ASTM G6-07(2020)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Pipeline Coatings
Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Pipeline Coatings
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This procedure defines a test method for comparing the relative resistance of pipeline coatings to abrasion.
5.2 Abrasion resistance may be used to specify optimum coating thickness of candidate materials both in development and research work to study new coating systems or methods and in quality control.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method of accelerated test is a procedure for determining the relative resistance of steel pipeline coatings to abrasion by a slurry of coarse abrasive and water. The method is intended to apply to the testing of all types of electrical insulating pipeline coatings and tapes, including thermoplastics, thermoset, and bituminous materials.
1.2 Pipeline coatings are not normally subjected to the type of abrasion herein specified.
1.3 Metallic protective coatings such as zinc may be compared visually, but do not meet the electrical requirements of this test method.
1.4 The values stated in SI units to three significant decimals are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: G6 − 07 (Reapproved 2020)
Standard Test Method for
1
Abrasion Resistance of Pipeline Coatings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G6; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This test method of accelerated test is a procedure for
G12 Test Method for Nondestructive Measurement of Film
determining the relative resistance of steel pipeline coatings to
Thickness of Pipeline Coatings on Steel (Withdrawn
abrasion by a slurry of coarse abrasive and water. The method
3
2013)
is intended to apply to the testing of all types of electrical
G62 Test Methods for Holiday Detection in Pipeline Coat-
insulating pipeline coatings and tapes, including
ings
thermoplastics, thermoset, and bituminous materials.
1.2 Pipeline coatings are not normally subjected to the type
3. Terminology
of abrasion herein specified.
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 holidays, n—small faults or pinholes which permit
1.3 Metallic protective coatings such as zinc may be com-
current drainage through protective coatings on steel pipe.
pared visually, but do not meet the electrical requirements of
this test method.
4. Summary of Test Method
1.4 The values stated in SI units to three significant deci-
4.1 Apparatus and materials are described whereby coatings
mals are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in
on steel pipe are worn away by an abrasive slurry contained in
parentheses are for information only.
a horizontally revolving drum. Specimens extend through both
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
ends of the drum and are electrically insulated from contact
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
with the test apparatus.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.2 Periodic measurement of the electrical resistance be-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
tween the specimen and the drum indicates the degree of
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
abrasion resistance of the coating.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
5. Significance and Use
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
5.1 This procedure defines a test method for comparing the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
relative resistance of pipeline coatings to abrasion.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5.2 Abrasion resistance may be used to specify optimum
coating thickness of candidate materials both in development
and research work to study new coating systems or methods
and in quality control.
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Subcommittee D01.48 on Durability of Pipeline Coating and Linings. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2020. Published August 2020. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1969. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as G6 – 07 (2013). DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/G0006-07R20. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
G6 − 07 (2020)
NOTE 1—Low voltage detectors are used to locate pinholes, voids, or
6. Apparatus
thin spots in pipeline coatings. The potential used with wet-sponge
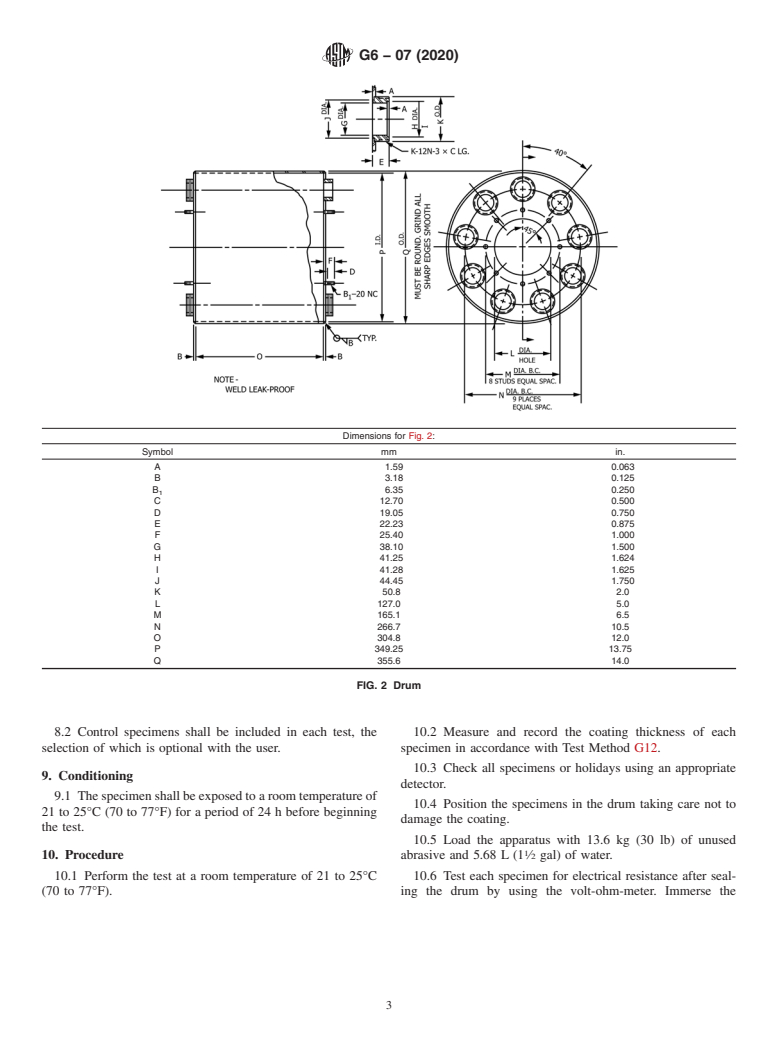
6.1 Drum—A cylindrical steel container suitable for testing
detectors can be up to 100 V DC. Procedures for using these detectors are
nine specimens simultaneously. Figs. 1-3 show construction
found in MethodAof G62. For use of high voltage detectors operating in
the 900 to 20 000 Vdc range, see Method B of G62.
details which may be altered at the cap assembly if desired. A
valve shall be provided to release any pressure built up during
6.5 Volt-ohm-meter—Anyelectricaltestinstrumentformea-
test.
suring electrical resistance of the circuit.
6.2 Apparatus for Revolving the Drum—Any suitable appa-
7. Reage
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.