ASTM C686-17
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Parting Strength of Mineral Fiber Batt- and Blanket-Type Insulation
Standard Test Method for Parting Strength of Mineral Fiber Batt- and Blanket-Type Insulation
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 Tensile strength is a fundamental property associated with mineral fiber manufacture since it is influenced by the type of fiber, the deposition of fiber, the type and the amount of bonding agent, and the method of curing the resin to form a bonded insulation product. The test is an indication of product integrity and the ability of the product to be successfully handled and applied in the field.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers evaluation of strength in tension on mineral fiber batt- and blanket-type insulation products. It is useful for determining the comparative tensile properties of these products, specimens of which cannot be held by the more conventional clamp-type grips. This is a quality control method, and the results shall not be used for design purposes. It is not suitable for board-type products.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C686 − 17
Standard Test Method for
Parting Strength of Mineral Fiber Batt- and Blanket-Type
1
Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C686; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Significance and Use
1.1 This test method covers evaluation of strength in tension 3.1 Tensile strength is a fundamental property associated
on mineral fiber batt- and blanket-type insulation products. It is with mineral fiber manufacture since it is influenced by the
useful for determining the comparative tensile properties of type of fiber, the deposition of fiber, the type and the amount of
these products, specimens of which cannot be held by the more bonding agent, and the method of curing the resin to form a
conventional clamp-type grips. This is a quality control bonded insulation product. The test is an indication of product
