ASTM D6905-20
(Practice)Standard Practice for Impact Flexibility of Organic Coatings
Standard Practice for Impact Flexibility of Organic Coatings
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Coatings attached to substrates are subjected to damaging impacts during the manufacture of articles and their use in service. This impact resistance practice has been found to be useful in predicting the performance of organic coatings for their ability to resist cracking caused by impacts.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers a procedure for determining the ability of a coating film and its substrate to resist shattering, cracking, or chipping when the film and substrate are distended beyond their original form by impact.
1.2 This practice does not measure impact resistance but uses rapid impact to improve Test Methods D522, a test method for flexibility. Since the impact of the coating is almost instantaneous, all of the problems associated with time variables in the mandrel tests are eliminated.
1.3 This practice is similar in content but not technically equivalent to Test Method D2794.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D6905 − 20
Standard Practice for
1
Impact Flexibility of Organic Coatings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6905; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* Related Coating Products
D823 Practices for Producing Films of Uniform Thickness
1.1 This practice covers a procedure for determining the
of Paint, Coatings and Related Products on Test Panels
ability of a coating film and its substrate to resist shattering,
D2240 Test Method for Rubber Property—Durometer Hard-
cracking,orchippingwhenthefilmandsubstratearedistended
ness
beyond their original form by impact.
D2794 Test Method for Resistance of Organic Coatings to
1.2 This practice does not measure impact resistance but
the Effects of Rapid Deformation (Impact)
uses rapid impact to improve Test Methods D522, a test
D7091 Practice for Nondestructive Measurement of Dry
method for flexibility. Since the impact of the coating is almost
Film Thickness of Nonmagnetic Coatings Applied to
instantaneous, all of the problems associated with time vari-
Ferrous Metals and Nonmagnetic, Nonconductive Coat-
ables in the mandrel tests are eliminated.
ings Applied to Non-Ferrous Metals
1.3 This practice is similar in content but not technically
3. Terminology
equivalent to Test Method D2794.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3.1.1 impact flexibility, n—of a coating, the percent area
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
increase required to produce cracking in the deformed coating.
only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4. Summary of Practice
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.1 The organic coating under test is applied to suitable thin
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
metal panels (see Practice D609). After the coating has cured,
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
a standard weight/indenter is dropped from a measured dis-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
tance so as to strike the substrate which deforms the coating
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
and the substrate. The percent elongation is the highest area of
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
distensibility in which there is no film breaks that the film can
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
stand.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
5. Significance and Use
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5.1 Coatings attached to substrates are subjected to damag-
2. Referenced Documents
ing impacts during the manufacture of articles and their use in
2
service. This impact resistance practice has been found to be
2.1 ASTM Standards:
useful in predicting the performance of organic coatings for
D522 Test Methods for Mandrel Bend Test of Attached
their ability to resist cracking caused by impacts.
Organic Coatings
D609 Practice for Preparation of Cold-Rolled Steel Panels
6. Apparatus
for Testing Paint, Varnish, Conversion Coatings, and
3
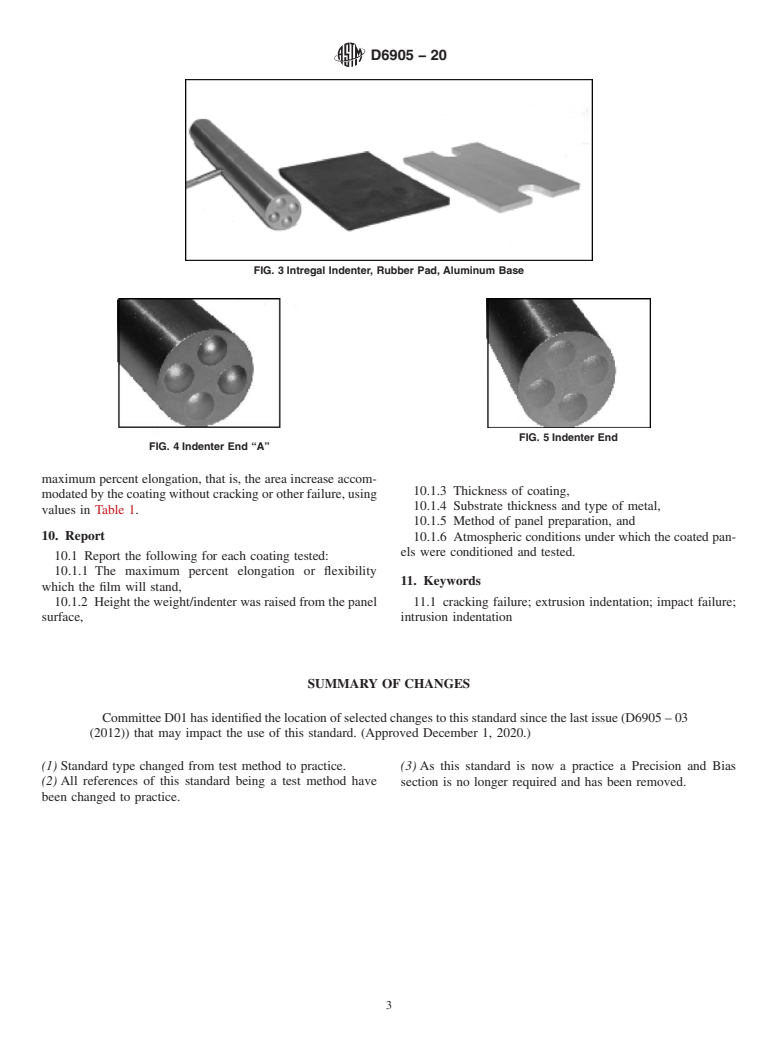
6.1 Impact Flexibility Tester ,assemblyillustratedinFigs.1
and 2. The instrument contains a 1.63 kg (3.6 lb) weight/
