ASTM A600-92a(1999)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Tool Steel High Speed
Standard Specification for Tool Steel High Speed
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers tungsten-type and molybdenum-type high-speed steels available as annealed, hot-rolled bars, forgings, plate, sheet, or strip, and annealed, cold-finished bars or forgings used primarily in the fabrication of tools.
1.2 Seven types of tungsten high-speed tool steels designated T1, T2, etc., seventeen types of molybdenum high-speed tool steels designated M1, M2, etc., and two intermediate high speed steels designated as M50 and M52 are covered. Selection will depend upon design, service conditions, and mechanical properties.
1.3 The term "high-speed steel" is described and its minimum requirements are covered in the Annex.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A 600 – 92a (Reapproved 1999)
Standard Specification for
Tool Steel High Speed
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 600; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2.2 Military Standard:
MIL-STD-163 Steel Mill Products, Preparation for Ship-
1.1 This specification covers tungsten-type and
ment and Storage
molybdenum-type high-speed steels available as annealed,
2.3 Federal Standards:
hot-rolled bars, forgings, plate, sheet, or strip, and annealed,
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
cold-finished bars or forgings used primarily in the fabrication
Fed. Std. No. 183 Continuous Identification Marking of
of tools.
Iron and Steel Products
1.2 Seven types of tungsten high-speed tool steels desig-
nated T1, T2, etc., seventeen types of molybdenum high-speed
3. Classification
tool steels designated M1, M2, etc., and two intermediate high
3.1 Material in accordance with this specification is classi-
speedsteelsdesignatedasM50andM52arecovered.Selection
fied by chemical composition. Types correspond to respective
will depend upon design, service conditions, and mechanical
AISI designations.
properties.
3.1.1 Types T1, T2, T4, T5, T6, T8, and T15 are character-
1.3 The term “high-speed steel” is described and its mini-
ized by a controlled high tungsten content along with other
mum requirements are covered in the Annex.
alloying elements.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3.1.2 Types M1, M2, M3, M4, M6, M7, M10, M30, M33,
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided
M34, M36, M41, M42, M43, M44, M46, M47, M48, and M62
for information only.
are characterized by a controlled high molybdenum content
2. Referenced Documents along with other alloying elements.
3.1.3 Types M2, M3, and M10 are further classified accord-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ing to carbon range. Type M3 is further classified according to
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for MechanicalTesting
vanadium range.
of Steel Products
3.1.4 Types M50 and M52 are considered intermediate high
A 388/A 388M Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of
3 speed steels in view of their lower total alloy content than the
Heavy Steel Forgings
standard types. These leaner alloy grades normally are limited
A 561 Practice for Macroetch Testing of Tool Steel Bars
to less severe service conditions.
A 700 Practices for Packaging, Marking, and Loading
Methods for Steel Products for Domestic Shipment
4. Ordering Information
E 3 Methods of Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
4.1 Orders for material under this specification shall include
E 30 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Steel, Cast
5 the following information, as required to describe adequately
Iron, Open-Hearth Iron, and Wrought Iron
the desired material:
E 45 Practice for Determining the Inclusion Content of
4 4.1.1 Name of material (high-speed tool steel),
Steel
4.1.2 Type,
E 59 PracticeforSamplingSteelandIronforDetermination
4.1.3 Shape (sheet, strip, plate, flat bar, round bar, square
of Chemical Composition
bar, hexagon bar, octagon, special shapes),
4.1.4 Dimensions (thickness, width, diameter, length). (For
coils, include the minimum inside diameter or inside diameter
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A-1 on Steel,
range, the maximum outside diameter, and maximum or
Stainless Steel and RelatedAlloys , and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.29 on Tool Steel. minimum coil weight if required. (Minimum coil weights are
Current edition approved Aug 15, 1992. Published October 1992. Originally
subject to negotiation.)),
published as A 600 – 69. Last previous edition A 600 – 92.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.05.
4 6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01. Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.05. Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A 600 – 92a (1999)
4.1.5 Finish (hot rolled, forged, blasted or pickled, cold latest issue of Method E 59. The chemical analysis of the
drawn, rough machined, ground, precision ground and pol- drilling chips shall be made in accordance with the latest issue
ished), of Methods E 30. The chemical composition thus determined
4.1.6 Condition (annealed), shall not vary from the limits specified in Table 1.
4.1.7 ASTM designation and date of issue, and
7. Hardness Requirements
4.1.8 Special or supplementary requirements.
7.1 Annealed hardness values when obtained in accordance
5. Materials and Manufacture
with the latest issue of Test Methods and Definitions A 370
5.1 Unless otherwise specified, material covered by this shall not exceed the Brinell hardness values (or equivalent
specification shall be made by an electric melting process. Rockwell hardness values) specified in Table 2.