method, and the results shall not be used for design purposes. integrity and the ability of the product to be successfully
It is not suitable for board-type products. handled and applied in the field.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
4. Apparatus
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
4.1 Constant Rate of Traverse Tension Test Unit of 50-lbf
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
(223-N) capacity calibrated in increments of 0.1 lbf (0.4 N) and
and are not considered standard.
having a moving head speed of 12 in. (305 mm)/min or
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
equivalent (see Fig. 1).
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 4.2 Post-Type Grips with 1-in. (25.4-mm) diameter rods
(see Fig. 2).
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
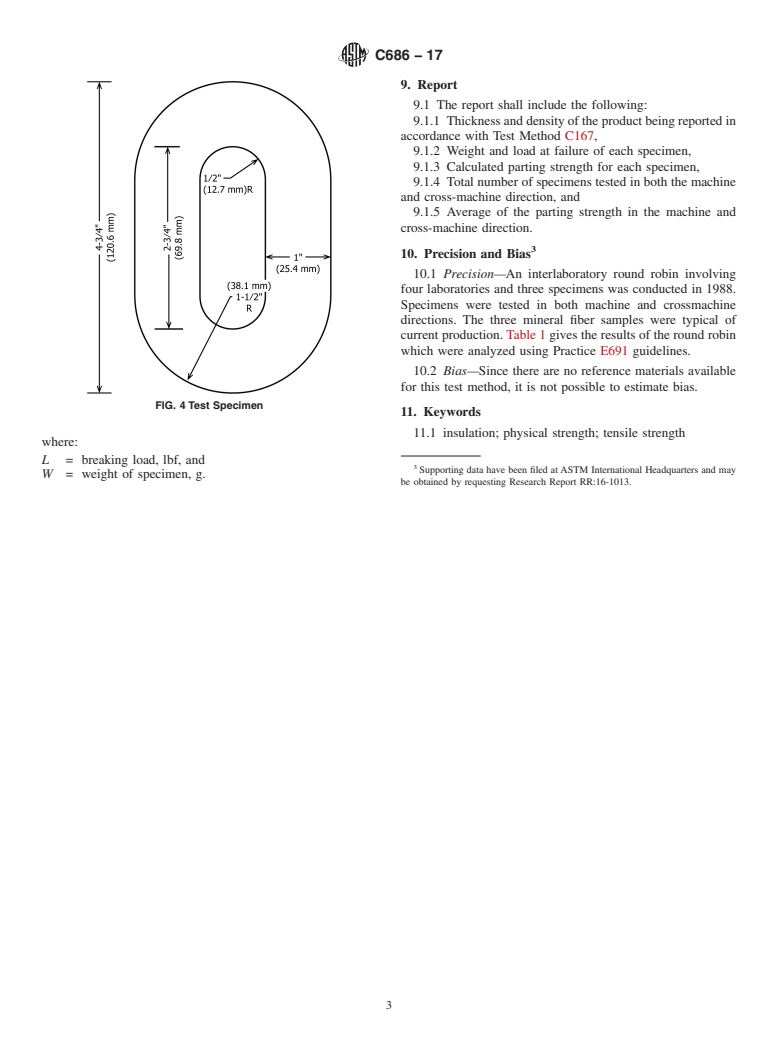
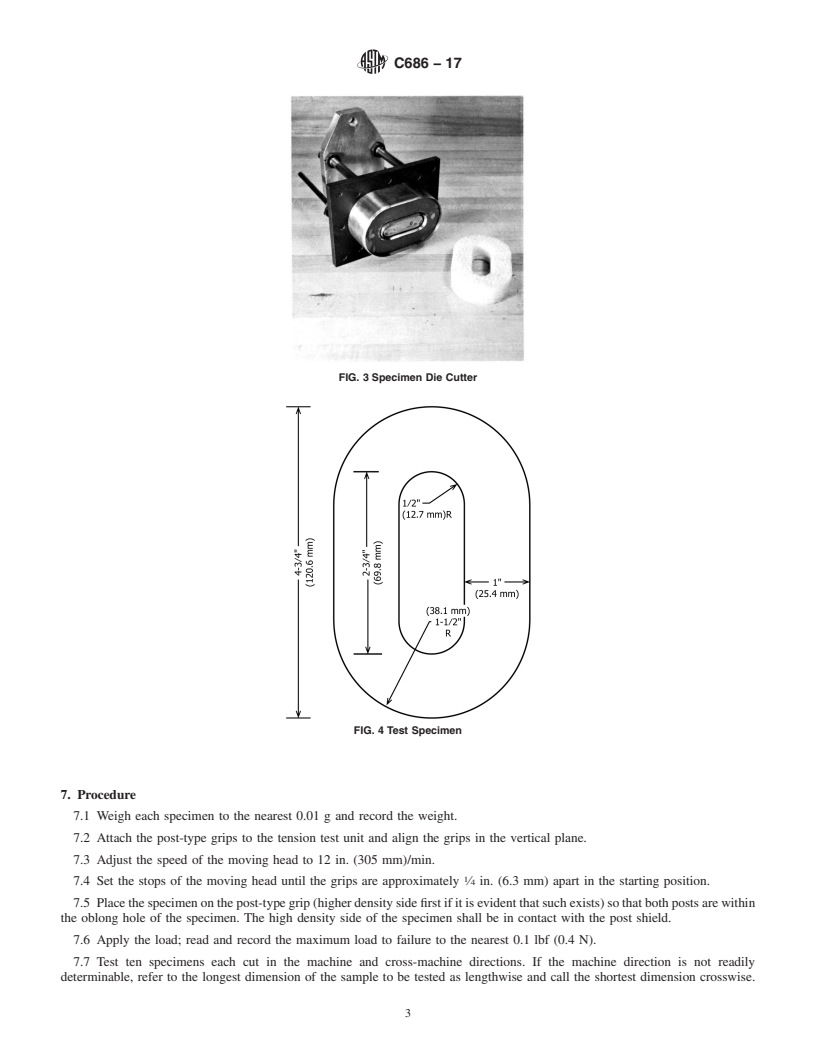
4.3 Die for cutting specimens (see Fig. 3). The O-ring
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
specimen dimensions are 3 by 4.75 in. (76 by 120.6 mm) in
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
outside diameter, and 1 by 2.75 in. (25 by 69.8 mm) in inside
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
diameter (see Fig. 4).
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4.4 Balance to weigh to an accuracy of 0.01 g.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5. Test Specimen
2. Referenced Documents 5.1 The test specimen shall consist of the entire O-ring cut
2
from the full thickness of the product to be tested.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C167 Test Methods for Thickness and Density of Blanket or 5.2 Specimens shall not be cut from a product that varies in
Batt Thermal Insulations
thickness 65 % from normal when tested in accordance with
E171 Practice for Conditioning and Testing Flexible Barrier Test Method C167.
