ASTM D7133-05
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Polyurethane Raw Materials: Instrumental Measurement of Tristimulus CIELAB Color and Yellowness Index of Liquids
Standard Test Method for Polyurethane Raw Materials: Instrumental Measurement of Tristimulus CIELAB Color and Yellowness Index of Liquids
SCOPE
1.1 This test method provides an instrumental method for measuring the CIELAB color and Yellowness Index (YI) of liquid polyurethane raw materials. The CIELAB and YI results are derived from mathematical manipulation of CIE tristimulus values in accordance with Practices E 308 and E 313, respectively.
1.2 See Section 5 for cautions in using this test method.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.Note 1
There is no equivalent ISO standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D7133–05
Standard Test Method for
Polyurethane Raw Materials: Instrumental Measurement of
Tristimulus CIELAB Color and Yellowness Index of Liquids
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7133; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Summary of Test Method
1.1 This test method provides an instrumental method for 4.1 The color of the total transmitted light is measured by a
measuring the CIELAB color and Yellowness Index (YI) of spectrophotometer in CIE tristimulus values under CIE stan-
liquid polyurethane raw materials.The CIELAB andYI results dard illuminant D65 and CIE 1964 supplementary standard
arederivedfrommathematicalmanipulationofCIEtristimulus observer commonly called the 10° standard observer. These
values in accordance with Practices E308 and E313, respec- values are then converted by the appropriate equations to the
tively. CIELAB color scale and theYellowness Index. L*a*b* andYI
1.2 See Section 5 for cautions in using this test method. values are reported.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
5. Significance and Use
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
5.1 CIELAB is a visual-based scale that can be used to
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- specify color and set color tolerances for the polyurethane
industry.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5.2 Yellowness Index specifies the degree of departure of
NOTE 1—There is no equivalent ISO standard.
the sample from colorless towards yellow. This index is only
suitable for clear liquids with degrees of saturation in yellow
2. Referenced Documents
(dominant transmission wavelength in the 570 to 580 nm
2.1 ASTM Standards:
range). It can be used to set tolerances for appropriate
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
polyurethane raw materials.
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
5.3 This test method does not include provisions for mate-
E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM
rialswithfluorescenceorvisiblehaze(usuallygreaterthan5 %
Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Spe-
haze).
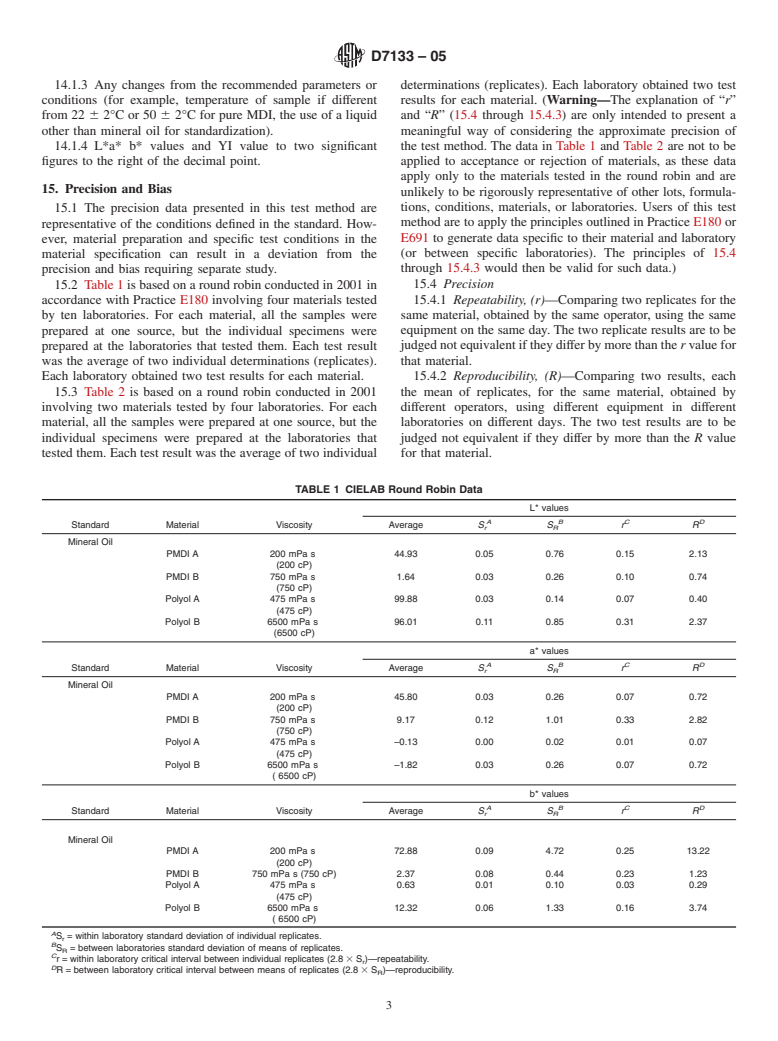
cialty Chemicals
5.4 Beforeproceedingwiththistestmethod,makereference
E284 Terminology of Appearance
to the specification of the material being tested. Any test
E308 Practice for Computing the Colors of Objects by
specimen preparation, conditioning, dimensions, or testing
Using the CIE System
parameters or combination thereof, covered in the materials
E313 Practice for Calculating Yellowness and Whiteness
specificationshalltakeprecedenceoverthosementionedinthis
Indices from Instrumentally Measured Color Coordinates
test method. If there are no material specifications, then the
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
default conditions apply.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
6. Interferences
3. Terminology
6.1 This test method is to be used to compare samples only
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms that appear in this
when they are measured under the same conditions.