7.2 Specimens for determination of minimum response to
6. Chemical Composition
hardening shall be ⁄4-in. (6.4-mm) thick disks cut so as to
6.1 An analysis of each heat of steel shall be made by the represent either the full cross-sectional area or that midway
manufacturer to determine the percentage of the elements between the center and outer surface of the material. If the
specified and these values shall conform to the requirements as material form or size does not lend itself to accurate hardness
to chemical composition specified in Table 1. If requested or determination on ⁄4-in. thick cross-sectional disks, then longi-
required, the chemical composition shall be reported to the tudinal specimens may be used for hardness testing. Examples
purchaser or his representative. are round bars less than ⁄2 in. (12.7 mm) in diameter; sheet;
6.2 Analysis may be made by the purchaser from finished and strip. In this case, the specimen shall be a minimum of 3
bars and forgings by machining off the entire cross section and in.(76.2mm)inlength,andparallelflatsshallbegroundonthe
drilling parallel to the axis of the bar or forging at any point original mill surfaces. The specimens shall be heat treated in
midway between the center and surface in accordance with the two furnaces, one operating as a preheat furnace and the other
A
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements, %
C
UNS Type Carbon Manganese Phos- Sulfur Silicon Chromium Vanadium Tungsten Molybdenum Cobalt
Designa- phorus
B
tion
min max min max max max min max min max min max min max min max min max
Tungsten-Type High-Speed Steels
T12001 T1 0.65 0.80 0.10 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.40 3.75 4.50 0.90 1.30 17.25 18.75 . . . . . . . . . . . .
T12002 T2 0.80 0.90 0.20 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.40 3.75 4.50 1.80 2.40 17.50 19.00 . . . 1.00 . . . . . .
T12004 T4 0.70 0.80 0.10 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.40 3.75 4.50 0.80 1.20 17.50 19.00 0.40 1.00 4.25 5.75
T12005 T5 0.75 0.85 0.20 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.40 3.75 5.00 1.80 2.40 17.50 19.00 0.50 1.25 7.00 9.50
T12006 T6 0.75 0.85 0.20 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.40 4.00 4.75 1.50 2.10 18.50 21.00 0.40 1.00 11.00 13.00
T12008 T8 0.75 0.85 0.20 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.40 3.75 4.50 1.80 2.40 13.25 14.75 0.40 1.00 4.25 5.75
T12015 T15 1.50 1.60 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.15 0.40 3.75 5.00 4.50 5.25 11.75 13.00 . . . 1.00 4.75 5.25
Molybdenum-Type High-Speed Steels
T11301 M1 0.78 0.88 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.50 3.50 4.00 1.00 1.35 1.40 2.10 8.20 9.20 . . . . . .
T11302 M2 regular C 0.78 0.88 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.45 3.75 4.50 1.75 2.20 5.50 6.75 4.50 5.50 . . . . . .
high C 0.95 1.05 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.45 3.75 4.50 1.75 2.20 5.50 6.75 4.50 5.50 . . . . . .
T11313 M3 Class 1 1.00 1.10 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.45 3.75 4.50 2.25 2.75 5.00 6.75 4.75 6.50 . . . . . .
T11323 Class 2 1.15 1.25 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.45 3.75 4.50 2.75 3.25 5.00 6.75 4.75 6.50 . . . . . .
T11304 M4 1.25 1.40 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.45 3.75 4.75 3.75 4.50 5.25 6.50 4.25 5.50 . . . . . .
T11306 M6 0.75 0.85 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.45 3.75 4.50 1.30 1.70 3.75 4.75 4.50 5.50 11.00 13.00
T11307 M7 0.97 1.05 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.55 3.50 4.00 1.75 2.25 1.40 2.10 8.20 9.20 . . . . . .
T11310 M10 regular C 0.84 0.94 0.10 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.45 3.75 4.50 1.80 2.20 . . . . . . 7.75 8.50 . . . . . .
high C 0.95 1.05 0.10 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.45 3.75 4.50 1.80 2.20 . . . . . . 7.75 8.50 . . . . . .