Packaging
5.3 No specimen shall be tested that exhibits any obvious
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
damage in the insulation or that shows delamination within the
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
insulation thickness.
6. Conditioning
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on Thermal
Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.32 on Mechanical 6.1 Condition the specimens for 1 h in a room maintained at
Properties.
atmospheric conditions of 73.4 6 1.8°F (23 6 1°C) and 50 6
Current edition approved May 1, 2017. Published May 2017. Originally
2 % relative humidity in accordance with Specification E171.
ε1
approved in 1971. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as C686 – 90 (2011) .
DOI: 10.1520/C0686-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or 7. Procedure
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
7.1 Weigh each specimen to the nearest 0.01 g and record
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. the weight.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C686 − 17
FIG. 1 Tension Test Units
FIG. 3 Specimen Die Cutter
FIG. 2 Post-Type Grips
7.6 Apply the load; read and record the maximum load to
failure to the nearest 0.1 lbf (0.4 N).
7.2 Attach the post-type grips to the tension test unit and
7.7 Test ten specimens each cut in the machine and cross-
align the grips in the vertical plane.
machine directions. If the machine direction is
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: C686 − 90 (Reapproved 2011) C686 − 17
Standard Test Method for
Parting Strength of Mineral Fiber Batt- and Blanket-Type
1
Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C686; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—1.2 was editorially inserted in October 2011.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers evaluation of strength in tension on mineral fiber batt- and blanket-type insulation products. It is
useful for determining the comparative tensile properties of these products, specimens of which cannot be held by the more
conventional clamp-type grips. This is a quality control method, and the results shouldshall not be used for design purposes. It is
not normally used suitable for board-type products.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C167 Test Methods for Thickness and Density of Blanket or Batt Thermal Insulations
E171 Practice for Conditioning and Testing Flexible Barrier Packaging
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Significance and Use
3.1 Tensile strength is a fundamental property associated with mineral fiber manufacture since it is influenced by the type of
fiber, the deposition of fiber, the type and the amount of bonding agent, and the method of curing the resin to form a bonded
insulation product. The test is an indication of product integrity and the ability of the product to be successfully handled and applied
in the field.
4. Apparatus
4.1 Constant Rate of Traverse Tension Test Unit of 50-lbf (223-N) capacity calibrated in increments of 0.1 lbf (0.4 N) and having
a moving head speed of 12 in. (305 mm)/min or equivalent (see Fig. 1).
4.2 Post-Type Grips with 1-in. (25.4-mm) diameter rods (see Fig. 2).
4.3 Die for cutting specimens (see Fig. 3). The O-ring specimen dimensions are 3 by 4.75 in. (76 by 120.6 mm) in outside
diameter, and 1 by 2.75 in. (25 by 69.8 mm) in inside diameter (see Fig. 4).
4.4 Balance to weigh to an accuracy of 0.01 g.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on Thermal Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.32 on Mechanical
Properties.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2011May 1, 2017. Published October 2011May 2017. Originally published as approved in 1971. Last previous edition approved in
ε1
20072011 as C686 – 90 (2007).(2011) . DOI: 10.1520/C0686-90R11E01.10.1520/C0686-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C686 − 17
FIG. 1 Tension Test UnitUnits
FIG. 2 Post-Type Grips
5. Test Specimen
5.1 The test specimen shall consist of the entire O-ring cut from the full thickness of the product to be tested.
5.2 Specimens shall not be cut from a product that varies in thickness 65 % from normal when tested in accordance with Test
Method C167.
5.3 No specimen shall be tested that exhibits any obvious damage in the insulation or that shows delamination within the
insulation thickness.
6. Conditioning
6.1 Condition the specimens for 1 h in a room maintained at atmospheric conditions of 73.4 6 1.8°F (23 6 1°C) and 50 6 2 %
relative humidity in acc
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.