ASTM B533-85(1998)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Peel Strength of Metal Electroplated Plastics
Standard Test Method for Peel Strength of Metal Electroplated Plastics
SCOPE
1.1 This test method gives two procedures for measuring the force required to peel a metallic coating from a plastic substrate. One procedure (Procedure A) utilizes a universal testing machine and yields reproducible measurements that can be used in research and development, in quality control and product acceptance, in the description of material and process characteristics, and in communications. The other procedure (Procedure B) utilizes an indicating force instrument that is less accurate and that is sensitive to operator technique. It is suitable for process control use.
1.2 The tests are performed on standard molded plaques. This method does not cover the testing of production electroplated parts.
1.3 The tests do not necessarily measure the adhesion of a metallic coating to a plastic substrate because in properly prepared test specimens, separation usually occurs in the plastic just beneath the coating-substrate interface rather than at the interface. It does, however, reflect the degree that the process is controlled.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Endorsed by American
Designation: B 533 – 85 (Reapproved 1998) Electroplaters’ Society
Endorsed by National
Association of Metal Finishers
Standard Test Method for
Peel Strength of Metal Electroplated Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 533; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope coating. The coated plaque is either tested as is, or it is
conditioned by a low-temperature bake and then tested. The
1.1 This test method gives two procedures for measuring the
coating is cut through to the plastic substrate in a way that
force required to peel a metallic coating from a plastic
forms two strips of coating (see Fig. 1). Each strip is peeled
substrate. One procedure (Procedure A) utilizes a universal
from the substrate at a right angle using an instrument that
testing machine and yields reproducible measurements that can
indicates the force required to separate it from its substrate.
be used in research and development, in quality control and
product acceptance, in the description of material and process
4. Significance and Use
characteristics, and in communications. The other procedure
4.1 The force required to separate a metallic coating from its
(Procedure B) utilizes an indicating force instrument that is less
plastic substrate is determined by the interaction of several
accurate and that is sensitive to operator technique. It is
factors: the generic type and quality of the plastic molding
suitable for process control use.
compound, the molding process, the process used to prepare
1.2 The tests are performed on standard molded plaques.
the substrate for electroplating, and the thickness and mechani-
This method does not cover the testing of production electro-
cal properties of the metallic coating. By holding all others
plated parts.
constant, the effect on the peel strength by a change in any one
1.3 The tests do not necessarily measure the adhesion of a
of the above listed factors may be noted. Routine use of the test
metallic coating to a plastic substrate because in properly
in a production operation can detect changes in any of the
prepared test specimens, separation usually occurs in the
above listed factors.
plastic just beneath the coating-substrate interface rather than
4.2 The peel test values do not directly correlate to the
at the interface. It does, however, reflect the degree that the
adhesion of metallic coatings on the actual product.
process is controlled.
4.3 When the peel test is used to monitor the coating
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
process, a large number of plaques should be molded at one
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
time from a same batch of molding compound used in the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
production moldings to minimize the effects on the measure-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
ments of variations in the plastic and the molding process.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. Apparatus
2. Referenced Document
5.1 Procedure A—A tension testing machine that has self-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3 aligning grips and that has a loading range that includes the
E 4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
forces to be measured, 5 to 200 N, shall be used to separate the
3. Summary of Test Method coating from the substrate, and measure the force required. The
machine shall meet the verification requirements of Practices
3.1 A properly prepared standard test specimen, called a
E4. The speed of separation of the crossarms of the machine
plaque, is copper electroplated, with no additional metal
shall be adjusted to give a separation rate of 25 6 3 mm/min.
The machine shall automatically and continuously record on a
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B-8 on Metallic chart the load on one coordinate and the amount of peel on the
and Inorganic Coatingsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B08.08.03
other coordinate. The amount of peel may be obtained from
on Decorative Coatings.
calculation, using a known chart speed.
Current edition approved Feb. 22, 1985. Published May 1985. Originally
published as B 533 – 70. Last previous edition B 533 – 79.
This test is also known as the Jacquet Test. A detailed treatment of the test has
been published by Saubestre et al in Plating, Vol 52, 1965, p. 982. The Instron universal testing machine, Instron Corp., Canton, MA, has been
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01. found to be satisfactory.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
B 533
FIG. 1 Plaque
NOTE 2—When the test is used as a control of the coating process,
5.2 Procedure B—A spring-loaded, force-indicating instru-
commercially prepared plaques can be used.
ment with a measurement range that includes the force to be
measured, 5 to 200 N, shall be used to measure the force
9.2 Clean, activate, and electroplate the plaques as speci-
required to separate the coating. The indicated force shall be
fied. The thickness of the metallic coating in the test area (see
accurate to 610 %.
