ASTM E1920-97
(Guide)Standard Guide for Metallographic Preparation of Thermal Sprayed Coatings
Standard Guide for Metallographic Preparation of Thermal Sprayed Coatings
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers recommendations for sectioning, cleaning, mounting, grinding, and polishing to reveal the microstructural features of thermal sprayed coatings (TSCs) and the substrates to which they are applied when examined microscopically. Because of the diversity of available equipment, the wide variety of coating and substrate combinations, and the sensitivity of these specimens to preparation technique, the existence of a series of recommended methods for metallographic preparation of thermal sprayed coating specimens is helpful. Adherence to this guide will provide practitioners with consistent and reproducible results. Additional information concerning standard practices for metallographic preparation can be found in Practice E3.
This standards does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
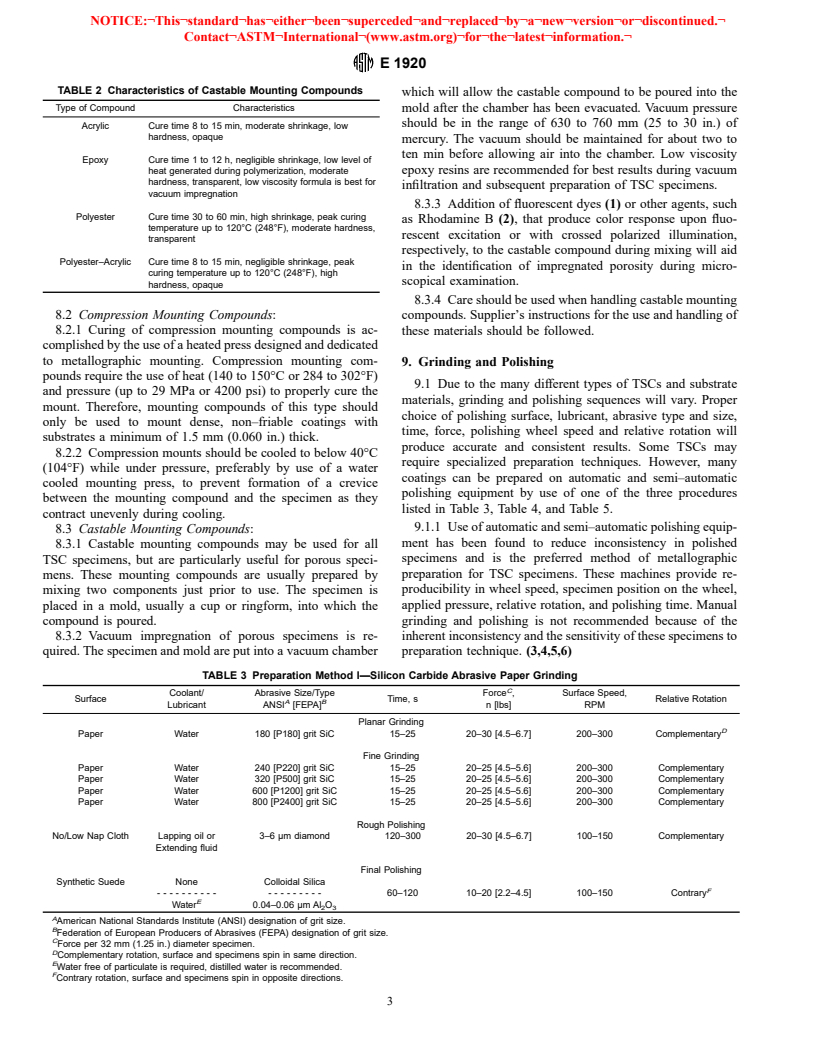
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact
ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: E 1920 – 97
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Guide for
1
Metallographic Preparation of Thermal Sprayed Coatings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 1920; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Significance and Use
1.1 This guide covers recommendations for sectioning, 4.1 TSCs are used in a number of critical industrial compo-
cleaning, mounting, grinding, and polishing to reveal the nents. TSCs can be expected to contain measurable levels of
microstructural features of thermal sprayed coatings (TSCs) porosity and linear detachment. Accurate and consistent evalu-
and the substrates to which they are applied when examined ation of specimens is essential to ensure the integrity of the
microscopically. Because of the diversity of available equip- coating and proper adherence to the substrate.
ment, the wide variety of coating and substrate combinations, 4.1.1 Example 1: By use of inappropriate metallographic
and the sensitivity of these specimens to preparation technique, methods, the apparent amount of porosity and linear detach-
the existence of a series of recommended methods for metal- ment displayed by a given specimen can be increased, by
lographic preparation of thermal sprayed coating specimens is excessive edge rounding, or decreased by smearing of material
helpful. Adherence to this guide will provide practitioners with into voids. Therefore inaccurate levels of porosity and linear
consistent and reproducible results. Additional information detachment will be reported even when the accuracy of the
concerning standard practices for metallographic preparation measurement technique is acceptable.
can be found in Practice E 3. 4.1.2 Example 2: Inconsistent metallographic preparation
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the methods can cause the apparent amount of voids to vary
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the excessively indicating a poorly controlled thermal spray pro-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- cess, while the use of consistent practice will regularly display
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- the true microstructure and verify the consistency of the
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. thermal spray process.
4.2 During the development of TSC procedures, metallo-
2. Referenced Documents
graphic information is necessary to validate the efficacy of a
2.1 ASTM Standards:
specific application.
2
E 3 Practice of Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
4.3 Cross sections are usually taken perpendicular to the
2
E 7 Terminology Relating to Metallography
long axis of the specimen and prepared to reveal information
concerning the following:
3. Terminology
4.3.1 Variations in structure from surface to substrate,
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this guide,
4.3.2 The distribution of unmelted particles throughout the
see Terminology E 7.
coating,
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
4.3.3 The distribution of linear detachment throughout the
3.2.1 linear detachment, n—a region within a TSC in which
coating,
two successively deposited splats of coating material have not
4.3.4 The distribution of porosity throughout the coating,
metallurgically bonded.
4.3.5 The presence of contamination within the coating,
3.2.2 splat, n—an individual globule of thermal sprayed
4.3.6 The thickness of the coating (top coat and bond coat,
material that has been deposited on a substrate.
where applicable),
3.2.3 taper mount, n—a metallographic specimen created
4.3.7 The presence of interfacial contamination,
by mounting a feature, typically an interface or thin coating, at
4.3.8 The integrity of the interface between the coating and
a small angle to the polishing plane, such that the visible width
substrate, and,
exhibited by the feature is expanded.
4.3.9 The integrity of the coating microstructure with re-
3.2.4 TSC, n—thermal sprayed coating, including, but not
spect to chemistry.
limited to, those formed by plasma, flame, and high velocity
oxyfuel. 5. Selection of Metallographic Specimens
5.1 Selection of specimens for metallographic examination
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E–4 on Metallography
is critical if their interpretation is to be of value. Specimens
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E04.01 on Sampling, Specimen
must be representative of the coating. G
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.