ASTM A681-08(2015)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Tool Steels Alloy
Standard Specification for Tool Steels Alloy
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the chemical, mechanical, and physical requirements for available wrought alloy tool steel products. The material shall be made by an electric melting process. It shall be made from ingots that have been reduced in cross section in such a manner and to such a degree as to ensure proper refinement of the ingot structure. Chemical composition, hardness, macrostructure and decarburization of the material shall conform to the requirements in accordance to the referenced ASTM documents itemized herein.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the chemical, mechanical, and physical requirements for available wrought alloy tool steel products.
1.2 These products, which include hot or cold finished bar, plate, sheet, strip, rod, wire, or forgings, are normally fabricated into tools, dies, or fixtures. The selection of a material for a particular application will depend upon design, service conditions, and desired properties.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A681 −08 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Specification for
1
Tool Steels Alloy
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A681; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope Unified Numbering System (UNS)
4
2.2 Military Standard:
1.1 This specification covers the chemical, mechanical, and
MIL-STD-163 Steel Mill Products, Preparation for Ship-
physical requirements for available wrought alloy tool steel
ment and Storage
products.
4
2.3 Federal Standards:
1.2 These products, which include hot or cold finished bar,
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking and Shipment (Civil Agencies)
plate, sheet, strip, rod, wire, or forgings, are normally fabri-
Fed. Std. No. 183 Continuous Identification Marking of Iron
cated into tools, dies, or fixtures.The selection of a material for
and Steel Products
a particular application will depend upon design, service
5
conditions, and desired properties. 2.4 Other Standards:
SAE J1086 Recommended Practice for Numbering Metals
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
and Alloys (UNS)
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
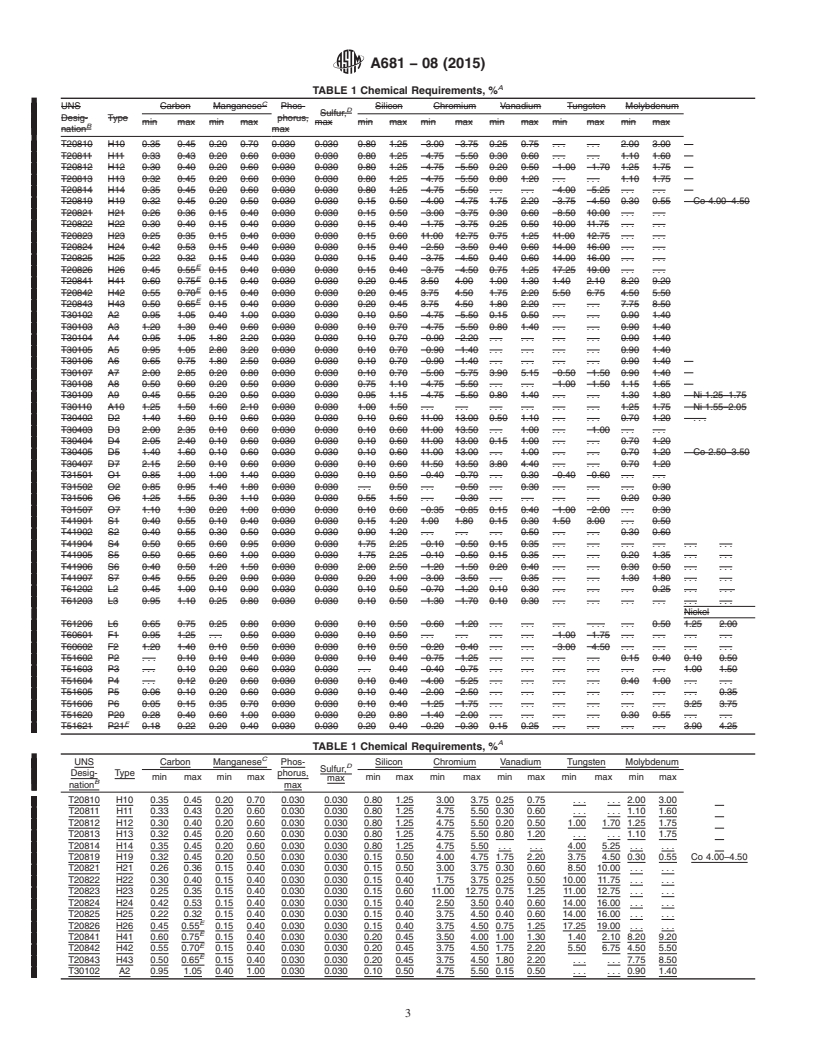
3. Classification
and are not considered standard.