Fig. 1) shall be 40 6 4 μm.
NOTE 3—It is necessary to have a ductile copper coating to perform this
6. Sampling
test. The thickness and uniformity of thickness of the metallic coating
6.1 A sampling procedure is not applicable to this test
directly influence the peel strength; therefore, in order to standardize this
method.
test, the coating thickness is specified. If a different coating thickness is
used, the results will not be comparable to other test results. It may be
7. Test Specimen
necessary to use shielding during plating to obtain the required coating
7.1 Perform the test using a flat, molded plastic plaque such thickness uniformity.
as shown in Fig. 1. Plaque dimensions may vary up to 610 %
9.3 Cut through the coating along the dashed lines shown in
provided that the edges of slit peel strips are not closer than 11
Fig. 1, and also along the centerline so as to produce two
mm from any plaque edge.
parallel strips of coating that are 25.00 6 0.25 mm wide and
approximately 75 mm long.
8. Conditioning
NOTE 4—Following are methods that can be used to cut the coating:
8.1 Condition the electroplated plaques requiring condition-
(a) Slit the coating with a milling machine equipped with a slitting saw.
ing by baking for1hinanair-circulating oven operated at
Operate the saw at a peripheral speed of 300 mm/s and a feed of 5 mm/s.
70 6 3°C. Place the plaques in the oven in a way that permits
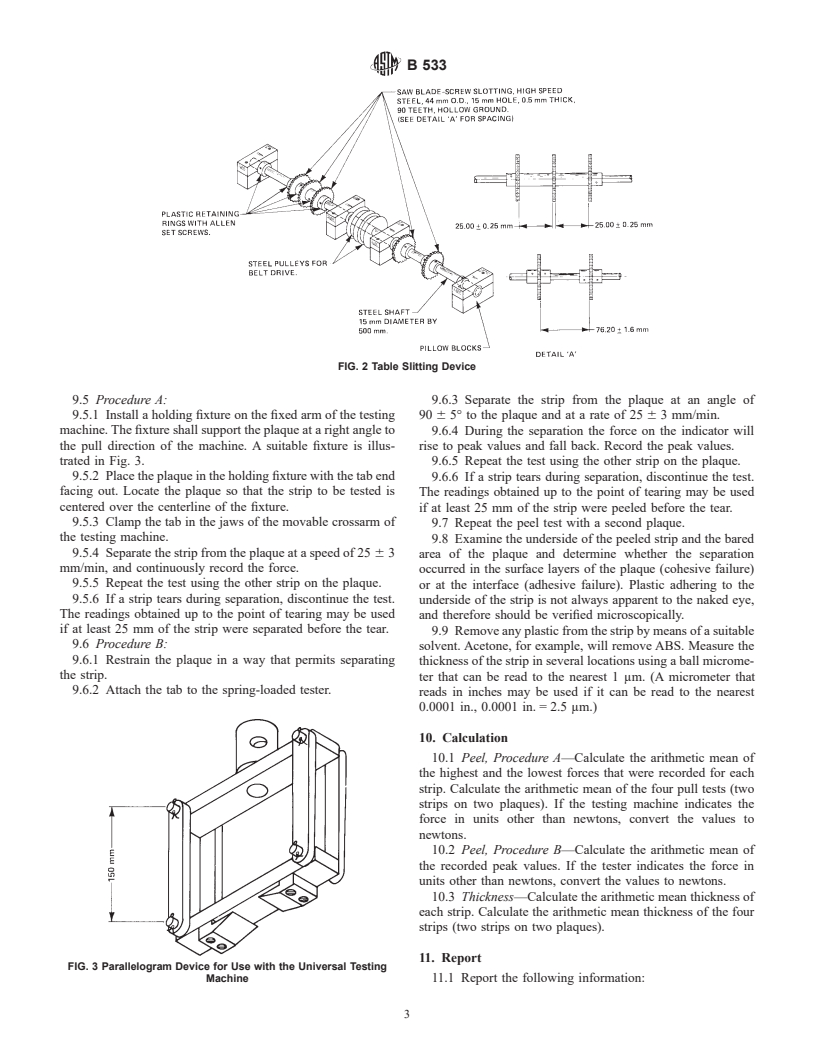
(b) Slit with a device such as shown in Fig. 2.
free circulation of air around all surfaces of the plaques. Allow 9
(c) Cut the coating with a sharp blade guided by a straighte
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.