T11330 M30 0.75 0.85 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.45 3.50 4.25 1.00 1.40 1.30 2.30 7.75 9.00 4.50 5.50
T11333 M33 0.85 0.92 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.15 0.50 3.50 4.00 1.00 1.35 1.30 2.10 9.00 10.00 7.75 8.75
T11334 M34 0.85 0.92 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.45 3.50 4.00 1.90 2.30 1.40 2.10 7.75 9.20 7.75 8.75
T11336 M36 0.80 0.90 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.45 3.75 4.50 1.75 2.25 5.50 6.50 4.50 5.50 7.75 8.75
T11341 M41 1.05 1.15 0.20 0.60 0.03 0.03 0.15 0.50 3.75 4.50 1.75 2.25 6.25 7.00 3.25 4.25 4.75 5.75
T11342 M42 1.05 1.15 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.15 0.65 3.50 4.25 0.95 1.35 1.15 1.85 9.00 10.00 7.75 8.75
T11343 M43 1.15 1.25 0.20 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.15 0.65 3.50 4.25 1.50 1.75 2.25 3.00 7.50 8.50 7.75 8.75
T11344 M44 1.10 1.20 0.20 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.30 0.55 4.00 4.75 1.85 2.20 5.00 5.75 6.00 7.00 11.00 12.25
T11346 M46 1.22 1.30 0.20 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.40 0.65 3.70 4.20 3.00 3.30 1.90 2.20 8.00 8.50 7.80 8.80
T11347 M47 1.05 1.15 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.45 3.50 4.00 1.15 1.35 1.30 1.80 9.25 10.00 4.75 5.25
. . . M48 1.42 1.52 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.07 0.15 0.40 3.50 4.00 2.75 3.25 9.50 10.50 4.75 5.50 8.00 10.00
. . . M62 1.25 1.35 0.15 0.40 0.03 0.07 0.15 0.40 3.50 4.00 1.80 2.10 5.75 6.50 10.00 11.00 . . . . . .
Intermediate High Speed Steels
T11350 M50 0.78 0.88 0.15 0.45 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.60 3.75 4.50 0.80 1.25 . . . . . . 3.90 4.75 . . . . . .
T11352 M52 0.85 0.95 0.15 0.45 0.03 0.03 0.20 0.60 3.50 4.30 1.65 2.25 0.75 1.50 4.00 4.90 . . . . . .
A
Chemistry limits include product analysis tolerances. Unless otherwise specified, nickel plus copper equals 0.75 % max for all types.
B
New designation established in accordance with Practice E 527 and SAE J 1086.
C
Where specified, sulfur may be 0.06 to 0.15 % to improve machinability.
A 600 – 92a (1999)
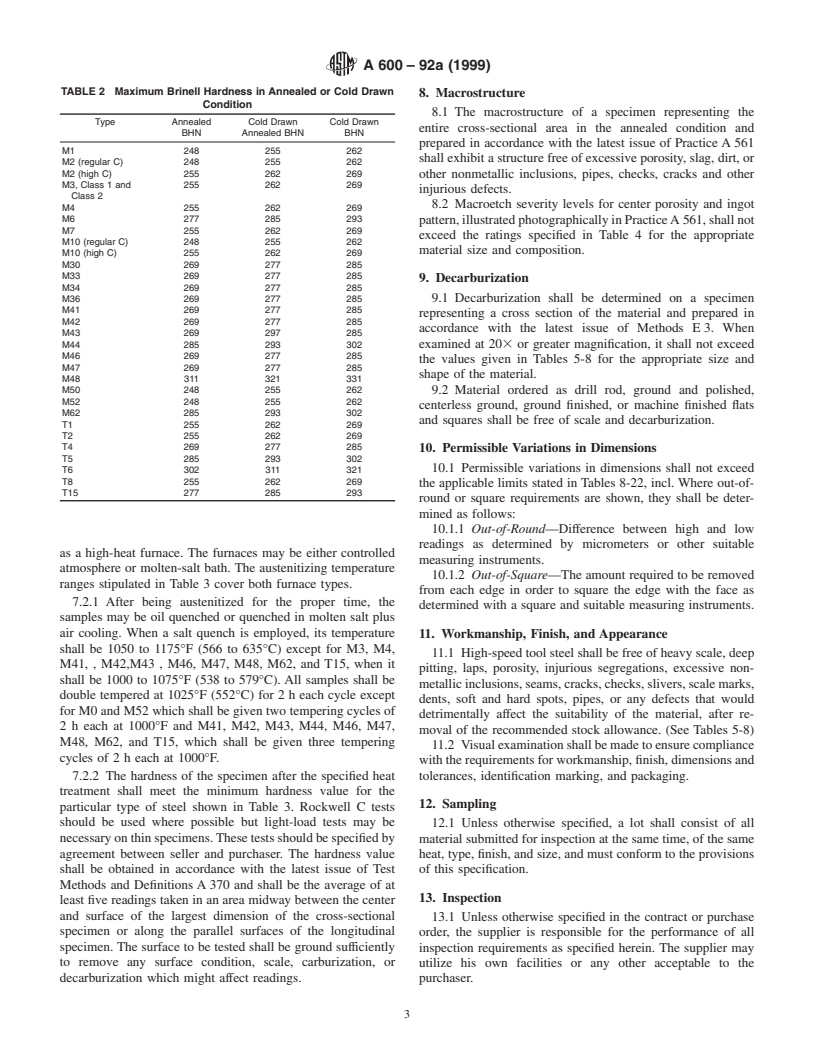
TABLE 2 Maximum Brinell Hardness in Annealed or Cold Drawn
8. Macrostructure
Condition
8.1 The macrostructure of a specimen representing the
Type Annealed Cold Drawn Cold Drawn
entire cross-sectional area in the annealed condition and
BHN Annealed BHN BHN
prepared in accordance with the latest issue of Practice A 561
M1 248 255 262
shall exhibit a structure free of excessive porosity, slag, dirt, or
M2 (regular C) 248 255 262
M2 (high C) 255 262 269
other nonmetallic inclusions, pipes, checks, cracks and other
M3, Class 1 and 255 262 269
injurious defects.
