ASTM F711-17(2022)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Rod and Tube Used in Live Line Tools
Standard Specification for Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Rod and Tube Used in Live Line Tools
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the technical characteristics of and test methods for insulating rods and foam-filled tubes made from fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) that are intended for use in live line tools. This specification does not include insulating foam-filled tubes and rods made from other materials, as well as fittings and attachments to the rods and foam-filled tubes for complete tools are not covered in this specification. The rods and tubes shall undergo four types of tests, namely: design test, sample test, routine test, and acceptance test. Tests shall be conducted to evaluate the following mechanical and electrical properties: wicking, bending deflection, horizontal crush, tension, shear, compression, modulus of elasticity, and mechanical aging; and dielectric current and leakage.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers insulating rods and foam-filled tubes made from fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) that are intended for use in live line tools.
1.2 This specification does not include insulating foam-filled tubes and rods from other materials. Specifications for fittings and attachments to rods and foam-filled tubes for complete tools are not covered in this specification.
1.3 This specification establishes the technical characteristics that the tubes and rods must satisfy.
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 12, of this specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:F711 −17 (Reapproved 2022)
Standard Specification for
Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Rod and Tube Used in
Live Line Tools
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF711;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 Thisspecificationcoversinsulatingrodsandfoam-filled 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
tubes made from fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) that are 3.1.1 acceptance test—a type of test made at the option of
intended for use in live line tools. the purchaser.
3.1.2 design test—atypeoftestmadeonasampletreatedas
1.2 This specification does not include insulating foam-
representative of an industrial product. These tests will not
filled tubes and rods from other materials. Specifications for
generally be repeated in quantity production.
fittings and attachments to rods and foam-filled tubes for
complete tools are not covered in this specification.
3.1.3 insulating tubes and rods—fiberglass-reinforced plas-
tic (FRP) products manufactured using processes so that the
1.3 This specification establishes the technical characteris-
tubes and rods produced will meet the electrical and mechani-
tics that the tubes and rods must satisfy.
cal tests prescribed in this specification.
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
3.1.4 interior foam-filled tube—homogeneous unicellular
test method portion, Section 12, of this specification. This
thermosetting foam filling with closed cells blown with non-
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
combustible gases. The foam filling shall be bonded to the
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
interior tube wall. The foam filling should be free of voids,
of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and
separations, holes, cracks, etc.
environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1.5 routine test—a type of test made regularly on produc-
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
tion material.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.1.6 visual inspection—a visual check made to detect
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
constructional defects.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4. Ordering Information
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4.1 Outside Diameter Sizes—Foam-filled FRP tube and
solid FRP rod shall meet the outside diameter dimensions
2. Referenced Documents
shown in Table 1.The tolerances shown will assist in ensuring
2.1 ASTM Standards:
interchangeability with interfacing equipment.
D149Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and
4.2 Inspection of the material shall be agreed upon between
DielectricStrengthofSolidElectricalInsulatingMaterials
the purchaser and the seller as part of the purchase contract.
at Commercial Power Frequencies
D638Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics 5. Materials and Manufacture
D695Test Method for Compressive Properties of Rigid
5.1 Except for those test methods leading to destruction,
Plastics
neither the FRP tube, foam, or the bond between them shall
deteriorate during the prescribed mechanical and electrical
tests of this specification.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F18 on
Electrical Protective Equipment for Workers and is the direct responsibility of
6. Physical Requirements
Subcommittee F18.35 on Tools & Equipment.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2022. Published January 2023. Originally
6.1 The materials shall conform to the diameters prescribed
approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as F711–17. DOI:
in Table 1 for tube and rod.