test method, refer to Terminologies E284, D883, and the
6.1.1 The medium in the cuvette used during standardiza-
terminology section of Practice E308.
tion of the instrument will have an effect on the measured
results. Light mineral oil is recommended, however, distilled
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
water can be used as a substitute but a note of the substitution
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.22 on Cellular Materials—
must be included in any report of the results.
Plastics and Elastomers.
6.1.2 The temperature of the sample is also expected to
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2005. Published January 2006. DOI: 10.1520/
D7133-05. affect the results obtained.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D7133–05
7. Apparatus 10.1.3.2 Select the total transmission (TTRAN) mode un-
less instructed by the manufacturer to use a different mode for
7.1 Instrument—A hemispherical geometry (integrating
the verification procedure.
sphere) spectrophotometer capable of total transmission (TT-
10.2 Pourmineraloilintoacleancuvette.Ensurethatliquid
RAN) CIE tristimulus measurement through a cuvette. TT-
completely covers the measurement area and that no air
RAN includes both the regularly transmitted portion and the
bubblesremainbelowthemeniscus.Followthemanufacturer’s
diffused portion of the incident light. The instrument must be
instructions to perform the following steps before sample
capable of converting CIE XYZ tristimulus values to the
analyses and at least every four hours when samples are being
CIELAB color scale as defined in Practice E308 using CIE
analyzed.
D65 standard illuminant and 10° standard observer. The
10.2.1 Full-Scale Standardization—Use a cuvette filled
instrument must also be capable of converting CIE XYZ
with mineral oil to set the top of the neutral axis scale to 100
tristimulus values to the Yellowness Index value defined in
bysimulatingthecasewherealllightistransmittedthroughthe
Practice E313 using CIE D65 standard illuminant and 10°
sample.
standard observer. The instrument is to meet the manufactur-
10.2.2 Zero Scale Standardization—Set the bottom of the
er’s requirements for calibration. For highly transparent
neutral axis scale to 0 by simulating the case where all light is
samples, such as the polyols below, spectrophotometers or
absorbed by the sample. Block the light beam by replacing the
tristimulus colorimeters without a spherical geometry can be
cuvette with an opaque object supplied by the manufacturer.
used with equivalent results.
7.2 Sample Cuvettes—The cuvette must have a 20 6 0.06
11. Conditioning
mm pathlength. The entrance and exit windows shall be
11.1 Condition liquids for measurement at 23 6 2°C unless
parallel, colorless, clear and unaffected by the material being
otherwise specified by contract or relevant material specifica-
analyzed. The optical properties of the cuvette used during
tion.
standardization of the instrument and the cuvette used for
measuring samples (if not the same cuvette) must be matched.
NOTE 2—The pure 4,4’ isomer of methylene–bis-(phenylisocyanate)
This can be determined by proving that the variation, if any, in
(MDI) is a solid at 23°C. Condition it for measurement at 50 6 2°C.
the different cuvettes used do not affect the measured value of
12. Procedure
a standard sample. Glass or plastic cuvettes can be used.
12.1 Sample Preparation—Pour the sample into a clean
8. Reagents cuvette. Ensure that liquid completely covers the measurement
area and that no air bubbles remain below the meniscus.
8.1 Mineral Oil—Colorless NF or FCC grade light mineral
12.2 Selection of Instrument Variables
oil.
12.2.1 Select CIE illuminant D65 and 10 standard observer.
8.2 Distilled Water—Colorless distilled water conforming
12.2.2 Select the total transmission (TTRAN) mode.
to Type IV of Specification D1193.
12.3 Selection of Color Scale and Index—Select the
CIELAB color calculated as defined in Practice E308 and the
9. Sampling and Test Specs and Units
Yellowness Index calculated as defined in Practice E313.
9.1 Test samples are to be homogeneous and representative
12.4 Analysis
of the liquid being tested.
12.4.1 The mineral oil is read as a sample to ensure that the
9.2 Do not touch the entrance and exit windows of the
instrument is set up and reading correctly prior to sample
cuvette through which incident and transmitted light will pass
analysis. Therefore, measure the cuvette of mineral oil in
except to clean them.
duplicate by following the manufacturer’s instructions for
9.3 The CIELAB values, L*, a*, and b*, have no units
sample measurement in TTRAN mode. The average of two
associated with them.
readings is to meet the following tolerances: L* =100 6 0.1;
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.