ASTM D2112-01a
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Inhibited Mineral Insulating Oil by Pressure Vessel
Standard Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Inhibited Mineral Insulating Oil by Pressure Vessel
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is intended as a rapid method for the evaluation of the oxidation stability of new mineral insulating oils containing a synthetic oxidation inhibitor. This test is considered of value in checking the oxidation stability of new mineral insulating oils containing 2,6-ditertiary-butyl para-cresol or 2,6-ditertiary-butyl phenol, or both, in order to control the continuity of this property from shipment to shipment. The applicability of this procedure for use with inhibited insulating oils of more than 12 cSt at 40°C (approximately 65 SUS at 100°F) has not been established.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of whoever uses this standard to consult and establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1—A modification of this test method which uses the same procedure and apparatus but a higher (150°C) bath temperature has been published as Test Method D2272.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 2112 – 01a
Standard Test Method for
Oxidation Stability of Inhibited Mineral Insulating Oil by
1
Pressure Vessel
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2112; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is intended as a rapid method for the
evaluation of the oxidation stability of new mineral insulating
oils containing a synthetic oxidation inhibitor. This test is
considered of value in checking the oxidation stability of new
mineral insulating oils containing 2,6-ditertiary-butyl para-
cresolor2,6-ditertiary-butylphenol,orboth,inordertocontrol
the continuity of this property from shipment to shipment. The
applicability of this procedure for use with inhibited mineral
insulating oils of more than 12 cSt at 40°C (approximately 65
SUS at 100°F) has not been established.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of whoever uses this standard to consult and
establish appropriate safety and health practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
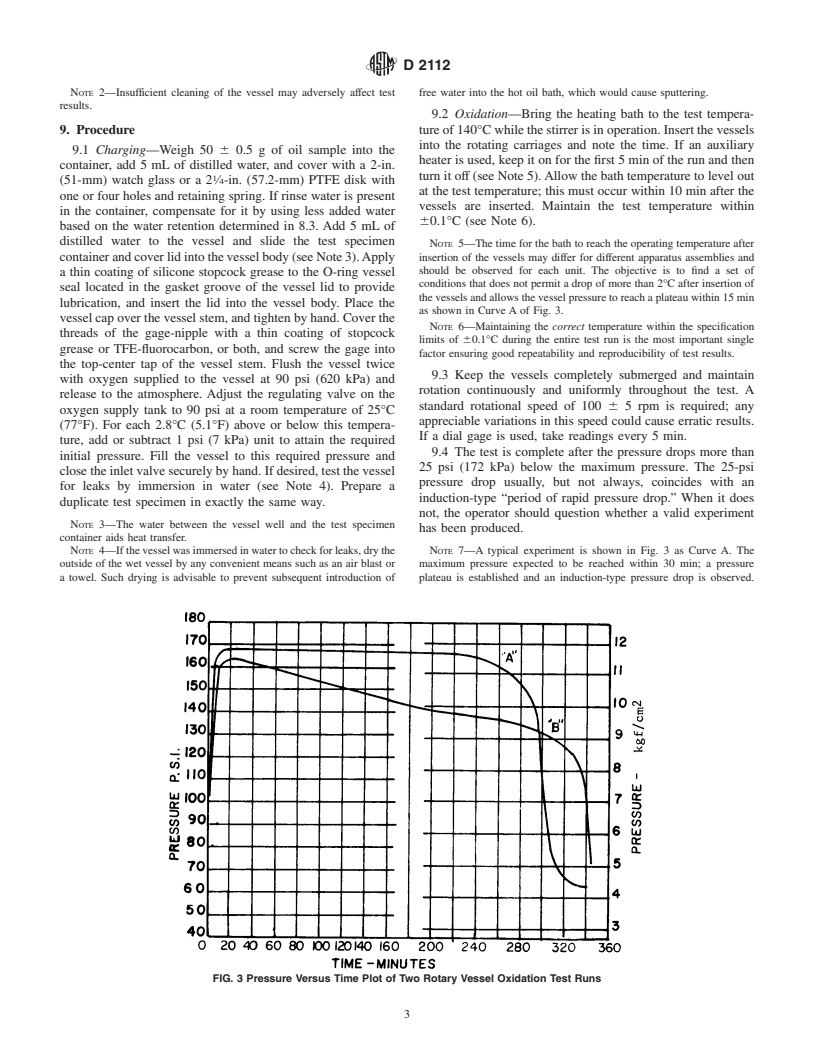
FIG. 1 Rotating Vessel Oxidation Test Apparatus
(See 6.7).
NOTE 1—A modification of this test method, which uses the same
oxygen pressure of 90 psi (620 kPa), in a stainless steel or
procedure and apparatus but a higher (150°C) bath temperature, has been
copper vessel (for rapid temperature equilibrium), with a glass
published as Test Method D 2272.
test specimen container and copper catalyst coil, in the pres-
ence of water, at a bath temperature of 140°C. The time for an
2. Referenced Documents
oil to react with a given volume of oxygen is measured;
2.1 ASTM Standards:
completion of the test is indicated by a specific drop in
2
B 1 Specification for Hard-Drawn Copper Wire
pressure.
D 2272 Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Steam
3
Turbine Oils by Rotating Pressure Vessel
4. Signifance and Use
4
E 1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers
4.1 This is a control test of oxidation stability of new,
inhibited mineral insulating oils for determining the induction
3. Summary of Test Method
period of oxidation inhibitors under prescribed accelerated
3.1 The test specimen is agitated by rotating axially at 100
aging conditions. There is no proven correlation between oil
rpm at an angle of 30° from the horizontal, under an initial
performance in this test and performance in service. However,
the test method may be used to check the continuity of
oxidation stability of production oils.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D27 on
Electrical Insulating Liquids and Gases and is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
5. Apparatus
mittee D27.06 on Chemical Test.
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 2001. Published December 2001. Originally
5.1 Oxidation Vessel— Glass test specimen container with
published as D 2112 – 62 T. Last previous edition D 2112 – 01.
cover and catalyst coil, pressure gage, thermometer, test bath,
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.03.
3
and accessories as described in Annex A1. The assembled
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03. apparatus is shown in Fig. 1, and its design shown schemati-
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2112
cally in Fig. 2. 8. Preparation ofApparatus
8.1 Catalyst Preparation—Immediately before use, polish
6. Reagents and Materials
the copper wire with silicon carbide abrasive cloth and wipe
6.1 Purity of Reagents—Use reagent grade chemicals in all
freefromabrasiveswithacleandrycloth.Windapproximately
tests. Unless otherwise indicated, all reagents shall conform to
3 m of the wire into a coil having an outside diameter of 44 to
the specifications of the Committee on Analytical Reagents of
48 mm and stretched to a height of 40 to 42 mm. Clean the coil
the American Chemical Society, where such specifications are
5 thoroughly with acetone and allow it to air-dry. Immediately
available.
after air drying, insert the coil with a twisting motion into the
6.2 Hydrochloric Acid, 10 vol %.
glass test specimen container. Handle the coil only with clean
6.3 Silicon Carbide Abrasive Cloth, 100-grit with cloth
tongs to avoid contamination. Weigh the coil and the container
backing.
to the nearest 0.1 g and record the weight. Prepare a new coil
6.4 Acetone, cp.
for each test s
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.