10.1520/F0711-17R22.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
6.2 The standard sizes listed by nominal diameter are
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
recommended and do not preclude the manufacture of other
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. sizes or shapes.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F711−17 (2022)
TABLE 1 Standard Tube and Rod Outside Diameters
design rod
Visual design tube
Nominal Diameter Min Diameter Max Diameter
TYPE design rod
in. (mm) in. (mm) in. (mm)
acceptance tube
Tube 1 (25.4) 0.98 (24.9) 1.02 (25.9)
acceptance rod
1 ⁄4 (31.8) 1.22 (31.0) 1.27 (32.3)
Dimensional acceptance tube
1 ⁄2 (38.1) 1.47 (37.3) 1.53 (38.9)
acceptance rod
1 ⁄4 (44.5) 1.73 (43.9) 1.78 (45.2) routine tube
2 (50.8) 1.97 (50.0) 2.04 (51.8)
routine rod
2 ⁄2 (63.5) 2.47 (62.7) 2.54 (64.5)
10.2 Electrical:
3 (76.2) 2.97 (75.3) 3.04 (77.2)
Rod ⁄8 (9.5) 0.369 (9.4) 0.385 (9.8)
Test Type Material
⁄2 (12.7) 0.490 (12.4) 0.510 (13.0)
Dielectric current (leakage) design rod
⁄8 (15.9) 0.610 (15.5) 0.635 (16.1)
(before moisture conditioning) design tube
⁄4 (19.1) 0.720 (18.3) 0.765 (19.4)
Dielectric current (leakage) design rod
(after moisture conditioning) design tube
Withstand (either method 1 or 2) routine rod
routine tube
7. Weight
11. Number of Tests and Samples (Three each)
7.1 It has not been found necessary to specify the weight of
11.1 Tubes:
the product produced under this specification in order for it to
11.1.1 Wicking Test—Three samples, each 1-in. (25-mm)
comply with performance requirements.
long.
8. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
11.1.2 Bending Deflection Test—8ft,5in.(2.6m)orlonger.
See Fig. 13.
8.1 The external surface shall be uniform, symmetrical, and
11.1.3 Horizontal Crush Test—Three diameters long. See
free of abrasions, scratches, blemishes, and surface defects.
Fig. 14.
8.2 Any defect that may capture an impurity or impair the
11.1.4 Tension Test—12-in. (300-mm) long, prepared in
dielectric integrity of the product shall be cause for rejection.
accordance with Fig. 1 and Test Method D638.
8.3 FRP rod or tube material after which a finish coating,
such as paint, is applied must meet all physical, electrical, and
mechanical requirements.
9. Sampling
9.1 Design Test—Perform the test on a minimum of three
samples only when changes are made to a new or existing
design of the product that may affect the mechanical and
electrical characteristics.
9.1.1 The design test will be used to qualify a specific item
and normally will not be repeated during production.
9.2 Sample Test—A test specimen shall consist of one or
more items, dependent on 1% of the lot being tested.
9.2.1 Alotisrepresentedeitherbyallitemsproducedinone
production run or in one shipment.
9.2.2 Lots of new, unused items shall have test specimens
selected at random.
9.3 Routine Test—Performthetestonallpiecesdeliveredto
the purchaser.
9.4 Acceptance Test—A test made at the option of the
purchaser.