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and
indenter, a rubber pad and an aluminum pad, Fig. 3. The round
Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.23 on Physical Properties of Applied Paint Films.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2020. Published December 2020. Originally
3
approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D6905 – 03 (2012). The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time
DOI: 10.1520/D6905-20. is the IM-172-GE ImpactTester, available from the Paul N. Gardner Company, Inc.,
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or 316 N.E. First Street, Pompano Beach, FL 33060. If you are aware of alternative
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International Headquarters.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the responsible
1
the ASTM website.
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6905 − 03 (Reapproved 2012) D6905 − 20
Standard Test Method Practice for
1
Impact Flexibility of Organic Coatings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6905; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the ability of a coating film and its substrate to resist shattering, cracking,
or chipping when the film and substrate are distended beyond their original form by impact.
1.2 This test method does not measure impact resistance but uses rapid impact to improve Test Methods D522, another test method
for flexibility. Since the impact of the coating is almost instantaneous, all of the problems associated with time variables in the
mandrel tests are eliminated.
1.3 This test method is similar in content but not technically equivalent to Test Method D2794.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D522 Test Methods for Mandrel Bend Test of Attached Organic Coatings
D609 Practice for Preparation of Cold-Rolled Steel Panels for Testing Paint, Varnish, Conversion Coatings, and Related Coating
Products
D823 Practices for Producing Films of Uniform Thickness of Paint, Coatings and Related Products on Test Panels
D1186 Test Methods for Nondestructive Measurement of Dry Film Thickness of Nonmagnetic Coatings Applied to a Ferrous
3
Base (Withdrawn 2006)
D1400 Test Method for Nondestructive Measurement of Dry Film Thickness of Nonconductive Coatings Applied to a
3
Nonferrous Metal Base (Withdrawn 2006)
D2240 Test Method for Rubber Property—Durometer Hardness
D2794 Test Method for Resistance of Organic Coatings to the Effects of Rapid Deformation (Impact)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1
This test method practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility
of Subcommittee D01.23 on Physical Properties of Applied Paint Films.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2012Dec. 1, 2020. Published November 2012December 2020. Originally approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 20082012
as D6905 – 03 (2008).(2012). DOI: 10.1520/D6905-03R12.10.1520/D6905-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6905 − 20
3.1.1 impact flexibility, n—of a coating, the percent area increase required to produce cracking in the deformed coating.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The organic coating under test is applied to suitable thin metal panels. After the coating has cured, a standard weight/indenter
is dropped from a measured distance so as to strike the substrate which deforms the coating and the substrate. The percent
elongation is the highest area of distensibility in which there is no film breaks that the film can stand.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 Coatings attached to substrates are subjected to damaging impacts during the manufacture of articles and their use in service.
This impact resistance test method has been found to be useful in predicting the performance of organic coatings for their ability
to resist cracking caused by impacts.
6. Apparatus
4
6.1 Impact Flexibility Tester ,assembly illustrated in Figs. 1 and 2. The instrument contains a 1.63 kg (3.6 lb) weight/indenter, a
rubber pad and an aluminum pad, Fig. 3. The round rod weight/indenter’s two spherical ends (Marked “A” and “B”) are shown
in Figs. 4 and 5. The dimensions for the Spherical weight/indenter are shown in Table 1. The rod slides in a vertical, slotted guide
and serves as a falling
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.