3.1 Material in accordance with this specification is classi-
fied by chemical composition. Types correspond to respective
2. Referenced Documents
2 AISI designations.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.1 Hot Work Tool Steels, Identification H:
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
3.1.1.1 Types H10 to H19 are characterized by a controlled
of Steel Products
chromium content along with other alloying elements.The first
A561 Practice for Macroetch Testing of Tool Steel Bars
four, containing molybdenum, offer excellent toughness and
A600 Specification for Tool Steel High Speed
high hardenability and are frequently used in cold work
A700 Guide for Packaging, Marking, and Loading Methods
applications requiring toughness at relatively high hardness
for Steel Products for Shipment
levels.
E3 Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
3.1.1.2 Types H21 to H26 are characterized by a controlled
E30 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Steel, Cast Iron,
3 tungsten content along with other alloying elements. These
Open-Hearth Iron, and Wrought Iron (Withdrawn 1995)
steels offer greater resistance to the softening effect of elevated
E45 Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of
service temperatures but exhibit a lower degree of toughness.
Steel
3.1.1.3 Types H41 to H43 are low-carbon modifications of
E59 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determination
3 molybdenum high speed tool steels (Note 1) and have charac-
of Chemical Composition (Withdrawn 1996)
teristics similar to the tungsten types.
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the
NOTE 1—High-speed tool steels are covered in Specification A600.
3.1.2 Cold Work Tool Steels, Identification A—Types A2 to
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
A10 cover a wide range of carbon and alloy contents but all
Stainless Steel and Related Alloysand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
have high hardenability and may be hardened in air. The low
A01.29 on Tool Steels.
carbon Types A8 and A9 have less wear resistance but offer
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2015. Published September 2015. Originally
approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as A681 – 08. DOI:
greater toughness than others in this group.TypeA7, with high
10.1520/A0681-08R15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from DLA Document Services, Building 4/D, 700 Robbins Ave.,
the ASTM website. Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, http://quicksearch.dla.mil.
3 5
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on Available from SAE International (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr.,Warrendale,
www.astm.org. PA 15096, http://www.sae.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A681−08 (2015)
carbon and vanadium, offers exceptional wear resistance but at 6.2 Analysis may be made by the purchaser from finished
a very low level of toughness. bars and forgings by machining off the entire cross sec
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A681 − 08 A681 − 08 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Specification for
1
Tool Steels Alloy
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A681; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers the chemical, mechanical, and physical requirements for available wrought alloy tool steel
products.
1.2 These products, which include hot or cold finished bar, plate, sheet, strip, rod, wire, or forgings, are normally fabricated into
tools, dies, or fixtures. The selection of a material for a particular application will depend upon design, service conditions, and
desired properties.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A561 Practice for Macroetch Testing of Tool Steel Bars
A600 Specification for Tool Steel High Speed
A700 Guide for Packaging, Marking, and Loading Methods for Steel Products for Shipment
E3 Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
3
E30 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Steel, Cast Iron, Open-Hearth Iron, and Wrought Iron (Withdrawn 1995)
E45 Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of Steel
3
E59 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determination of Chemical Composition (Withdrawn 1996)
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering System (UNS)
4
2.2 Military Standard:
MIL-STD-163 Steel Mill Products, Preparation for Shipment and Storage
4
2.3 Federal Standards:
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking and Shipment (Civil Agencies)
Fed. Std. No. 183 Continuous Identification Marking of Iron and Steel Products
5
2.4 Other Standards:
SAE J1086 Recommended Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS)
3. Classification
3.1 Material in accordance with this specification is classified by chemical composition. Types correspond to respective AISI
designations.
3.1.1 Hot Work Tool Steels, Identification H:
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and Related Alloysand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A01.29
on Tool Steels.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2008Sept. 1, 2015. Published October 2008September 2015. Originally approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 20072008
ε1
as A681 – 07A681 – 08. . DOI: 10.1520/A0681-08.10.1520/A0681-08R15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
4
Available from the Standardization Documents, Order Desk, Bldg. 4, Section DLA Document Services, Building 4/D, 700 D700Robbins Ave.Ave., Philadelphia, PA
19111-5094 Attn: NPODS.19111-5094, http://quicksearch.dla.mil.
5
Available from the Society of Automotive Engineers, 400 Commonwelth drive, Warrendale, PA 15096.SAE International (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale,
PA 15096, http://www.sae.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A681 − 08 (2015)
3.1.1.1 Types H10 to H19 are characterized by a controlled chromium content along with other alloying elements. The first four,
containing molybdenum, offer excellent toughness and high hardenability and are frequently used in cold work applications
requiring toughness at relatively high hardness levels.
3.1.1.2 Types H21 to H26 are characterized by a controlled tungsten content along with other alloying elements. These steels
offer greater resistance to the softening effect of elevated service temperatures but exhibit a lower degree of toughness.
3.1.1.3 Types H41 to H43 are low-carbon modifications of molybdenum high speed tool steels (Note 1) and have characteristics
similar to the tungsten types.
NOTE 1—High-speed tool steels are covered in S
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.