10. Conduct of Tests on Samples
10.1 Mechanical:
Test Type Material
Wicking design tube
Bending deflection design tube
Horizontal crush design tube
acceptance tube
Tension design tube
design rod
Shear design tube
Compression design rod
Modulus of elasticity (tension) design rod
Mechanical aging (flexure) design tube
FIG. 1 Tension Test
F711−17 (2022)
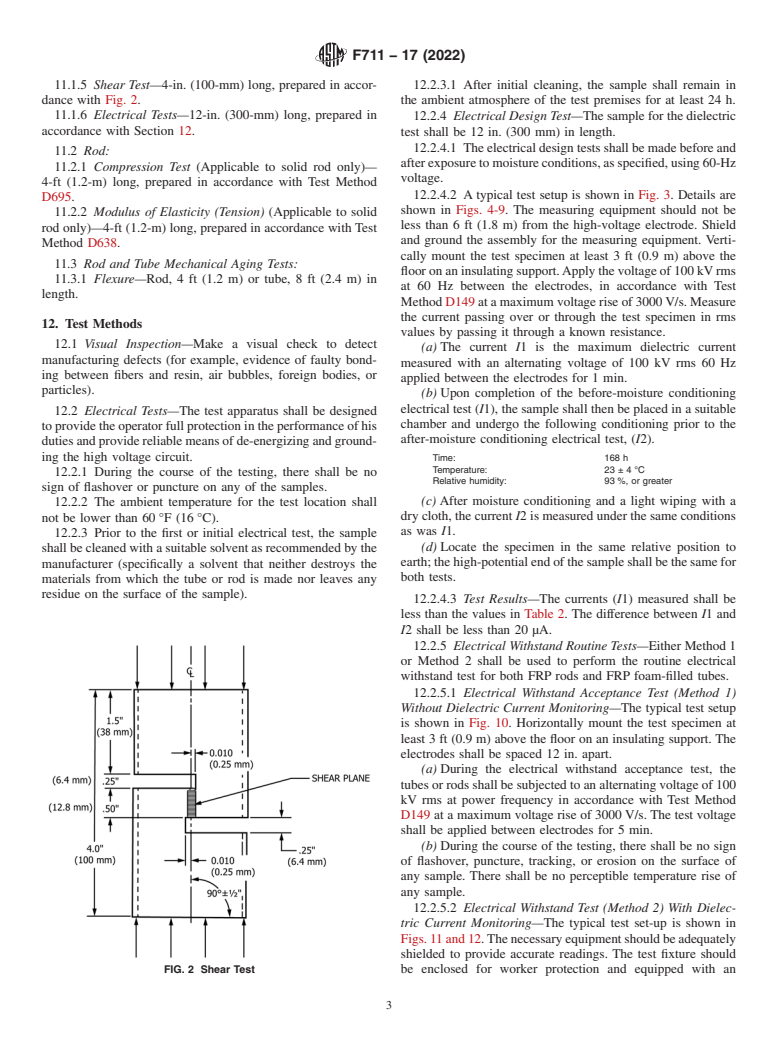
11.1.5 Shear Test—4-in. (100-mm) long, prepared in accor- 12.2.3.1 After initial cleaning, the sample shall remain in
dance with Fig. 2. the ambient atmosphere of the test premises for at least 24 h.
11.1.6 Electrical Tests—12-in. (300-mm) long, prepared in
12.2.4 Electrical Design Test—Thesampleforthedielectric
accordance with Section 12. test shall be 12 in. (300 mm) in length.
12.2.4.1 Theelectricaldesigntestsshallbemadebeforeand
11.2 Rod:
afterexposuretomoistureconditions,asspecified,using60-Hz
11.2.1 Compression Test (Applicable to solid rod only)—
voltage.
4-ft (1.2-m) long, prepared in accordance with Test Method
12.2.4.2 A typical test setup is shown in Fig. 3. Details are
D695.
shown in Figs. 4-9. The measuring equipment should not be
11.2.2 Modulus of Elasticity (Tension) (Applicable to solid
less than 6 ft (1.8 m) from the high-voltage electrode. Shield
rod only)—4-ft (1.2-m) long, prepared in accordance withTest
and ground the assembly for the measuring equipment. Verti-
Method D638.
cally mount the test specimen at least 3 ft (0.9 m) above the
11.3 Rod and Tube Mechanical Aging Tests:
flooronaninsulatingsupport.Applythevoltageof100kVrms
11.3.1 Flexure—Rod, 4 ft (1.2 m) or tube, 8 ft (2.4 m) in
at 60 Hz between the electrodes, in accordance with Test
length.
MethodD149atamaximumvoltageriseof3000V/s.Measure
the current passing over or through the test specimen in rms
12. Test Methods
values by passing it through a known resistance.
12.1 Visual Inspection—Make a visual check to detect
(a)The current I1 is the maximum dielectric current
manufacturing defects (for example, evidence of faulty bond-
measured with an alternating voltage of 100 kV rms 60 Hz
ing between fibers and resin, air bubbles, foreign bodies, or
applied between the electrodes for 1 min.
particles).
(b)Upon completion of the before-moisture conditioning
electricaltest(I1),thesampleshallthenbeplacedinasuitable
12.2 Electrical Tests—The test apparatus shall be designed
chamber and undergo the following conditioning prior to the
toprovidetheoperatorfullprotectionintheperformanceofhis
after-moisture conditioning electrical test, (I2).
dutiesandprovidereliablemeansofde-energizingandground-
ing the high voltage circuit.
Time: 168 h
Temperature: 23 ± 4 °C
12.2.1 During the course of the testing, there shall be no
Relative humidity: 93 %, or greater
sign of flashover or puncture on any of the samples.
(c)After moisture conditioning and a light wiping with a
12.2.2 The ambient temperature for the test location shall
drycloth,thecurrent I2ismeasuredunderthesameconditions
not be lower than 60°F (16°C).
as was I1.