Class 2
8.2 Macroetch severity levels for center porosity and ingot
M4 255 262 269
M6 277 285 293
pattern,illustratedphotographicallyinPracticeA 561,shallnot
M7 255 262 269
exceed the ratings specified in Table 4 for the appropriate
M10 (regular C) 248 255 262
material size and composition.
M10 (high C) 255 262 269
M30 269 277 285
M33 269 277 285
9. Decarburization
M34 269 277 285
M36 269 277 285 9.1 Decarburization shall be determined on a specimen
M41 269 277 285
representing a cross section of the material and prepared in
M42 269 277 285
accordance with the latest issue of Methods E 3. When
M43 269 297 285
M44 285 293 302 examined at 203 or greater magnification, it shall not exceed
M46 269 277 285
the values given in Tables 5-8 for the appropriate size and
M47 269 277 285
shape of the material.
M48 311 321 331
M50 248 255 262 9.2 Material ordered as drill rod, ground and polished,
M52 248 255 262
centerless ground, ground finished, or machine finished flats
M62 285 293 302
and squares shall be free of scale and decarburization.
T1 255 262 269
T2 255 262 269
T4 269 277 285
10. Permissible Variations in Dimensions
T5 285 293 302
10.1 Permissible variations in dimensions shall not exceed
T6 302 311 321
T8 255 262 269
the applicable limits stated in Tables 8-22, incl. Where out-of-
T15 277 285 293
round or square requirements are shown, they shall be deter-
mined as follows:
10.1.1 Out-of-Round—Difference between high and low
readings as determined by micrometers or other suitable
as a high-heat furnace. The furnaces may be either controlled
measuring instruments.
atmosphere or molten-salt bath. The austenitizing temperature
10.1.2 Out-of-Square—The amount required to be removed
ranges stipulated in Table 3 cover both furnace types.
from each edge in order to square the edge with the face as
7.2.1 After being austenitized for the proper time, the
determined with a square and suitable measuring instruments.
samples may be oil quenched or quenched in molten salt plus
air cooling. When a salt quench is employed, its temperature
11. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
shall be 1050 to 1175°F (566 to 635°C) except for M3, M4,
11.1 High-speed tool steel shall be free of heavy scale, deep
M41, , M42,M43 , M46, M47, M48, M62, and T15, when it
pitting, laps, porosity, injurious segregations, excessive non-
shall be 1000 to 1075°F (538 to 579°C). All samples shall be
metallic inclusions, seams, cracks, checks, slivers, scale marks,
double tempered at 1025°F (552°C) for 2 h each cycle except
dents, soft and hard spots, pipes, or any defects that would
for M0 and M52 which shall be given two tempering cycles of
detrimentally affect the suitability of the material, after re-
2 h each at 1000°F and M41, M42, M43, M44, M46, M47,
moval of the recommended stock allowance. (See Tables 5-8)
M48, M62, and T15, which shall be given three tempering
11.2 Visualexaminationshallbemadetoensurecompliance
cycles of 2 h each at 1000°F.
with the requirements for workmanship, finish, dimensions and
7.2.2 The hardness of the specimen after the specified heat tolerances, identification marking, and packaging.
treatment shall meet the minimum hardness value for the
12. Sampling
particular type of steel shown in Table 3. Rockwell C tests
should be used where possible but light-load tests may be
12.1 Unless otherwise specified, a lot shall consist of all
necessaryonthinspecimens.Thesetestsshouldbespecifiedby material submitted for inspection at the same time, of the same
agreement between seller and purchaser. The hardness value heat, type, finish, and size, and must conform to the provisions
shall be obtained in accordance with
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.