans may be used.
4.13.3 Mixing Tool, either a steel trowel (garden type) or
spatula, for spading and hand mixing.
4.13.4 Thermometers for determining temperatures of ag-
gregates, bitumen, and bituminous mixtures.Armored-glass or
dial-type thermometers with metal stems are recommended. A
range from 50 to 400°F (9.9 to 204°C), with sensitivity of 5°F
(2.8°C) is required.
4.13.5 Thermometers for water and air baths with a range
from 68 to 158°F (20 to 70°C) sensitive to 0.4°F (0.2°C).
4.13.6 Balance, 10-kg capacity, sensitive to 1.0 g.
4.13.7 Gloves for handling hot equipment.
4.13.8 Rubber Gloves for removing specimens from water
FIG. 4 Breaking Head
bath.
4.13.9 Marking Crayons for identifying specimens.
4.13.10 Scoop, flat bottom, for batching aggregates.
required mixing and molding temperatures. It is recommended
4.13.11 Spoon, large, for placing the mixture in the speci-
that the heating units be thermostatically controlled so as to
men molds.
maintain the required temperature within 5°F (2.8°C). Suitable
shields, baffle plates or sand baths shall be used on the surfaces
5. Test Specimens
of the hot plates to minimize localized overheating.
4.11 Mixing Apparatus— Mechanical mixing is recom- 5.1 NumberofSpecimens—Prepare at least three specimens
mended. Any type of mechanical mixer may be used provided for ea
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.