12.2.3 Prior to the first or initial electrical test, the sample
(d)Locate the specimen in the same relative position to
shallbecleanedwithasuitablesolventasrecommendedbythe
earth;thehigh-potentialendofthesampleshallbethesamefor
manufacturer (specifically a solvent that neither destroys the
both tests.
materials from which the tube or rod is made nor leaves any
residue on the surface of the sample).
12.2.4.3 Test Results—The currents (I1) measured shall be
less than the values in Table 2. The difference between I1 and
I2 shall be less than 20 µA.
12.2.5 Electrical Withstand Routine Tests—EitherMethod1
or Method 2 shall be used to perform the routine electrical
withstand test for both FRP rods and FRP foam-filled tubes.
12.2.5.1 Electrical Withstand Acceptance Test (Method 1)
Without Dielectric Current Monitoring—The typical test setup
is shown in Fig. 10. Horizontally mount the test specimen at
least 3 ft (0.9 m) above the floor on an insulating support. The
electrodes shall be spaced 12 in. apart.
(a)During the electrical withstand acceptance test, the
tubesorrodsshallbesubjectedtoanalternatingvoltageof100
kV rms at power frequency in accordance with Test Method
D149 at a maximum voltage rise of 3000V/s.The test voltage
shall be applied between electrodes for 5 min.
(b)During the course of the testing, there shall be no sign
of flashover, puncture, tracking, or erosion on the surface of
any sample. There shall be no perceptible temperature rise of
any sample.
12.2.5.2 Electrical Withstand Test (Method 2) With Dielec-
tric Current Monitoring—The typical test set-up is shown in
Figs.11and12.Thenecessaryequipmentshouldbeadequately
shielded to provide accurate readings. The test fixture should
FIG. 2 Shear Test be enclosed for worker protection and equipped with an
F711−17 (2022)
NOTE 1—For details of Fig. 3 see Figs. 4-9.
FIG. 3Typical AC Test Set Up
FIG. 4 Assembly Detail
exhaust fan to provide a stable atmosphere. A motor drive (b) Acceptableriseaboveambientoflessthan I1aslisted
should be utilized to ensure a uniform rate of feed. The feed in Table 2. During the course of the testing, there shall be no
rateshouldbeproportionaltotheresponsetimeofthemetering
sign of flashover, puncture, tracking, or erosion on the surface
circuit; that is, it shall be run slowly enough that maximum
of any sample.
readings are obtained. At no time should this rate of feed
12.3 Mechanical Testing of FRP Tube:
exceed 40 ft/min.
12.3.1 Bending Deflection Test (design)—A tube 8 ft 5 in.
(a) With 6-in. electrode spacing, the applied voltage will
be 50 kV. The equipment shall be designed such that a (2.6 m) or longer shall be placed in a testing device such that
flashover, excessive dielectric current will disable the motor the overhang arm is 60 in. (1.5 m) in length, and the distance
drive so that intentional action on the part of the operator is
between supports is as shown in Fig. 13.
required to reset the equipment.
F711−17 (2022)
FIG. 5 Electrode Detail
FIG. 6 Electrode Cap Detail
12.3.1.1 The support shall be of the pole clamp-type (ap-
proximately 4-in. (100-mm) long) with the back clamp tight-
ened to hold specimen in place while the front clamp remains FIG. 7 Brass Electrode Detail
loose and serves only as a fulcrum. Both clamps shall be free
to pivot as load (in Table 3) is applied 60 in. (1.5 m) from 12.3.1.2 The deflection of each tube tested shall not exceed
center of front clamping device (see Fig. 13). the value specified in Table 3.
F711−17 (2022)
12.3.2.2 The distance between the two plates is then con-
tinuouslydecreasedataconstantratebetween0.08to0.2in.(2
to 5 mm)/min. Once selected this constant rate shall not be
changed for that test.
NOTE 1—It is recognized that horizontal crush tests performed at a
higher constant displacement rate are more severe.
12.3.2.3 Record the constant displacement rate selected.
Recordthemaximumforceappliedtothetestspecimenduring
the first 0.25-in. (6-mm) displacement. All tubes shall be
capable of exhibiting a crush strength equal to or in excess of
minimum values listed in Table 4.
12.3.3 Tension Test (design)—The FRP tube shall exhibit
axial tension strength equal to or in excess of the minimum
values listed in Table 5. Cut the test specimens from the wall
of a tube and accurately measur
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.